(Press-News.org) SAN DIEGO — Mayo Clinic neurology experts will present research findings on Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, sleep disorders, concussions, multiple sclerosis and more at the American Academy of Neurology annual meeting in San Diego, March 16. They also are available to offer expert comment on other research findings.
Mayo studies being presented and their embargo times include:
Cognitively normal people with high amyloid levels likelier to develop dementia
EMBARGOED until Monday, March 18, 2013, 1:30 p.m. EDT
People who aren't showing signs of cognitive decline but have evidence of amyloid in their brains, showed a greater rate of shrinkage of their hippocampus — the part of the brain involved with memory function — later on than cognitively normal people without amyloid in the brain.
Researchers evaluated people without cognitive decline, but who showed evidence on brain imaging of amyloid deposits in their brain. They measured the size of their hippocampus over time (it tends to shrink very early in the progression of Alzheimer's disease). They concluded that when amyloid is deposited in the brain, damage to the hippocampus is very likely to occur down the road.
Researchers develop test to gauge severity of concussions
EMBARGOED until Monday, March 18, 5 p.m. EDT
Neurologists at Mayo Clinic in Arizona have used autonomic reflex testing to find physical signs a concussion has occurred, a step toward creating a diagnostic test to gauge the severity of concussions.
In the study of 21 patients, each patient displayed the same abnormality, viewed as a sign a concussion has occurred. The hope is that, with more testing, what happens with this abnormality over time will prove a reliable physical sign of recovery.
Right now, physicians rely on a patient reporting when symptoms have subsided to determine stages of recovery. Doctors know from functional imaging studies that there is a lag between when the person reports that their symptoms have resolved and the time they are actually healed.
Heart attack victims who get therapeutic hypothermia unlikely to have cognitive impairment
EMBARGOED until Tuesday, March 19, 4:45 p.m. EDT
The majority of heart attack victims who receive therapeutic hypothermia after entering a coma don't suffer cognitive decline and are able to return to everyday tasks such as going to work, according to Mayo Clinic researchers.
Most studies of comatose survivors of cardiac arrest focus on mortality or functional outcome based on physical limitations. This study looked at the long-term cognitive abilities of patients surviving out-of-hospital cardiac arrest who were treated with therapeutic hypothermia.
Head trauma, pesticide use and lack of coffee linked to Parkinson's in men
EMBARGOED until Tuesday, March 19, 5 p.m. EDT
Men who have had head trauma, used pesticides and don't drink coffee are more likely to be associated with Parkinson's disease. When those characteristics were coupled with immunologic diseases such as multiple sclerosis and lupus and when coupled with a family history of dementia, men were even likelier to have Parkinson's. By contrast, anemia was the most important factor in women developing Parkinson's.
###
About Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic is a nonprofit worldwide leader in medical care, research and education for people from all walks of life. For more information, visit http://www.mayoclinic.com and http://www.mayoclinic.org/news.
Journalists can become a member of the Mayo Clinic News Network for the latest health, science and research news and access to video, audio, text and graphic elements that can be downloaded or embedded.
Mayo Clinic neurologists present research at American Academy of Neurology Annual Meeting
2013-03-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New disorder could classify millions of people as mentally ill
2013-03-20
Personal View: The new somatic symptom disorder in DSM-5 risks mislabeling many people as mentally ill
Millions of people could be mislabeled as mentally ill when psychiatry's bible of diagnoses is updated in May, warns a senior doctor in this week's BMJ.
The next edition of the American Psychiatric Association's Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) – used around the world to classify mental disorders - will include a new category of somatic symptom disorder.
But Allen Frances, Chair of the current (DSM-IV) task force warns that the DSM-5 ...
Studies for approval of new drugs have insufficient patients to evaluate safety
2013-03-20
For medicines intended for chronic use, the number of patients studied before regulatory approval is insufficient to properly evaluate safety and long-term efficacy, requiring the need for new legislation, according to a study by European researchers published in this week's PLOS Medicine.
Current European guidelines specify that in order to fully evaluate the safety of medicines being developed for chronic (long-term) treatment of non-life threatening diseases, at least 1000 patients must take the new drug and that 300 and 100 patients must use the drug for 6 and 12 ...
