(Press-News.org) Parasitoid wasps of the family Braconidae are known for their deadly reproductive habits. Most of the representatives of this group have their eggs developing in other insects and their larvae, eventually killing the respective host, or in some cases immobilizing it or causing its sterility. Three new species of the parasitoid wasp genus Cystomastacoides, recently described in the Journal of Hymenoptera Research, reflect this fatal behavior.
Two of the new species were discovered in Papua New Guinea, while the third one comes from Thailand. The Thai species, Cystomastacoides kiddo, was named after the character Beatrix Kiddo in Quentin Tarantino's 'Kill Bill' films. The deadly biology of the wasp inspired this reference to the protagonist played by Uma Thurman, where she embodies a deadly assassin and a master of the Tiger/Crane style of kung fu. She is a master of the "Five Point Palm Exploding Heart Technique", a method of killing a person by quickly striking five pressure points around the heart with the fingertips. After the victim takes five steps, the heart explodes and the person falls dead.
The macabre in the name of one of the new species from Papua New Guinea references back to another strand of contemporary pop culture: Cystomastacoides nicolepeelerae is named after Nicole Peeler, the favourite novelist of Donald Quicke, the lead author of this article. Peeler's writing deals with murder mystery, dark powers, the subconscious and the supernatural. The name of the third species, Cystomastacoides asotaphaga, also from Papua New Guinea, lacks the popular culture element but still brings up the deadly survival techniques of the wasps described. In translation, it means feeding on Asota, described genus of moths whose caterpillar is eaten from the inside by the wasp's larva and thus eventually killed.
Asota plana is the first host record for the genus to which the new species belong. It is a widespread moth species known to feed on multiple fig tree (Ficus) species. With three new species from Papua New Guinea and Thailand, this paper also extends the known range of the genus considerably. Previously, Cystomastacoides had been known only from a single species, Cystomastacoides coxalis, which was found only in mainland China (Yunnan).
INFORMATION:
Original Source:
Quicke DLJ, Smith MA, Hrcek J, Butcher BA (2013) Cystomastacoides van Achterberg (Braconidae, Rogadinae): first host record and descriptions of three new species from Thailand and Papua New Guinea. Journal of Hymenoptera Research 31: 65, doi: 10.3897/JHR.31.3385
Licensing:
This press release is available under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. It is expected to link back to the original article.
Posted by Pensoft Publishers.
'Kill Bill' character inspires the name of a new parasitoid wasp species
1 of 3 recently discovered wasp species was named after Beatrix Kiddo, referring to the deadly parasitoid practices of the animal
2013-03-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Max Planck Florida Institute study points to major discovery for Alzheimer's disease
2013-03-20
FLORIDA, March 19, 2013 – The Journal of Neuroscience has published a study led by researchers at the Max Planck Florida Institute for Neuroscience, the first and only U.S. extension of the prestigious Max Planck Society, that may hold a stunning breakthrough in the fight to treat Alzheimer's disease. The study potentially identifies a cause of Alzheimer's disease—based on a newly-discovered signaling pathway in cellular models of Alzheimer's disease—and opens the door for new treatments by successfully blocking this pathway. The Institute, which recently opened in December ...
First of its kind study in Canada looks at who is taking aspirin to prevent heart attack or stroke
2013-03-20
A new study out of the Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry shows a large population of healthy people are taking Aspirin to prevent cardiovascular disease, despite the fact that new literature shows it isn't as beneficial as once thought.
Olga Szafran and Mike Kolber, in the Department of Family Medicine at the University of Alberta, surveyed patients over the age of 50 at two clinics in Alberta. They found that more than 40 per cent of people who don't suffer from cardiovascular disease are popping pills daily to prevent a heart attack or stroke – a practice called primary ...
More career options may explain why fewer women pursue jobs in science and math
2013-03-20
Women may be less likely to pursue careers in science and math because they have more career choices, not because they have less ability, according to a new study published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
Although the gender gap in mathematics has narrowed in recent decades, with more females enrolling and performing well in math classes, females are still less likely to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) than their male peers.
