(Press-News.org) CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — New research suggests that elite athletes – Olympic medalists in volleyball, for example – perform better than the rest of us in yet another way. These athletes excel not only in their sport of choice but also in how fast their brains take in and respond to new information – cognitive abilities that are important on and off the court.
The study, of 87 top-ranked Brazilian volleyball players (some of them medalists in the Beijing and London Olympics) and 67 of their nonathletic contemporaries, also found that being an athlete minimizes the performance differences that normally occur between women and men. Female athletes, the researchers found, were more like their male peers in the speed of their mental calculations and reaction times, while nonathletic females performed the same tasks more slowly than their male counterparts.
The study appears in the journal Frontiers in Psychology.
"I think we have learned that athletes are different from us in some ways," said University of Illinois psychology professor and Beckman Institute Director Arthur Kramer, who led the study with graduate student Heloisa Alves.
"We found that athletes were generally able to inhibit behavior, to stop quickly when they had to, which is very important in sport and in daily life, " Kramer said. "They were also able to activate, to pick up information from a glance and to switch between tasks more quickly than nonathletes. I would say these were modest differences, but they were interesting differences nonetheless."
Overall, the athletes were faster at memory tests and tasks that required them to switch between tasks. They were quicker to notice things in their peripheral vision and to detect subtle changes in a scene. And in general, they were better able to accomplish tasks while ignoring confusing or irrelevant information.
Perhaps the most interesting discovery was that female athletes had significant cognitive advantages over their nonathletic counterparts, Kramer said, advantages that minimized the subtle speed differences between them and the men. The female athletes were faster than their nonathletic peers at detecting changes in a scene and could more quickly pick out relevant details from a distracting background. Their performance on these and the other tasks was on par with the male athletes, whereas nonathletic males consistently outperformed their female peers.
Nonathletes excelled at only one of the cognitive tests the researchers administered. In this test, called the stopping task, participants were asked to type a "Z" or "/" key as soon as they saw it on a computer screen – unless they heard a tone shortly after the character appeared, in which case they were told to refrain from responding. Nonathletes tended to be faster in cases where the tone never sounded, while athletes were better at inhibiting their responses after hearing a tone.
The ability to inhibit a response is one marker of what brain researchers call "executive function," the capacity to control, plan and regulate one's behavior, Kramer said. While it has obvious advantages in sport, the ability to quickly inhibit an action also is useful in daily life, he said.
"One way to think about it is you're in your car and you're ready to start off at a light and you catch in your side vision a car or a bicyclist that you didn't see a second ago," he said. Being able to stop after having decided to go can be a lifesaver in that situation.
"So both facilitating and inhibiting behavior is important," he said.
Kramer said the athletes' slower performance on this one task might be the result of a strategic decision they had made to wait and see if the tone sounded before they committed to pressing a key.
"My bet is that the athletes were just learning to read the task a little better," he said. "So if I'm a little slower in going, I'll be a little better at stopping if I need to."
All in all, the new findings add to the evidence that those who spend years training on specific physical tasks tend to also have enhanced cognitive abilities, Kramer said.
"Our understanding is imperfect because we don't know whether these abilities in the athletes were 'born' or 'made,' " he said. "Perhaps people gravitate to these sports because they're good at both. Or perhaps it's the training that enhances their cognitive abilities as well as their physical ones. My intuition is that it's a little bit of both."
INFORMATION:
Editor's notes: To reach Arthur Kramer, call 217-244-8373; email a-kramer@illinois.edu.
The paper, "Perceptual-cognitive expertise in elite volleyball players," is available online.
Elite athletes also excel at some cognitive tasks
2013-03-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Las Cumbres Observatory: First light at Saao for third 1-meter node of global telescope
2013-03-19
18 March 2013 – Goleta, CA., USA -- The first truly global telescope came a significant step closer to completion this month with the installation and first light on three new 1-meter telescopes at the South Africa Astronomical Observatory (SAAO) near Sutherland, South Africa. A team of five Las Cumbres engineers, technicians, and a postdoc, convened at Sutherland for three weeks during late February and early March to achieve this feat.
"The South African Astronomical Observatory is pleased to collaborate with the Las Cumbres Observatory Global Telescope project, and ...
Researchers create map of 'shortcuts' between all human genes
2013-03-19
Some diseases are caused by single gene mutations. Current techniques for identifying the disease-causing gene in a patient produce hundreds of potential gene candidates, making it difficult for scientists to pinpoint the single causative gene. Now, a team of researchers led by Rockefeller University scientists have created a map of gene "shortcuts" to simplify the hunt for disease-causing genes.
