(Press-News.org) For the first time, a study has compared water quality trends in forested streams across the country that are largely undisturbed by land use or land cover changes.
The study, which draws on decades' worth of data from reference streams in six U.S. states and Puerto Rico, underscores the value of long-term data in understanding the patterns and causes of water quality changes in streams and rivers. It is published in the current issue of the journal Environmental Research Letters.
"Much of what we know about changes in stream water quality comes from studies where basins have been impacted by human activity," said Alba Argerich, a postdoctoral research associate with Oregon State University and the study's lead author. "Our work intentionally focused on relatively undisturbed streams, the very reference sites that serve as benchmarks for evaluating water quality trends."
In the study, Argerich and colleagues analyzed concentrations of stream nitrogen, which, despite regulations, have been on the rise across the country as energy and food production release reactive forms of the compound into waterways. Once there, reactive nitrogen—nitrate and ammonium—can alter stream function and cause substantial changes in stream communities.
The study focused on sites that are part of the USDA Forest Service's Experimental Forest and Range network, a system of 80 locations across the country that provide settings for long-term science and management studies. Many of the sites have long-term monitoring programs and data sets spanning decades and so provide unique opportunities to evaluate long-term trends.
"These long-term water quality data from experimental forests are a treasure," said Sherri Johnson, a research ecologist with the Pacific Northwest Research Station and a co-author of the study. "Some sites have over 40 years of weekly data."
The researchers analyzed 559 years of stream nitrate and 523 years of stream ammonium data from 22 streams in 7 experimental forests across the country. They found that even these near-pristine forested streams are subject to change, as stream nitrate has declined in the Pacific Northwest, in the Northeast, and in Puerto Rico, but has increased in the Mountain West and the South. They also observed that, within a forest, trends were not always in sync—at some sites, two streams within an experimental forest had opposing trends for the same type of nitrogen for the same period of time, suggesting that the controls on stream nitrogen concentrations may vary among and within sites.
"Understanding how nutrient concentrations are changing over time in reference streams is vital for informing best management practices that are aimed at protecting water resources," Argerich said.
INFORMATION:
To learn more about the study, visit http://iopscience.iop.org/1748-9326/8/1/014039. To browse a cross-site database of stream chemistry data, visit http://web.fsl.orst.edu/streamchem/.
The Pacific Northwest Research Station—headquartered in Portland, Ore.—generates and communicates scientific knowledge that helps people make informed choices about natural resources and the environment. The station has 11 laboratories and centers located in Alaska, Oregon, and Washington and about 390 employees. Learn more online at http://www.fs.fed.us/pnw.
Study explores long-term water quality trends in near-pristine streams
Drawing on 500-plus-years of data, study highlights value of long-term stream monitoring
2013-03-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ben-Gurion U. researchers and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. develop psoriasis drug
2013-03-20
BEER-SHEVA, Israel, March 20, 2013 -- Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU) researchers, in collaboration with Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., have developed a promising drug candidate to treat psoriasis. The finding was reported in a new paper published in Chemistry and Biology.
Psoriasis is a chronic, non-contagious disease characterized by inflamed lesions covered with silvery-white scabs of dead skin. An auto-immune disease, psoriasis affects at least four million Americans. It is caused by the disturbance in the natural balance between pro-inflammatory signals ...
'End of men'? Not even close
2013-03-20
It's March 2013 – 50 years after Betty Friedan's explosive book launched feminism's "second wave," 41 after Title IX, the equal-opportunity amendment banning sex discrimination in education, was signed into law – and some exceptionally successful women are making a lot of news. Former U.S. Secretary of State Hillary Clinton is riding high in public opinion, winning straw polls for the 2016 presidency. Yahoo CEO Marissa Mayer, after shrugging off maternity leave, has sparked the "Great Telecommuting Debate" with a company-wide ban on working from home. And Sheryl Sandberg, ...
Mechanical forces play key role in assembly and disassembly of an essential cell protein
2013-03-20
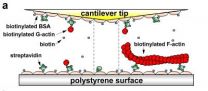
Researchers have for the first time demonstrated that mechanical forces can control the depolymerization of actin, a critical protein that provides the major force-bearing structure in the cytoskeletons of cells. The research suggests that forces applied both externally and internally may play a much larger role than previously believed in regulating a range of processes inside cells.
