(Press-News.org) LAWRENCE — University of Kansas researchers have found that the infants of mothers who were given 600 milligrams of the omega-3 fatty acid DHA during pregnancy weighed more at birth and were less likely to be very low birth weight and born before 34 weeks gestation than infants of mothers who were given a placebo. This result greatly strengthens the case for using the dietary supplement during pregnancy.
Susan CarlsonThe results are from the first five years of a 10-year, double-blind randomized controlled trial to be published in the April issue of the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. It is also available online. A followup of this sample of infants is ongoing to determine whether prenatal DHA nutritional supplementation will benefit children's intelligence and school readiness.
"A reduction in early preterm and very low birth weight delivery could have clear clinical and public health significance," said Susan Carlson, A.J. Rice Professor of Dietetics and Nutrition at the KU Medical Center, who directed the study with John Colombo, KU professor of psychology and director of the Life Span Institute.
John Colombo"We believe that supplementing U.S. women with DHA could safely increase mean birth weight and gestational age to numbers that are closer to other developed countries such as Norway and Australia," she said.
DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) occurs naturally in cell membranes with the highest levels in brain cells, but levels can be increased by diet or supplements. An infant obtains DHA from his or her mother in utero and postnatally from human milk, but the amount received depends upon the mother's DHA status.
"U.S. women typically consume less DHA than women in most of the developed world," said Carlson.
During the first five years of the study, children of women enrolled in the study received multiple developmental assessments at regular intervals throughout infancy and at 18 months of age. In the next phase of the study, the children will receive twice-yearly assessments until they are 6 years old. The researchers will measure developmental milestones that occur in later childhood and are linked to lifelong health and welfare.
Previous research has established the effects of postnatal feeding of DHA on infant cognitive and intellectual development, but DHA is accumulated most rapidly in the fetal brain during pregnancy, said Colombo. "That's why we are so interested in the effects of DHA taken prenatally, because we will really be able to see how this nutrient affects development over the long term."
###
The study is funded by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development.
The University of Kansas is a major comprehensive research and teaching university. The university's mission is to lift students and society by educating leaders, building healthy communities and making discoveries that change the world. The KU News Service is the central public relations office for the Lawrence campus.
Prenatal DHA reduces early preterm birth, low birth weight
2013-02-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Some family physicians' offices discriminate against people with low socio-economic status
2013-02-26
TORONTO, Feb. 25, 2013—Some family physicians' offices discriminate against people of low socio-economic status, even when there is no economic incentive to do so under Canada's system of publicly funded universal health insurance, new research has shown.
At the same time, offices appear to give preference to people with chronic health conditions, according to the research led by Dr. Stephen Hwang of St. Michael's Hospital.
In his study, published today in the Canadian Medical Association Journal, researchers telephoned the offices of family physicians and general practitioners ...
2 vortex trails with 1 stroke
2013-02-26
VIDEO:
The video shows that the hummingbird produces two trails of vortices -- one under each wing per stroke -- that help generate the aerodynamic forces it requires to power and...
Click here for more information.
RIVERSIDE, Calif. — As of today, the Wikipedia entry for the hummingbird explains that the bird's flight generates in its wake a single trail of vortices that helps the bird hover. But after conducting experiments with hummingbirds in the lab, researchers at ...
Virus shows promise as prostate cancer treatment
2013-02-26
A recombinant Newcastle disease virus kills all kinds of prostate cancer cells, including hormone resistant cells, but leaves normal cells unscathed, according to a paper published online ahead of print in the Journal of Virology. A treatment for prostate cancer based on this virus would avoid the adverse side effects typically associated with hormonal treatment for prostate cancer, as well as those associated with cancer chemotherapies generally, says corresponding author Subbiah Elankumaran of Virginia Polytechnic Institute, Blacksburg. The modified virus is now ready ...
