(Press-News.org) NEW BRUNSWICK, N.J. – Married couples who have attained higher levels of education are less likely to divorce than less-educated couples, but a new study conducted at Rutgers School of Social Work points to significant racial differences.
"African-American women don't seem to enjoy the same degree of protection that education confers on marriage," said Jeounghee Kim, assistant professor at the school. "For white Americans, higher education is related to a lower chance of divorce, and this protective effect of education on marriage increased consistently among the recent generations. But for African-American women, higher education is not necessarily related to a lower chance of divorce."
In her study, published in the journal Family Relations and funded by the Silberman Fund Faculty Grant Program, Kim observed that researchers have found the overall divorce rate has leveled off since the 1980s after more than a century-long rise. But the rate has increasingly diverged by race and socioeconomic class, as measured by educational attainment. The divorce rate has remained steady for white women since 1980, while the trend has been less stable for African-American women.
Kim separately studied white and African-American women in five-year marriage cohorts starting from 1975 to 1979 and ending in 1995 to 1999. She took into account demographic characteristics including age, motherhood status and post-secondary education (associate degree at minimum) when married, and geographic region. Kim also measured marital dissolution (within nine years of first marriage) rather than by legal divorce, which many African-American women eschew in favor of a permanent separation.
Kim's analysis revealed that the percentage of white women with some postsecondary education continuously increased throughout the cohorts. This was not the case with African-American women, whose educational attainment peaked in the 1985-1994 cohorts before declining.
Concurrently, she found the percentage of white women having marital breakups declined throughout the study period, while African-American women experienced an increase in the 1980s' cohort before declining in the 1990 to 1994 cohort.
Kim's findings were consistent with much existing literature: Women with higher levels of education, and thus greater earning potential, would make more attractive marriage partners than women without in more recent marriage cohorts. Also, their marriages tend to last longer than those of their counterparts – particularly among white women – with less education.
Kim's research raises questions as to why African-American women's higher education does not have a strong marriage protective effect. "One possibility is that college education does not translate into the higher earnings that would help protect marriage for African Americans, she said. "Another could be that educational attainment may be insufficient to address the high levels of economic inequality that even well-educated African Americans experience. Many are the first in their families to have attained a post-secondary education and do not benefit from the cushion of intergenerational wealth possessed by some white families."
A third possibility involves the gender gap in African Americans' educational attainment; there are nearly twice as many African-American women college graduates as men. "We see the increasing power of education protecting marriage within the same socioeconomic class," Kim said. "Well-educated white women may still have power to select an equally well-educated mate. Then, there may be a synergy factor – higher incomes, better and healthier lives, smarter kids – that helps sustain their marriage.
"On the other hand, the return on higher education may not be the same for many African-American women, who have less chance to marry their educational equals. Also, because they are less likely to marry outside their race, their choices are limited."
### END
Education's protective effect on marriage differs between white and African-American women
2013-03-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Prairie dogs disperse when all close kin have disappeared
2013-03-08
FROSTBURG, MD (March 7, 2013)—Prairie dogs pull up stakes and look for a new place to live when all their close kin have disappeared from their home territory--a striking pattern of dispersal that has not been observed for any other species. This is according to a new study published in Science by behavioral ecologist John Hoogland, Professor at the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science's Appalachian Laboratory. He has been studying the ecology and social behavior of prairie dogs in national parks in Arizona, South Dakota, and Utah for the last 40 years.
For ...
Drugs targeting blood vessels may be candidates for treating Alzheimer's
2013-03-08
University of British Columbia researchers have successfully normalized the production of blood vessels in the brain of mice with Alzheimer's disease (AD) by immunizing them with amyloid beta, a protein widely associated with the disease.
While AD is typically characterized by a build-up of plaques in the brain, recent research by the UBC team showed a near doubling of blood vessels in the brain of mice and humans with AD.
The new study, published online last week in Scientific Reports, a Nature journal, shows a reduction of brain capillaries in mice immunized with ...
