(Press-News.org) February 26, 2013, New York, N.Y. and San Diego, Calif. – Glioblastoma, the most common and lethal form of brain tumor in adults, is challenging to treat because the tumors rapidly become resistant to therapy. As cancer researchers are learning more about the causes of tumor cell growth and drug resistance, they are discovering molecular pathways that might lead to new targeted therapies to potentially treat this deadly cancer.
Scientists at the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research in San Diego worked collaboratively across the laboratories of Drs. Paul Mischel, Web Cavenee and Frank Furnari to investigate one such molecular pathway called the mammalian target of rapamycin or mTOR. This signaling pathway is hyperactivated in close to 90 percent of glioblastomas and plays a critical role in regulating tumor growth and survival. Therapies that inhibit mTOR signaling are under investigation as drug development targets, but results to date have been disappointing: mTOR inhibitors halt the growth but fail to kill the tumor cells.
A study published this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences uncovers an unexpected but important molecular mechanism of mTOR inhibitor resistance and identifies a novel drug combination that reverses this resistance.
The story begins with a closer look at a gene-encoded protein called promyleocytic leukemia gene or PML. The study investigators explored the role of PML in causing resistance to mTOR inhibitor treatment. They found that when glioblastoma patients are treated with drugs that target the mTOR pathway, the levels of PML rise dramatically. Further, they showed that PML upregulation made the tumor cells resistant to mTOR inhibitors, and that if they suppressed the ability of the tumor cells to upregulate the PML protein, the tumor cells died in response to the mTOR inhibitor therapy.
"When we looked at cells in in vivo models and patients treated in the clinic, it became clear that the glioblastoma cells massively regulated PML enabling them to escape the effects of mTOR inhibitor therapy," reported senior author Paul Mischel, MD, Ludwig Institute member based at the University of California at San Diego.
"Our team hypothesized that if we could use a pharmacological approach to get rid of PML and combine it with an mTOR inhibitor, it could change the response from halting growth to cell death. The question was how?" added Mischel.
Previous research had shown that the use of low-dose arsenic could cause degradation of the PML protein in patients with leukemia. The team hypothesized that if arsenic could degrade PML, it may reverse resistance to mTOR inhibitors. The combination of mTOR and low-dose arsenic in mice indeed showed a synergistic effect, with massive tumor cell death along with very significant shrinkage of the tumor in mice with no ill side effects.
"Current therapy upregulates PML, turning off the mTOR signaling pathway. The tumor cells hide, waiting for the target signal to return," said Mischel. "When low-dose arsenic is added, not only does it stop the cell from returning, it shuts down the escape route killing the tumor cell."
These results present the first clinical evidence that mTOR inhibition promotes PML upregulation in mice and patients, and that it mediates drug resistance. The clinical relevance was confirmed when researchers looked at before- and after-treatment tissue samples from patients treated with mTOR inhibitors, confirming that PML goes up significantly in post treatment of mTOR inhibitors.
"These data suggest a new approach for potential treatment of glioblastoma," said
Mischel. "We are moving forward to test that possibility in people."
Post-doctoral students Akio Iwanami and Beatrice Gini from the Mischel lab as well as Ciro Zanca from the Furnari/Cavenee lab, also contributed significantly to this paper.
###This work was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, the Uehara Memorial Foundation, three NIH grants: NS73831, CA 119347 and P01-CA95616, the Ziering Family Foundation in Memory of Sigi Ziering and the Ben and Catherine Ivy Foundation.
About The Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research
The Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research is an international non-profit organization committed to improving the understanding and control of cancer through integrated laboratory and clinical discovery. Leveraging its worldwide network of investigators and the ability to sponsor and conduct its own clinical trials, Ludwig is actively engaged in translating its discoveries into applications for patient benefit. Since its establishment in 1971, the Ludwig Institute has expended more than $1.5 billion on cancer research.
For further information please contact Rachel Steinhardt, rsteinhardt@licr.org or +1-212-450-1582.
Novel combination therapy shuts down escape route, killing glioblastoma tumor cells
2013-02-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
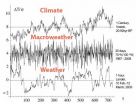
Macroweather is what you expect
2013-02-26
While short-term weather is notoriously volatile, climate is thought to represent a kind of average weather pattern over a long period of time. This dichotomy provides the analytical framework for scientific thinking about atmospheric variability, including climate change.
But the weather-climate dichotomy paints an incomplete picture – one that may be complicating efforts to untangle natural variations in climate from man-made effects, according to McGill University physics professor Shaun Lovejoy. In a paper published recently in the journal Eos, Transactions, American ...
Gender gap disappears in school math competitions, study shows
2013-02-26
The idea that boys are better at math and in competitions has persisted for a long time, and now we know why: Nobody bothered to schedule the rematch.