Higher levels of several toxic metals found in children with autism
2013-02-26
TEMPE, Ariiz. -- In a recently published study in the journal Biological Trace Element Research, Arizona State University researchers report that children with autism had higher levels of several toxic metals in their blood and urine compared to typical children. The study involved 55 children with autism ages 5 years compared to 44 controls of similar age and gender.
The autism group had significantly higher levels of lead in their red blood cells (+41 percent) and significantly higher urinary levels of lead (+74 percent), thallium (+77 percent), tin (+115 percent), ...
Study reveals stem cells in a human parasite
2013-02-26
CHAMPAIGN, lll. — From the point of view of its ultimate (human) host, the parasitic flatworm Schistosoma mansoni has a gruesome way of life. It hatches in feces-tainted water, grows into a larva in the body of a snail and then burrows through human skin to take up residence in the veins. Once there, it grows into an adult, mates and, if it's female, starts laying eggs. It can remain in the body for decades.
A new study offers insight into the cellular operations that give this flatworm its extraordinary staying power. The researchers, from the University of Illinois, ...
Global surveys show environmental concerns rank low among public concerns
2013-02-26
2/25/2013, Chicago, IL--A newly released international study reveals that the issue of climate change is not a priority for people in the United States and around the world.
The surveys showed that when asked to rank priority worries, people were five times more likely to point to the economy over the environment. Additionally, when asked about climate change, people identified the issue as more of a national problem than a personal concern.
Coordinated surveys, conducted by the International Social Survey Programme (ISSP) in 33 countries from 1993 through 2010, "are ...
Researchers explore PKC role in lung disease
2013-02-26
New research examines the role of PKC in airway smooth muscle contraction and raises the possibility that this enzyme could be a therapeutic target for treating asthma, COPD, and other lung diseases.
In the lungs, pathological increases in the contraction of the smooth muscle cells (SMCs) lining airway walls—a process that decreases airflow—contribute to the chain of events leading to asthma and COPD, two common lung diseases. Jose Perez-Zoghbi and colleagues from Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center designed a series of experiments to investigate the role of ...
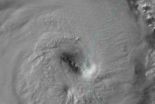
NASA sees Cyclone Rusty threatening Western Australia
2013-02-26
Tropical Cyclone Rusty formed on Feb. 24 and has already caused warnings up for the residents of northwestern West Australia, including Port Hedland. NASA's Terra satellite saw that outer bands of this quick-forming tropical cyclone were already affecting land.
The Australian Bureau of Meteorology (ABOM) has posted cyclone warnings and a yellow and blue alert for Western Australia as Rusty approaches for a landfall. A Cyclone Warning is in effect from Broome to Mardie, and adjacent inland areas of the Pilbara, including Marble Bar, Nullagine and Millstream. A Cyclone ...
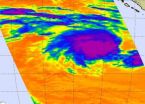
Infrared NASA data shows Cyclone Haruna being blown away
2013-02-26
Ex-cyclone Haruna is expected to dissipate in the Southern Indian Ocean under increasing wind shear in the next day or two. Infrared imagery from a NASA satellite shows that Haruna is being blown apart several hundred miles away from La Reunion Island.
Wind shear has been a problem for Haruna for days. A night-time image from the VIIRS instrument aboard NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite taken on Feb. 21 at 22:23 UTC showed the eye of Cyclone Haruna had elongated from northwest to southeast as a result of wind shear. For more information about the Suomi NPP satellite, visit: ...
NASA spots active Southern Indian Ocean's Tropical Storm 18S
2013-02-26
The eighteenth tropical cyclone of the Southern Indian Ocean season formed over the weekend of Feb. 23-24 along with Cyclone Rusty as Cyclone Haruna crossed southern Madagascar. NASA's Aqua satellite measured Tropical Storm 18S' cloud top temperatures and saw powerful thunderstorms around the storm's core.
Cyclone Rusty is nearing a landfall in northwestern West Australia, while Tropical Storm 18S is headed in a similar direction.
Tropical Storm 18S (TS18S) was born on Feb. 24 and achieved tropical storm strengthe with maximum sustained winds near 35 knots (40 mph). ...