Gut microbiota plays important role in functional bowel disorders
Microbiota research opens up promising paths for improving diagnosis
2013-02-26
(Press-News.org) (24 February 2013) An estimated 50 per cent of patients consulting a gastroenterologist suffer from functional bowel disorders (FBD), such as dyspepsia or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). It is characteristic for these conditions that underlying physiological mechanisms are hard to be found. "However, recent research shows that the gut microbiota is a likely candidate for filling some of the gaps in the causal chain leading to FBD," says Professor Fernando Azpiroz, Chairman of the Gut Microbiota & Health Section of the European Society of Neurogastroenterology & Motility (ESNM). Further information on this issue — ¬one of three topics to be presented at Tuesday's online press conference on the occasion of the 2nd World Summit "Gut Microbiota For Health" in Madrid, Spain — can be found at http://bit.ly/SUN24PR.
World-leading experts will inform about the gut microbiota's impact on health during an online press conference on Tuesday, 26 February 2013, 8 a.m. ET (14.00-5.30 h CET), moderated by UK media medic Dr Mark Porter, best known for his television and radio work for the BBC. The following questions will be dealt with:
In what way does the gut microbiota influence functional bowel disorders?
Speaker: Prof. Fernando Azpiroz, Barcelona, Spain
Can faecal microbiota transplantation be used to treat recurrent Clostridium difficile infection?
Speaker: Prof. Lawrence Brandt, New York, USA
The gut–brain axis: can probiotics have a positive effect on mental health?
Speaker: Prof. Emeran Mayer, Los Angeles, USA
Attend the press conference from your office
If you would like to attend, please write an email to gutmicrobiota@impressum.de.
The online press conference will be held in English. Details on how to access the press conference will be sent to you after your registration.
###
For further information on the summit programme, please refer to the following website:
http://presscorner.gutmicrobiotaforhealth.com/scientific-information/program.
About the Gut Microbiota For Health Experts Exchange website
The www.gutmicrobiotaforhealth.com Experts Exchange, provided by the Gut Microbiota & Health Section of ESNM, is an online platform for health-care professionals, scientists, and other people interested in the field. Thanks to being an open, independent and participatory medium, this digital service enables a scientific debate in the field of gut microbiota.
Connected to www.gutmicrobiotaforhealth.com, the Twitter account @GMFHx, animated by experts, for experts from the medical and scientific community, actively contributes to the online exchanges about the gut microbiota. Follow @GMFHx on Twitter. Join the event on #GMFH2013
About the Gut Microbiota & Health Section of ESNM
ESNM stands for the European Society of Neurogastroenterology and Motility, a member of United European Gastroenterology (UEG). The mission of the ESNM is to defend the interests of all professionals in Europe involved in the study of neurobiology and pathophysiology of gastrointestinal function. The Gut Microbiota & Health Section was set up to increase recognition of the links between the gut microbiota and human health, to spread knowledge and to raise interest in the subject. The Gut Microbiota & Health Section is open to professionals, researchers, and practitioners from all fields related to gut microbiota and health. www.esnm.eu/gut_health/gut_micro_health.php?navId=68
About the AGA
The American Gastroenterological Association is the trusted voice of the GI community. Founded in 1897, the AGA has grown to include more than 16,000 members from around the globe who are involved in all aspects of the science, practice and advancement of gastroenterology. The AGA Institute administers the practice, research and educational programmes of the organisation. www.gastro.org
About Danone Dairy and Gut Microbiota For Health
Danone's conviction is that food plays an essential role in human health namely through the impact that gut microbiota may have on health. That is why Danone Dairy supports the Gut Microbiota For Health World Summit and Experts Exchange web platform with the aim to encourage research and increase knowledge in this promising area, in line with its mission to "bring health through food to as many people as possible.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2013-02-26
(26 February 2013) Clostridium difficile infections have developed into a virtual pandemic over the past two decades. The outcome of standard antibiotic treatment is unsatisfactory: the recurrence rates are high with every relapse increasing the risk of further follow-ups. Faecal microbiota transplantation offers a rapidly acting and highly effective alternative in treating recurrent Clostridium difficile infections (RCDI), as Professor Lawrence J. Brandt (Montefiore Medical Center, New York, USA) points out. According to him, more than 90 per cent of the patients are being ...
