(Press-News.org) Genetically modified (GM) crops have been a source of great controversy—particularly in Europe—but acts of vandalism and associated security costs have made scientific evidence about the health and ecological impacts of those crops hard to come by. A Swiss government-protected field site dedicated for use in GM crop studies could serve as an example to other European countries interested in pursuing crop biotechnology, according to an article published in Trends in Biotechnology, a Cell Press publication, on February 28.
The protected field site will now enable research groups to conduct experiments without having to install and pay for security measures. The research station is expected to operate with an annual budget of €600,000.
"This could be a model for other European countries that wish to evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of GM crops in an objective and scientific manner with less risk of vandalism," said Jörg Romeis of Zurich's Agroscope Reckenholz-Tänikon Research Station.
As of 2010, opponents of genetic modification had destroyed more than 100 field trials in Europe. At the Reckenholz site, a group of more than 30 masked activists threatened researchers and destroyed about 30 percent of the experimental plants in a 2008 field trial.
The new protected field site will provide GM crop researchers with all the technical security measures needed to guard against such attacks, including perimeter fencing, round-the-clock guarding and surveillance of the experimental field, and an alarm system.
Romeis and his colleagues say that vandalism and its associated costs appear to be a major factor in the steady decline of European GM research, a situation that they call unacceptable.
In many parts of the world, GM crops are gaining popularity. In 2011, as much as 10 percent of the world's arable crop area was planted with GM crops. However, the adoption of GM plants has been very low in Europe, with only two GM crops approved for cultivation: Bt maize and a starch-modified potato. No GM crop is approved for commercial release in Switzerland, where there is a voter-approved moratorium in place through 2017. However, scientific research, including field experiments with GM plants, is permitted.
Romeis says that the establishment of such protected sites could eventually reverse the decline in GM field trials and strengthen plant biotechnology research in Europe.
INFORMATION:
Trends in Biotechnology, Romeis et al. "Plant biotechnology: research behind fences"
Fighting GM crop vandalism with a government-protected research site
2013-02-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study identifies growth factor essential to the most common malignant pediatric brain tumor
2013-02-28
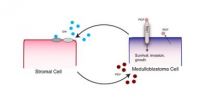
A multi-institutional team led by Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) researchers has identified a molecular pathway that appears to be essential for the growth and spread of medulloblastoma, the most common malignant brain tumor in children. In their report in the Feb. 28 issue of Cell, they show that blocking this pathway – which involves interactions between tumor cells and the surrounding tissues – leads to regression of all four molecular subtypes of medulloblastoma in several mouse models.
"Our finding that a pathway carrying signals from host cells to tumor cells ...
How did early primordial cells evolve?
2013-02-28
VIDEO:
L-form bacteria undergoes cell division. The time scale is in minutes.
Click here for more information.
Four billion years ago, soon after the planet cooled enough for life to begin, primordial cells may have replicated and divided without protein machinery or cell walls, relying instead on just a flimsy lipid membrane. New research on bacteria examines exactly how these primitive cells could have evolved without such crucial structures. While the vast majority of bacteria ...
Animas' development of a first-generation closed loop insulin delivery system progresses
2013-02-28
WEST CHESTER, Pa., February 28, 2013 – Animas Corporation announced today positive results from the second phase of human clinical trials of a first-generation, closed-loop insulin delivery system in development, designed to predict a rise or fall in blood glucose and correspondingly increase, decrease, suspend and resume insulin delivery. The data were presented at the Advanced Technologies & Treatments for Diabetes (ATTD) Conference in Paris, France.
The feasibility study of the predictive Hypoglycemia-Hyperglycemia Minimizer (HHM) System* in development was conducted ...
The birth of a giant planet?
2013-02-28
An international team led by Sascha Quanz (ETH Zurich, Switzerland) has studied the disc of gas and dust that surrounds the young star HD 100546, a relatively nearby neighbour located 335 light-years from Earth. They were surprised to find what seems to be a planet in the process of being formed, still embedded in the disc of material around the young star. The candidate planet would be a gas giant similar to Jupiter.
"So far, planet formation has mostly been a topic tackled by computer simulations," says Sascha Quanz. "If our discovery is indeed a forming planet, then ...
Secondary facelift achieves good results, reports plastic and reconstructive surgery
2013-02-28
Philadelphia, Pa. (February 28, 2013) – Performed an average of a decade after initial facelift surgery, a "secondary" facelift can achieve similarly lasting results with a low complication rate, according to a paper in the March issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS).
Dr. Rod J. Rohrich and colleagues of University of Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, report their 20-year experience with secondary facelift surgery, or "rhytidectomy." The researchers conclude that, with attention ...
Round or 'shaped,' implants yield good results in breast reconstruction
2013-02-28
Philadelphia, Pa. (February 28, 2013) –For women undergoing breast reconstruction using implants, most patient-reported outcomes are similar with two different shapes of silicone gel-filled implants, reports a study in the March issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS).
Assessment of key areas of quality of life after breast reconstruction shows few significant differences with conventional round implants versus newer "shaped" implants, according to the new research, led by Dr. Sheina ...
Progesterone may be why pregnant women are more vulnerable to certain infections
2013-02-28
Bethesda, MD—Women who are pregnant or using synthetic progesterone birth control injections have a conspicuous vulnerability to certain infections including malaria, Listeria, HIV, and herpes simplex virus. A new research report appearing in the March 2013 issue of the Journal of Leukocyte Biology offers strong evidence for a possible explanation: the progesterone receptor, a pregnancy hormone sensor, targets a part of the immune system responsible for protection against these and other invaders. In addition to helping explain why some women are more vulnerable to certain ...
Brown unveils novel wireless brain sensor
2013-02-28
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — A team of neuroengineers based at Brown University has developed a fully implantable and rechargeable wireless brain sensor capable of relaying real-time broadband signals from up to 100 neurons in freely moving subjects. Several copies of the novel low-power device, described in the Journal of Neural Engineering, have been performing well in animal models for more than year, a first in the brain-computer interface field. Brain-computer interfaces coud help people with severe paralysis control devces with their thoughts.
Arto Nurmikko, ...
Brain-to-brain interface allows transmission of tactile and motor information between rats
2013-02-28
DURHAM, N.C. -- Researchers have electronically linked the brains of pairs of rats for the first time, enabling them to communicate directly to solve simple behavioral puzzles. A further test of this work successfully linked the brains of two animals thousands of miles apart—one in Durham, N.C., and one in Natal, Brazil.
The results of these projects suggest the future potential for linking multiple brains to form what the research team is calling an "organic computer," which could allow sharing of motor and sensory information among groups of animals. The study was published ...
Replacing soybean meal in pig diets
2013-02-28
Canola, cottonseed, and sunflower products can replace soybean meal in diets fed to pigs, but they contain less protein and energy. To determine if it makes economic sense to use them, producers need to know the concentrations and digestibility of the nutrients they contain. To help them make the decision, University of Illinois researchers examined amino acid digestibility for these products.
"Soybean is by far the biggest oilseed crop in the world," said Hans Stein, professor of animal sciences. "But canola, cottonseed, and sunflowers are grown in areas where soybeans ...