African immunization systems fall short, African experts say
2013-03-20
In Africa, issues of vaccine supply, financing, and sustainability require urgent attention if the Millennium Development Goals are to be achieved, according to African experts writing in this week's PLOS Medicine.
Shingai Machingaidze, Charles Wiysonge, and Gregory Hussey from the University of Cape Town in South Africa commend African countries for their progress in immunisation programmes but infectious disease outbreaks, for example, polio and measles outbreaks, as well as high vaccine dropout rates across the region, indicate failures within the immunisation system. ...
For polar bears, it's survival of the fattest
2013-03-20
One of the most southerly populations of polar bears in the world – and the best studied – is struggling to cope with climate-induced changes to sea ice, new research reveals. Based on over 10 years' data the study, published in the British Ecological Society's Journal of Animal Ecology, sheds new light on how sea ice conditions drive polar bears' annual migration on and off the ice.
Lead by Dr Seth Cherry of the University of Alberta, the team studied polar bears in western Hudson Bay, where sea ice melts completely each summer and typically re-freezes from late November ...
Caffeine 'can significantly protect against crash risk' for long distance heavy vehicle drivers
2013-03-20
Research: Use of caffeinated substances and risk of crashes in long distance drivers of commercial vehicles: case-control study
Long distance commercial drivers who consume caffeinated substances such as coffee or energy drinks, to stay awake while driving, are significantly less likely to crash than those who do not, even though they drive longer distances and sleep less, finds a study published today on bmj.com.
Long distance drivers routinely experience monotonous and extended driving periods in a sedentary position, which has been associated with wake time drowsiness, ...
'Kill Bill' character inspires the name of a new parasitoid wasp species
2013-03-20
Parasitoid wasps of the family Braconidae are known for their deadly reproductive habits. Most of the representatives of this group have their eggs developing in other insects and their larvae, eventually killing the respective host, or in some cases immobilizing it or causing its sterility. Three new species of the parasitoid wasp genus Cystomastacoides, recently described in the Journal of Hymenoptera Research, reflect this fatal behavior.
Two of the new species were discovered in Papua New Guinea, while the third one comes from Thailand. The Thai species, Cystomastacoides ...
Max Planck Florida Institute study points to major discovery for Alzheimer's disease
2013-03-20
FLORIDA, March 19, 2013 – The Journal of Neuroscience has published a study led by researchers at the Max Planck Florida Institute for Neuroscience, the first and only U.S. extension of the prestigious Max Planck Society, that may hold a stunning breakthrough in the fight to treat Alzheimer's disease. The study potentially identifies a cause of Alzheimer's disease—based on a newly-discovered signaling pathway in cellular models of Alzheimer's disease—and opens the door for new treatments by successfully blocking this pathway. The Institute, which recently opened in December ...
First of its kind study in Canada looks at who is taking aspirin to prevent heart attack or stroke
2013-03-20
A new study out of the Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry shows a large population of healthy people are taking Aspirin to prevent cardiovascular disease, despite the fact that new literature shows it isn't as beneficial as once thought.
Olga Szafran and Mike Kolber, in the Department of Family Medicine at the University of Alberta, surveyed patients over the age of 50 at two clinics in Alberta. They found that more than 40 per cent of people who don't suffer from cardiovascular disease are popping pills daily to prevent a heart attack or stroke – a practice called primary ...
More career options may explain why fewer women pursue jobs in science and math
2013-03-20
Women may be less likely to pursue careers in science and math because they have more career choices, not because they have less ability, according to a new study published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
Although the gender gap in mathematics has narrowed in recent decades, with more females enrolling and performing well in math classes, females are still less likely to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) than their male peers.
Researchers tend to agree that differences in math ...
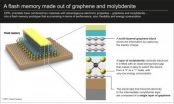
Fantastic flash memory combines graphene and molybdenite
2013-03-20
After the molybdenite chip, we now have molybdenite flash memory, a significant step forward in the use of this new material in electronics applications. The news is even more impressive because scientists from EPFL's Laboratory of Nanometer Electronics and Structures (LANES) came up with a truly original idea: they combined the advantages of this semiconducting material with those of another amazing material – graphene. The results of their research have recently been published in the journal ACS Nano.
Two years ago, the LANES team revealed the promising electronic ...