The investigation, spearheaded by Yuval Itan, a postdoctoral fellow in the St. Giles Laboratory of Human Genetics of Infectious Diseases, has led to the creation of what he calls ...
Human microbe study provides insight into health, disease
2013-03-19
Microbes from the human mouth are telling Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists something about periodontitis and more after they cracked the genetic code of bacteria linked to the condition.
The finding, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, profiles the SR1 bacteria, a group of microbes present in many environments, ranging from the mouth to deep within the Earth, that have never been cultivated in the laboratory. Human oral SR1 bacteria are elevated in periodontitis, a disease marked by inflammation and infection of the ligaments and bones ...
Slabs of ancient tectonic plate still lodged under California, researchers find
2013-03-19
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Large chunks of an ancient tectonic plate that slid under North America millions of years ago are still present under parts of central California and Mexico, according to new research led by Brown University geophysicists.
Around 100 million years ago, the Farallon oceanic plate lay between the converging Pacific and North American plates, which eventually came together to form the San Andreas fault. As those plates converged, much of the Farallon was subducted underneath North America and eventually sank deep into the mantle. Off ...
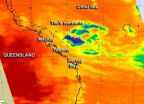
NASA sees remnants of Cyclone Tim fading near southeastern Queensland
2013-03-19
Infrared satellite imagery tells the temperature of the cloud tops within a tropical cyclone as well as the sea surface temperatures around the storms. A recent infrared image from NASA's Aqua satellite showed very little strength in the remnants of ex-cyclone Tim offshore from southeastern Queensland.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared image of Cyclone Tim on March 18 at 0355 UTC (March 17 at 11:55 p.m. EDT). The AIRS image showed that cloud top temperatures had warmed significantly since the previous ...
Uncontrolled hypertension could bring increased risk for Alzheimer's disease
2013-03-19
A study in the JAMA Neurology (formerly the Archives of Neurology) suggests that controlling or preventing risk factors such as hypertension earlier in life may limit or delay the brain changes associated with Alzheimer's disease and other age-related neurological deterioration.
Dr. Karen Rodrigue, assistant professor in the UT Dallas Center for Vital Longevity (CVL), was lead author on a study that looked at whether people with both hypertension and a common gene associated with risk of Alzheimer's disease (the APOE-4 gene carried by about 20 percent of the population) ...
Tourist-fed stingrays change their ways
2013-03-19
Stingrays living in one of the world's most famous and heavily visited ecotourism sites — Stingray City/Sandbar in the Cayman Islands — have profoundly changed their ways, raising questions about the impact of so-called "interactive ecotourism" on marine wildlife, reports a new study published March 18 in the journal PLOS ONE.
Researchers from Nova Southeastern University's Guy Harvey Research Institute in Hollywood, Fla., and the University of Rhode Island studied the southern stingray population of Stingray City — a sandbar in the Cayman Islands that draws nearly a ...
Discounts on purchases of healthy foods can improve diets, study finds
2013-03-19
Lowering the costs of healthy foods in supermarkets increases the amount of fruits, vegetables and whole grain foods that people eat, while also appearing to reduce consumption of nutritionally less-desirable foods, according to research from the RAND Corporation.
Researchers examined a program available to members of South Africa's largest private health insurance company that provides a rebate of 10 percent or 25 percent on purchases of healthy foods. The program, started in 2009, now has about 800 participating supermarkets and enrolls more than 260,000 households. ...
Cushioned heel running shoes may alter adolescent biomechanics, performance
2013-03-19
CHICAGO — Many of today's running shoes feature a heavy cushioned heel. New research presented today at the 2013 Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) found that these shoes may alter an adolescent runner's biomechanics (the forces exerted by muscles and gravity on the skeletal structure) and diminish performance.
Researchers recruited 12 adolescent competitive athletes from local track teams, and asked them to run on a treadmill in large heel trainers, track flats and without any shoes (barefoot) at four different speeds. Biomechanics ...
Sexual function improves significantly after hip or knee replacement surgery
2013-03-19
CHICAGO — Osteoarthritis of the hip or knee, affecting millions of Americans each year, is known to limit sexual activity. New research presented today at the 2013 Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) found that total hip (THR) or total knee replacement (TKR) surgery improves sexual function in 90 percent of patients.
In the study, 147 patients under age 70, scheduled for primary THR or TKR, agreed to participate in a study requiring the completion of questionnaires prior to surgery, at six months post surgery, and at one year post surgery. ...