(Press-News.org) The adsorption of ions in microporous materials governs the operation of technologies as diverse as water desalination, energy storage, sensing and mechanical actuation. Until now, however, researchers attempting to improve the performance of these technologies haven't been able to directly and unambiguously identify how factors such as pore size, pore surface chemistry and electrolyte properties affect the concentration of ions in these materials as a function of the applied potential.
To provide the needed information, researchers at the Georgia Institute of Technology and the Oak Ridge National Laboratory have demonstrated that a technique known as small angle neutron scattering (SANS) can be used to study the effects of ions moving into nanoscale pores. Believed to be the first application of the SANS technique for studying ion surface adsorption in-situ, details of the research were reported online Jan. 31, 2013, in the journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition.
Using conductive nanoporous carbon, the researchers conducted proof-of-concept experiments to measure changes in the adsorption of hydrogen ions in pores of different sizes within the same material due to variations in solvent properties and applied electrical potential. Systematic studies performed with such a technique could ultimately help identify the optimal pore size, surface chemistry and electrolyte solvent properties necessary for either maximizing or minimizing the adsorption of ions under varying conditions.
"We need to understand this system better so we can predict the kind of surface chemistry required and the kinds of solvents needed to control the levels of ion penetration and adsorption in pores of different sizes," said Gleb Yushin, an associate professor in the Georgia Tech School of Materials Science and Engineering. "Understanding these processes better could lead to the development of improved energy storage, water purification and desalination systems. This new experimental methodology may also give us paths to better understand ion transport in biological systems and contribute to the development of improved drugs and artificial organs."
The research was supported partially by the U.S. Army Research Office, the Georgia Institute of Technology and the Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL).
"The advantage of neutron scattering is that it can be used to study real systems," said Yushin. "You can study most electrode materials and electrolyte combinations as long as they have a high sensitivity for neutron scattering."
Yushin and his collaborators – Georgia Tech graduate research assistant Sofiane Boukhalfa, and Oak Ridge scientists Yuri Melnichenko and Lilin He – conducted the research using ORNL's High Flux Isotope Reactor, which produces a beam of high-energy neutrons. Their experimental setup allowed them to immerse activated carbon fabric samples – each sample containing pores of different sizes – in different electrolyte materials while varying the applied electrical potential.
By measuring how the neutron beam was scattered when it passed through the carbon fabric and electrolytes, the researchers could determine how the solvent, pore size and electrical potential affected the average ion concentration in the carbon material samples.
"You can learn whether the ions get adsorbed into small pores or large pores by simply comparing the changes in the neutron scattering," Yushin explained. "This experimental technique allows us to independently change the surface chemistry to see how that affects the ion concentrations, and we can use different solvents to observe how the interaction between electrolyte and pore walls affects the ion adsorption in pores of different sizes. We can further identify exactly where the ion adsorption takes place even when no potential is applied to an electrode."
Earlier work in this area had not provided clear results.
"There have been multiple prior studies on the pore size effect, but different research groups worldwide have obtained contradictory results depending on the material selection and the model used to determine the specific surface area and pore size distribution in carbon electrodes," Yushin said. "Neutron scattering should help us clarify existing controversies. We have already observed that depending on the solvent-pore wall interactions, either enhanced or reduced ion electro-adsorption may take place in sub-nanometer pores."
In their experiments, the researchers used two different electrolytes: water containing sulfuric acid and deuterium oxide – also known as heavy water – which also contained sulfuric acid. The two were chosen for the proof-of-concept experiments, though a wide range of other hydrogen-containing electrolytes could also be used.
Now that the technique has been shown to work, Yushin would like to expand the experimentation to develop better fundamental understanding about the complex interactions of solvent, ions and pore walls under applied potential. That could allow development of a model that could guide the design of future systems that depend on ion transport and adsorption.
"Once you gain the fundamental knowledge from SANS experiments, predictive theoretical models could be developed that would guide the synthesis of the optimal structures for these applications," he said. "Once you clearly understand the structure-property relationships, you can use materials science approaches to design and synthesize the optimal material with the desired properties."
Information developed through the research could lead to improvements in supercapacitors and hybrid battery-capacitor devices for rapidly growing applications in hybrid electrical vehicles, energy efficient industrial equipment, smart grid-distributed energy storage, hybrid-electric and electrical ships, high-power energy storage for wind power and uninterruptible power supplies.
INFORMATION:
This research was partially supported by the Georgia Institute of Technology and the U.S. Army Research Office under contract number W911NF-12-1-0259. The research at ORNL's High Flux Isotope Reactor was sponsored by the Laboratory Directed Research and Development Program and the Scientific User Facilities Division, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, U.S. Department of Energy. The conclusions are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official positions of the U.S. Army Research Office or the Department of Energy.
CITATION: Boukhalfa, S., et al., "Small-Angle Neutron Scattering for In Situ Probing of Ion Adsorption Inside Micropores." Angew. Chem. Int. Ed (2013). http://www.dx.doi.org/10.1002/anie.21209141.
Neutron scattering provides data on adsorption of ions in microporous materials
Improving energy storage
2013-02-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Physicists demonstrate the acceleration of electrons by a laser in a vacuum
2013-02-28
Accelerating a free electron with a laser has been a longtime goal of solid-state physicists.
