Educational app or digital candy? Helping parents choose quality apps for kids
2015-05-06
There are now over 80,000 apps marketed as "educational" in the Apple app store, the majority of which are targeted towards children and even babies. Parents are led to believe that these apps provide real learning opportunities for their children, but scientific research suggests that many of the apps are nothing more than digital candy.
"Many apps marketed as 'educational' are basically the equivalent of sugary foods," says Kathy Hirsh-Pasek of Temple University, co-author on a new report investigating educational apps. "At best, most of these apps will do no harm; ...
Conservationists 'on the fence' about barriers to protect wildlife in drylands
2015-05-06
NEW YORK (May 6, 2015) -- To fence or not to fence? That is the question facing conservationists concerned with barriers that keep wildlife in and people out.
According to a new study by the Zoological Society of London (ZSL), Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) and other groups, appearing in April 20 edition of the Journal of Applied Ecology, new policies must be developed before fences are erected - particularly in dryland ecosystems where mobility is essential for both humans and wildlife.
Some nations are considering fences as a means to protect remnant wildlife ...
Scientists X-ray chocolate
2015-05-06
This news release is available in German.
An X-ray study carried out at DESY allows to improve the quality of chocolate. The study offers new insights into the formation of fat bloom, an unwelcome white layer that occasionally forms on chocolate. "Although fat blooming is perfectly harmless, it causes millions in damage to the food industry as a result of rejects and customer complaints," explains the main author of the study, Svenja Reinke, from the Hamburg University of Technology (TUHH). "Despite this well known quality issue, comparatively little has been known ...
Springing into action: The Wyss Institute introduces its new biosafety process
2015-05-06
(BOSTON) - Increasingly, scientists across the world and in the Unites States are reporting new and groundbreaking innovations in biotechnology with transformative implications in human health and environmental sustainability. Examples range from synthetically created, metabolically-engineered bacteria for the sustainable production of fuel to gene editing therapies that could one day help in the prevention and treatment of a large number of human diseases.
While these technologies are developed in laboratories, researchers are not only giving utmost consideration to ...
Social network experiments create a tipping point to improve public health
2015-05-06
New Haven, Conn. - Convincing a large group of people to change its behavior is no popularity contest, a new study shows.
In a novel experiment, researchers found that certain public health interventions work best when key "influencers" in a face-to-face social network are exposed to the program. What's surprising, they say, is that those key influencers are not the most socially connected people in the network.
Furthermore, those individuals can be identified through a survey method informed by network structure rather than costly and time-consuming social network mapping. ...
From the depths of a microscopic world, spontaneous cooperation
2015-05-06
Maybe it's not such a dog-eat-dog world after all. A clever combination of two different types of computer simulations enabled a group of Illinois researchers to uncover an unexpectedly cooperative group dynamic: the spontaneous emergence of resource sharing among individuals in a community. Who were the members of this friendly, digitally represented collective? Escherichia coli, rod-shaped bacteria found in the digestive systems of humans and many other animals.
The finding, initially predicted by mathematical models and then confirmed through empirical testing, was ...
A step toward avoiding the dreaded chocolate 'bloom'
2015-05-06
Chocolate is one of the world's most popular foods, but when a whitish coating called a bloom appears on the confection's surface, it can make consumers think twice about eating it. The coating is made up of fats and is edible, but it changes the chocolate's appearance and texture -- and not for the better. Now scientists report in the journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces new information that could help chocolatiers prevent blooms from forming.
Svenja K. Reinke and colleagues explain that baked goods and confectionery products, including chocolate, contain a mix ...
New commentary in Women's Health Issues: Trauma-informed primary care
2015-05-06
WASHINGTON, DC (May 6, 2015) -- Patients with a history of trauma can benefit from working with healthcare providers who understand trauma's role in health and can offer resources to assist with healing. A commentary published today in the journal Women's Health Issues proposes an approach to providing such trauma-informed primary care (TIPC). Edward L. Machtinger, MD, director of the Women's HIV Program (WHP) at the University of California, San Francisco, and his co-authors identify four core components of a TIPC approach: environment, screening, response, and a robust ...
Thermometer-like device could help diagnose heart attacks
2015-05-06
Diagnosing a heart attack can require multiple tests using expensive equipment. But not everyone has access to such techniques, especially in remote or low-income areas. Now scientists have developed a simple, thermometer-like device that could help doctors diagnose heart attacks with minimal materials and cost. The report on their approach appears in the ACS journal Analytical Chemistry.
Sangmin Jeon and colleagues note that one way to tell whether someone has had a heart attack involves measuring the level of a protein called troponin in the person's blood. The protein's ...
The next step in DNA computing: GPS mapping?
2015-05-06
Conventional silicon-based computing, which has advanced by leaps and bounds in recent decades, is pushing against its practical limits. DNA computing could help take the digital era to the next level. Scientists are now reporting progress toward that goal with the development of a novel DNA-based GPS. They describe their advance in ACS' The Journal of Physical Chemistry B.
Jian-Jun Shu and colleagues note that Moore's law, which marked its 50th anniversary in April, posited that the number of transistors on a computer chip would double every year. This doubling has ...