Researchers tend to agree that differences in math ...
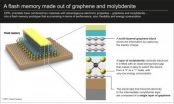
Fantastic flash memory combines graphene and molybdenite
2013-03-20
After the molybdenite chip, we now have molybdenite flash memory, a significant step forward in the use of this new material in electronics applications. The news is even more impressive because scientists from EPFL's Laboratory of Nanometer Electronics and Structures (LANES) came up with a truly original idea: they combined the advantages of this semiconducting material with those of another amazing material – graphene. The results of their research have recently been published in the journal ACS Nano.
Two years ago, the LANES team revealed the promising electronic ...
Are survivors of childhood leukemia and lymphoma at greater risk of chronic fatigue as adults?
2013-03-20
New Rochelle, NY, Mar 19, 2013—Chronic fatigue, a persistent lack of energy that does not improve with rest, is at least three times more prevalent among adult survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and lymphoma experienced during childhood or adolescence than in the general adult population, according to an article in Journal of Adolescent and Young Adult Oncology (JAYAO), (http://www.liebertpub.com/JAYAO) a multidisciplinary peer-reviewed publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. (http://www.liebertpub.com) JAYAO is the Official Journal of the Society for ...
Biennial mammograms best after 50, even for women with dense breasts
2013-03-20
Screening for breast cancer every two years appears just as beneficial as yearly mammograms for women ages 50 to 74, with significantly fewer "false positives" – even for women whose breasts are dense or who use hormone therapy for menopause.
That is the finding of a new national study involving more than 900,000 women.
The study was published on March 18 in JAMA Internal Medicine.
The same team of researchers from UC San Francisco and Seattle-based Group Health Research Institute recently reported similar results for older women ages 66 to 89 years old.
By contrast, ...
Record simulations conducted on Lawrence Livermore supercomputer
2013-03-20
LIVERMORE, Calif. -- Researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory have performed record simulations using all 1,572,864 cores of Sequoia, the largest supercomputer in the world. Sequoia, based on IBM BlueGene/Q architecture, is the first machine to exceed one million computational cores. It also is No. 2 on the list of the world's fastest supercomputers, operating at 16.3 petaflops (16.3 quadrillion floating point operations per second).
The simulations are the largest particle-in-cell (PIC) code simulations by number of cores ever performed. PIC simulations ...
To make health systems more effective, physicians say time is now for clinician-led innovation
2013-03-20
(Boston) –Physician experts in health system issues propose a timely alternative process for harnessing and supporting physician-led innovations to rapidly address front-line health care delivery problems and improve health. Published as a Viewpoint article in the March 20th issue of the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), the authors propose health systems adopt a strategy widely accepted in U.S. industries of "user-led" innovation.
User-led innovation is predicated on the idea that important enhancements to products and services are often made by users ...
University of Maryland researchers identify fish protein that may inhibit cancer metastasis
2013-03-20
BALTIMORE – March 19, 2013. Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine have identified a peptide, or protein, derived from Pacific cod that may inhibit prostate cancer and possibly other cancers from spreading, according to preclinical research published online in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
"The use of natural dietary products with anti-tumor activity is an important and emerging field of research," says senior author Hafiz Ahmed, Ph.D., assistant professor of biochemistry and molecular biology at the University of Maryland ...
Transportation study reveals potential for deep cuts to petroleum use and carbon emissions
2013-03-20
The U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) and Argonne National Laboratory (ANL) today announced the release of the Transportation Energy Futures (TEF) study, an assessment of avenues to reach deep cuts in petroleum use and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in the transportation sector.
"Transportation is an engine of our economic strength, but it also represents a key challenge for the future of U.S. energy use," NREL Senior Analyst Austin Brown said. "Transportation accounts for 71 percent of total U.S. petroleum consumption and 33 ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
[Press-News.org] 'Kill Bill' character inspires the name of a new parasitoid wasp species1 of 3 recently discovered wasp species was named after Beatrix Kiddo, referring to the deadly parasitoid practices of the animal