David Cline, a distinguished professor in the UCLA Department of Physics and Astronomy, and Xiaoping Ding, an assistant researcher at UCLA, have conducted research at Brookhaven National Laboratory in New York and have established that an electron beam can be accelerated by a laser in free space.
This has never been done before at high energies and represents a significant breakthrough, Cline said, adding that it also may have implications for fusion as a new energy source. ...
New protein quality method provides important information on sustainable diet
2013-02-28
Rosemont, IL (February 27, 2013) – A groundbreaking report by an Expert Consultation of the Food and Agriculture Organization of United Nations (FAO) has recommended a new, advanced method for assessing the quality of dietary proteins.
The report, "Dietary protein quality evaluation in human nutrition", recommends that the Digestible Indispensable Amino Acid Score (DIAAS) replace the Protein Digestibility Corrected Amino Acid Score (PDCAAS) as the preferred method of measuring protein quality. The report recommends that more data be developed to support full implementation, ...
Mutation location is the key to prognosis
2013-02-28
HOUSTON – (Feb. 28, 2013) – The three most important factors in real estate are location, location, location, and the same might be said for mutations in the gene MECP2, said researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute (NRI) at Texas Children's Hospital in a report in the journal Cell.
"Where a mutation occurs can affect the severity of the symptoms of the disease," said Dr. Huda Zoghbi, professor of molecular and human genetics at BCM and director of the NRI. Zoghbi, corresponding author of the report, found the ...
UCLA study could explain why some people get zits and others don't
2013-02-28
The bacteria that cause acne live on everyone's skin, yet one in five people is lucky enough to develop only an occasional pimple over a lifetime. What's their secret?
In a boon for teenagers everywhere, a UCLA study conducted with researchers at Washington University in St. Louis and the Los Angeles Biomedical Research Institute has discovered that acne bacteria contain "bad" strains associated with pimples and "good" strains that may protect the skin.
The findings, published in the Feb. 28 edition of the Journal of Investigative Dermatology, could lead to a myriad ...
Action video games boost reading skills
2013-02-28
Much to the chagrin of parents who think their kids should spend less time playing video games and more time studying, time spent playing action video games can actually make dyslexic children read better. In fact, 12 hours of video game play did more for reading skills than is normally achieved with a year of spontaneous reading development or demanding traditional reading treatments.
The evidence, appearing in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on February 28, follows from earlier work by the same team linking dyslexia to early problems with visual attention rather ...
Fighting GM crop vandalism with a government-protected research site
2013-02-28
Genetically modified (GM) crops have been a source of great controversy—particularly in Europe—but acts of vandalism and associated security costs have made scientific evidence about the health and ecological impacts of those crops hard to come by. A Swiss government-protected field site dedicated for use in GM crop studies could serve as an example to other European countries interested in pursuing crop biotechnology, according to an article published in Trends in Biotechnology, a Cell Press publication, on February 28.
The protected field site will now enable research ...
Study identifies growth factor essential to the most common malignant pediatric brain tumor
2013-02-28
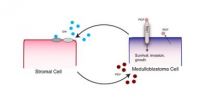
A multi-institutional team led by Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) researchers has identified a molecular pathway that appears to be essential for the growth and spread of medulloblastoma, the most common malignant brain tumor in children. In their report in the Feb. 28 issue of Cell, they show that blocking this pathway – which involves interactions between tumor cells and the surrounding tissues – leads to regression of all four molecular subtypes of medulloblastoma in several mouse models.
"Our finding that a pathway carrying signals from host cells to tumor cells ...
How did early primordial cells evolve?
2013-02-28
VIDEO:
L-form bacteria undergoes cell division. The time scale is in minutes.
Click here for more information.
Four billion years ago, soon after the planet cooled enough for life to begin, primordial cells may have replicated and divided without protein machinery or cell walls, relying instead on just a flimsy lipid membrane. New research on bacteria examines exactly how these primitive cells could have evolved without such crucial structures. While the vast majority of bacteria ...
Animas' development of a first-generation closed loop insulin delivery system progresses
2013-02-28
WEST CHESTER, Pa., February 28, 2013 – Animas Corporation announced today positive results from the second phase of human clinical trials of a first-generation, closed-loop insulin delivery system in development, designed to predict a rise or fall in blood glucose and correspondingly increase, decrease, suspend and resume insulin delivery. The data were presented at the Advanced Technologies & Treatments for Diabetes (ATTD) Conference in Paris, France.
The feasibility study of the predictive Hypoglycemia-Hyperglycemia Minimizer (HHM) System* in development was conducted ...
The birth of a giant planet?
2013-02-28
An international team led by Sascha Quanz (ETH Zurich, Switzerland) has studied the disc of gas and dust that surrounds the young star HD 100546, a relatively nearby neighbour located 335 light-years from Earth. They were surprised to find what seems to be a planet in the process of being formed, still embedded in the disc of material around the young star. The candidate planet would be a gas giant similar to Jupiter.
"So far, planet formation has mostly been a topic tackled by computer simulations," says Sascha Quanz. "If our discovery is indeed a forming planet, then ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
[Press-News.org] Neutron scattering provides data on adsorption of ions in microporous materialsImproving energy storage