Using atomic force microscopy (AFM) force-clamp experiments, the research found that tensile force regulates the kinetics of actin dissociation by prolonging the lifetimes of bonds at low ...
SMU Lyle School of Engineering course sparks CCL study
2013-03-20
DALLAS (SMU) – The Innovation Gym in SMU's Lyle School of Engineering was buzzing and clanking on a recent morning as students tested robots they built for a specific task – collecting and remediating water samples, as Lyle faculty and students have been doing by hand in refugee camps in Africa and Bangladesh.
The strong work dynamic that emerged among members of the first-year design class and their embrace of the inter-disciplinary team approach used to teach it has drawn the attention of the Center For Creative Leadership, which will send a team of researchers to ...
Altered brain activity responsible for cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia
2013-03-20
Cognitive problems with memory and behavior experienced by individuals with schizophrenia are linked with changes in brain activity; however, it is difficult to test whether these changes are the underlying cause or consequence of these symptoms. By altering the brain activity in mice to mimic the decrease in activity seen in patients with schizophrenia, researchers reporting in the Cell Press journal Neuron on March 20 reveal that these changes in regional brain activity cause similar cognitive problems in otherwise normal mice. This direct demonstration of the link between ...
Some Alaskan trout use flexible guts for the ultimate binge diet
2013-03-20
Imagine having a daylong Thanksgiving feast every day for a month, then, only pauper's rations the rest of the year.
University of Washington researchers have discovered Dolly Varden, a kind of trout, eating just that way in Alaska's Chignik Lake watershed.
Organs such as the stomach and intestines in the Dolly Varden doubled to quadrupled in size when eggs from spawning sockeye salmon became available each August, the researchers found. They were like vacuums sucking up the eggs and nipping at the flesh of spawned-out salmon carcasses.
Then, once the pulse of eggs ...
Spiral beauty graced by fading supernova
2013-03-20
Supernovae are amongst the most violent events in nature. They mark the dazzling deaths of stars and can outshine the combined light of the billions of stars in their host galaxies.
In 1999 the Lick Observatory in California reported the discovery of a new supernova in the spiral galaxy NGC 1637. It was spotted using a telescope that had been specially built to search for these rare, but important cosmic objects [1]. Follow-up observations were requested so that the discovery could be confirmed and studied further. This supernova was widely observed and was given the ...
Estrogen helps keep joint pain at bay after hysterectomy
2013-03-20
CLEVELAND, Ohio (March 20, 2013)—Estrogen therapy can help keep joint pain at bay after menopause for women who have had a hysterectomy. Joint pain was modestly, but significantly, lower in women who took estrogen alone than in women who took placebo in the Women's Health Initiative (WHI) trial. The findings were published online today in Menopause, the journal of The North American Menopause Society.
Studies looking at how estrogen affects joint pain in women after menopause have had mixed results. But this analysis of data on some 1,000 women who had hysterectomies—representative ...
Estrogen may relieve post-menopausal joint pain
2013-03-20
Post-menopausal women, who often suffer from joint pain, could find some long-term relief by taking estrogen-only medication, according to a new study based on the Women's Health Initiative (WHI) that was released online today by the journal, Menopause.
Previous studies of estrogen's influence on joint symptoms had produced mixed results, so researchers examined the findings of the WHI, the largest-ever study of the use of hormonal therapy in post-menopausal women. They examined the findings of the women enrolled in the Estrogen-Alone program, in which women who had undergone ...
Discovery of first motor with revolution motion in a virus-killing bacteria advances nanotechnology
2013-03-20
Scientists have cracked a 35-year-old mystery about the workings of the natural motors that are serving as models for development of a futuristic genre of synthetic nanomotors that pump therapeutic DNA, RNA or drugs into individual diseased cells. Their report revealing the innermost mechanisms of these nanomotors in a bacteria-killing virus — and a new way to move DNA through cells — is being published online today in the journal ACS Nano.
Peixuan Guo and colleagues explain that two motors have been found in nature: A linear motor and a rotating motor. Now they report ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
[Press-News.org] Study explores long-term water quality trends in near-pristine streamsDrawing on 500-plus-years of data, study highlights value of long-term stream monitoring