Engineers develop techniques to boost efficiency of cloud computing infrastructure
2013-03-08
Computer scientists at the University of California, San Diego, and Google have developed a novel approach that allows the massive infrastructure powering cloud computing as much as 15 to 20 percent more efficiently. This novel model has already been applied at Google. Researchers presented their findings at the IEEE International Symposium on High Performance Computer Architecture conference Feb. 23 to 27 in China.
Computer scientists looked at a range of Google web services, including Gmail and search. They used a unique approach to develop their model. Their first ...
The future of ion traps
2013-03-08
Recently Science Magazine invited JQI fellow Chris Monroe and Duke Professor Jungsang Kim to speculate on ion trap technology as a scalable option for quantum information processing. The article is highlighted on the cover of this week's issue, which is dedicated to quantum information. The cover portrays a photograph of a surface trap that was fabricated by Sandia National Labs and used to trap ions at JQI and Duke, among other laboratories.
Trapped atomic ions are a promising architecture that satisfies many of the critical requirements for constructing a quantum computer. ...
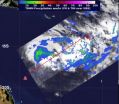
NASA's TRMM satellite sees Tropical Cyclone 19P form
2013-03-08
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite noticed areas of heavy rainfall in low pressure System 92P hours before it became the nineteenth tropical cyclone of the Southern Pacific Ocean.
NASA's TRMM satellite captured a look at the rainfall rates within low pressure System 92P on March 7 at 0023 UTC (March 6 at 7:23 p.m. EST), just hours before it became Tropical Cyclone 19P (TC 19P). TRMM data indicated that heavy rain was falling at a rate of 2 inches/50 mm per hour around the center of circulation, and that some of the thunderstorms were powerful as they ...
Trauma simulation technique makes better journalists
2013-03-08
This press release is available in French.
Montreal, March 7, 2013 – Just hours after the tragic shooting of 27 victims at Sandy Hook Elementary School, Twitter was overloaded with messages slamming reporters for interviewing children involved in the tragedy. While some of the journalists probably knew better but wanted the story at all costs, others were rookie reporters facing ethical decisions for the first time and unaware of the impact these interviews might have on the young survivors.
Past studies have documented that new journalists can cause a number of ...
Hubble finds birth certificate of oldest known star
2013-03-08
A team of astronomers using NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has taken an important step closer to finding the birth certificate of a star that's been around for a very long time.
"We have found that this is the oldest known star with a well-determined age," said Howard Bond of Pennsylvania State University in University Park, Pa., and the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, Md.
The star could be as old as 14.5 billion years (plus or minus 0.8 billion years), which at first glance would make it older than the universe's calculated age of about 13.8 billion ...
Small physician practices that care for children unprepared to become medical homes
2013-03-08
Ann Arbor, Mich. — Primary care practices around the country are being encouraged and even paid to become "medical homes," but small practices might be at a significant disadvantage in this race to improve health care for children, according to a new study by child health experts at C.S. Mott Children's Hospital.
Efforts around the country to improve health care for children have increasingly focused on the medical home as a model to make primary care practices more accessible, comprehensive, and focused on quality improvement. Since 2008, practices could become officially ...
Biologists produce rainbow-colored algae
2013-03-08
What can green algae do for science if they weren't, well, green?
That's the question biologists at UC San Diego sought to answer when they engineered a green alga used commonly in laboratories, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, into a rainbow of different colors by producing six different colored fluorescent proteins in the algae cells.
While fluorescent green, red, blue and yellow may be all the rage this year for running shoes and other kinds of sporting gear, fluorescent algae hasn't been a style trend yet in scientific laboratories. But in announcing their achievement in ...
Stocking Florida bass in Texas reservoirs may alter stream systems connected to stocked reservoirs
2013-03-08
WACO, Texas (March 7, 2013) - A genetic analysis by Baylor University biologists suggests that the stocking of Florida bass in Texas reservoirs impacts bass populations far beyond the actual stocking location.
The native largemouth bass has a long and nearly continuous stocking history in Texas. However, the Florida bass is widely considered a better sport fish because it grows to a greater size. Subsequently, stocking efforts in Texas reservoirs have transitioned from largemouth bass to Florida bass.
The Baylor researchers analyzed the genetic composition of 69 largemouth ...