2013-02-26
Boston – A first-of-its kind national survey of medical students and residents finds that despite recent efforts by medical schools and academic medical centers to restrict access of pharmaceutical sales representatives to medical trainees, medical students and residents still commonly receive meals, gifts, and industry-sponsored educational materials. The study was completed by a team of researchers led by fourth-year Harvard Medical School student Kirsten Austad and Aaron Kesselheim, M.D., J.D., M.P.H., an internist and health policy researcher in the Division of Pharmacoepidemiology ...
2013-02-26
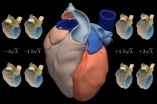
Researchers at Pompeu Fabra University (Spain) have created a high resolution atlas of the heart with 3D images taken from 138 people. The study demonstrates that an average image of an organ along with its variations can be obtained for the purposes of comparing individual cases and differentiating healthy forms from pathologies.
"This atlas is a statistical description of how the heart and its components – such as the ventricles and the atrium – look," as explained to SINC by Corné Hoogendoorn, researcher at the CISTIB centre of the Pompeu Fabra University.
Scientists ...
2013-02-26
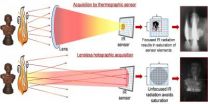
Firefighters put their lives on the line in some of the most dangerous conditions on Earth. One of their greatest challenges, however, is seeing through thick veils of smoke and walls of flame to find people in need of rescue. A team of Italian researchers has developed a new imaging technique that uses infrared (IR) digital holography to peer through chaotic conflagrations and capture potentially lifesaving and otherwise hidden details. The team describes its breakthrough results and their applications in a paper published today in the Optical Society's (OSA) open-access ...
2013-02-26
Scientists have used sugar-coated scaffolding to move a step closer to the routine use of stem cells in the clinic and unlock their huge potential to cure diseases from Alzheimer's to diabetes.
Stem cells have the unique ability to turn into any type of human cell, opening up all sorts of therapeutic possibilities for some of the world's incurable diseases and conditions.
The problem facing scientists is how to encourage stem cells to turn into the particular type of cell required to treat a specific disease.
But researchers at the University of Manchester's School ...
2013-02-26
Feeling comfortable and confident in sport, health, or PE can be very difficult for some young people who can be seen as a 'risk' of becoming obese. Young people from ethnic minorities, especially girls, are more likely to be physically inactive and unhealthy.
This perception needs to be addressed and challenged in school physical education (PE) according to research funded by the Economic and Social Research Council (ESRC), which shows how school provision could make use of visual approaches in developing young people's critical learning about the body.
When Dr Laura ...
2013-02-26
This press release is available in German.
Scientists have long been dreaming about building a computer that would work like a brain. This is because a brain is far more energy-saving than a computer, it can learn by itself, and it doesn't need any programming. Privatdozent [senior lecturer] Dr. Andy Thomas from Bielefeld University's Faculty of Physics is experimenting with memristors – electronic microcomponents that imitate natural nerves. Thomas and his colleagues proved that they could do this a year ago. They constructed a memristor that is capable of learning. ...
2013-02-26
In collaboration with the Royal Botanic Gardens of Madrid and the Slovenian Forestry Institute, researchers in the Basque Country have documented two new species of Hydnum, commonly known as ox tongue mushrooms, as part of their study published in the 'Mycologia' journal. This genus is known because many of its fungi are edible.
Spanish researchers have headed the discovery of two mushroom species belonging to the Hydnum genus, a type of fungus commonly used in cooking.
"During our study we discovered two new species: Hydnum ovoideisporum and Hydnum vesterholtii, which ...
2013-02-26
Alexandria, VA – On June 5, 2012, a massive dock made landfall on Oregon's Agate Beach, just north of Newport. The dock carried with it a host of castaways, including as many as a hundred species of mollusks, anemones, sponges, oysters, crabs, barnacles, worms, sea stars, mussels and sea urchins. A placard on the side written in Japanese revealed that the dock had been unmoored from the Japanese coastal city of Misawa during the catastrophic tsunami on March 11, 2011, bringing with it an essentially intact subtidal community of Asian species to the Pacific Northwest. Although ...
2013-02-26
If you accidently kick your toe against a doorframe you are probably going to find it very painful. As a purely intellectual experiment, imagine purposefully kicking a doorframe hard enough to potentially break your toe. When it turns out your toe has been battered but not broken, the pain may be interpreted more as a relief.
"It is not hard to understand that pain can be interpreted as less severe when an individual is aware that it could have been much more painful. Less expected, however, is the discovery that pain may be experienced as pleasant if something worse ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Gut microbiota plays important role in functional bowel disorders
Microbiota research opens up promising paths for improving diagnosis