Most school math contests are one-shot events where girls underperform relative to their male classmates. But a new study by a Brigham Young University economist presents a different picture.
Twenty-four local elementary schools changed the format to go across five different rounds. Once the first round was over, girls performed as well or better than boys for the rest of the contest.
"It's really encouraging that seemingly ...
OHSU scientists first to grow liver stem cells in culture, demonstrate therapeutic benefit
2013-02-26
PORTLAND, Ore. — For decades scientists around the world have attempted to regenerate primary liver cells known as hepatocytes because of their numerous biomedical applications, including hepatitis research, drug metabolism and toxicity studies, as well as transplantation for cirrhosis and other chronic liver conditions. But no lab in the world has been successful in identifying and growing liver stem cells in culture -- using any available technique – until now.
In the journal Nature, physician-scientists in the Papé Family Pediatric Research Institute at Oregon Health ...
Tweaking gene expression to repair lungs
2013-02-26
PHILADELPHIA — Lung diseases such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are on the rise, according to the American Lung Association and the National Institutes of Health.
These ailments are chronic, affect the small airways of the lung, and are thought to involve an injury-repair cycle that leads to the breakdown of normal airway structure and function. For now, drugs for COPD treat only the symptoms.
"A healthy lung has some capacity to regenerate itself like the liver," notes Ed Morrisey, Ph.D., professor of Medicine and Cell and Developmental ...
Prenatal DHA reduces early preterm birth, low birth weight
2013-02-26
LAWRENCE — University of Kansas researchers have found that the infants of mothers who were given 600 milligrams of the omega-3 fatty acid DHA during pregnancy weighed more at birth and were less likely to be very low birth weight and born before 34 weeks gestation than infants of mothers who were given a placebo. This result greatly strengthens the case for using the dietary supplement during pregnancy.
Susan CarlsonThe results are from the first five years of a 10-year, double-blind randomized controlled trial to be published in the April issue of the American Journal ...
Some family physicians' offices discriminate against people with low socio-economic status
2013-02-26
TORONTO, Feb. 25, 2013—Some family physicians' offices discriminate against people of low socio-economic status, even when there is no economic incentive to do so under Canada's system of publicly funded universal health insurance, new research has shown.
At the same time, offices appear to give preference to people with chronic health conditions, according to the research led by Dr. Stephen Hwang of St. Michael's Hospital.
In his study, published today in the Canadian Medical Association Journal, researchers telephoned the offices of family physicians and general practitioners ...
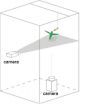
2 vortex trails with 1 stroke
2013-02-26
VIDEO:
The video shows that the hummingbird produces two trails of vortices -- one under each wing per stroke -- that help generate the aerodynamic forces it requires to power and...
Click here for more information.
RIVERSIDE, Calif. — As of today, the Wikipedia entry for the hummingbird explains that the bird's flight generates in its wake a single trail of vortices that helps the bird hover. But after conducting experiments with hummingbirds in the lab, researchers at ...
Virus shows promise as prostate cancer treatment
2013-02-26
A recombinant Newcastle disease virus kills all kinds of prostate cancer cells, including hormone resistant cells, but leaves normal cells unscathed, according to a paper published online ahead of print in the Journal of Virology. A treatment for prostate cancer based on this virus would avoid the adverse side effects typically associated with hormonal treatment for prostate cancer, as well as those associated with cancer chemotherapies generally, says corresponding author Subbiah Elankumaran of Virginia Polytechnic Institute, Blacksburg. The modified virus is now ready ...
Higher levels of several toxic metals found in children with autism
2013-02-26
TEMPE, Ariiz. -- In a recently published study in the journal Biological Trace Element Research, Arizona State University researchers report that children with autism had higher levels of several toxic metals in their blood and urine compared to typical children. The study involved 55 children with autism ages 5 years compared to 44 controls of similar age and gender.
The autism group had significantly higher levels of lead in their red blood cells (+41 percent) and significantly higher urinary levels of lead (+74 percent), thallium (+77 percent), tin (+115 percent), ...
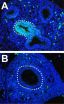
Study reveals stem cells in a human parasite
2013-02-26
CHAMPAIGN, lll. — From the point of view of its ultimate (human) host, the parasitic flatworm Schistosoma mansoni has a gruesome way of life. It hatches in feces-tainted water, grows into a larva in the body of a snail and then burrows through human skin to take up residence in the veins. Once there, it grows into an adult, mates and, if it's female, starts laying eggs. It can remain in the body for decades.
A new study offers insight into the cellular operations that give this flatworm its extraordinary staying power. The researchers, from the University of Illinois, ...