Study discovers negative regulator of natural killer cell maturation
2015-05-06
COLUMBUS, Ohio - A new study has identified a regulatory pathway in natural killer cells that inhibits their maturation and homing behavior. Natural killer cells are one of the body's first lines of defense against viruses and cancer. The findings could lead to new strategies for boosting natural-killer cell activity against cancer and viral infections.
The study was led by researchers at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center - Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute (OSUCCC - James). It showed that a protein called Foxo1 ...
Study finds foreclosures fueled racial segregation in US
2015-05-06
WASHINGTON, DC, May 6, 2015 -- Some 9 million American families lost their homes to foreclosure during the late 2000s housing bust, driving many to economic ruin and in search of new residences. Hardest hit were black, Latino, and racially integrated neighborhoods, according to a new Cornell University analysis of the crisis.
Led by demographer Matthew Hall, researchers estimate racial segregation grew between Latinos and whites by nearly 50 percent and between blacks and whites by about 20 percent as whites abandoned and minorities moved into areas most heavily distressed ...
Supreme Court to decide fate of EPA mercury rule with billions at stake
2015-05-06
The justices of the nation's highest court are weighing whether the Environmental Protection Agency should have considered potential compliance costs before proceeding with a rule that requires power plants to reduce their mercury emissions. In March, lawyers from the government and industry presented their sides to the Supreme Court, which could decide the matter in June, according to an article in Chemical & Engineering News (C&EN), the weekly newsmagazine of the American Chemical Society.
Glenn Hess, a senior correspondent at C&EN, notes that the EPA developed the ...
A 'super-cool' way to deliver drugs
2015-05-06
Water, when cooled below 32°F, eventually freezes -- it's science known even to pre-schoolers. But some substances, when they undergo a process called "rapid-freezing" or "supercooling," remain in liquid form -- even at below-freezing temperatures.
The supercooling phenomenon has been studied for its possible applications in a wide spectrum of fields. A new Tel Aviv University study published in Scientific Reports is the first to break down the rules governing the complex process of crystallization through rapid-cooling. According to the research, membranes can be ...
Insight into the Ebola virus nucleocapsid assembly mechanism
2015-05-06
The Ebola virus (EBOV) causes lethal hemorrhagic fever in humans, with extremely high morbidity and mortality. It was first discovered in two simultaneous outbreaks near the Ebola River in sub-Saharan Africa in 1976. Sporadic outbreaks followed until 2014, when it re-emerged in Western Africa and caused a widespread epidemic. As of 24 April 2015, the World Health Organization (WHO) has reported a total number of 26,101 suspected cases and 10,824 deaths. Despite the high death rate of the Ebola hemorrhagic disease, there are no FDA-approved treatments or vaccines available ...
New form of DNA modification may carry inheritable information
2015-05-06
Scientists at the University of Chicago, Harvard, and China have described the surprising discovery and function of a new DNA modification in insects, worms, and algae.
Common DNA modifications occur through methylation, a chemical process that can dramatically change gene expression, which regulates the eventual production of proteins that carry out the functions of an organism. It's all part of a growing new subfield of epigenetics being pioneered by the University of Chicago's Chuan He and his collaborators.
Through epigenetics, organisms sometimes bypass the genetic ...
We all want high social status
2015-05-06
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY'S HAAS SCHOOL OF BUSINESS--Not everyone may care about having an impressive job title or a big, fancy house but all human beings desire a high level of social status, according to a newly published study.
For decades, researchers have argued both sides of the question: is it human nature to want high standing in one's social circle, profession, or society in general?
Prof. Cameron Anderson sought to settle the debate. In "Is the desire for status a fundamental human motive? A review of the empirical literature" (Psychological Bulletin, ...
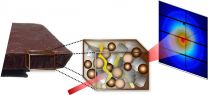
Attosecond physics: A new gateway to the microcosmos
2015-05-06
Ludwig Maximilians Universitaet (LMU) in Munich physicists at the Laboratory for Attosecond Physics have developed a new laser-light source that will lead to significant advances in research on fundamental physics.
The future of electronics lies in optical control of electron flows. That would enable data processing operations to be performed at frequencies equivalent to the rate of oscillation of visible light - some 100,000 times faster than is feasible with current techniques. Physicists at the Laboratory for Attosecond Physics (LAP), which is run jointly by LMU Munich ...
New method detects more breast cancer in screening
2015-05-06
Tomosynthesis detects 40% more breast cancers than traditional mammography does, according to a major screening study from Lund University, Sweden. This is the first large-scale study to compare the screening method with regular mammograms. The 3D X-ray technique is also more comfortable for women, as breast compression is halved.
A total of 7 500 women aged 40-74 took part in the first half of the study, which formed the basis for the findings.
"We see a change as inevitable. Breast tomosynthesis will be introduced, it is just a question of when and on what scale," ...
System model for calculating mine profitability
2015-05-06
A new system dynamic model makes it possible to plan the profitability of mining operations with greater precision than before. Researchers in business at Lappeenranta University of Technology, LUT have developed a model based on system thinking that supports investment decision-making by mining companies and helps optimise the guidance of production in mining investments. The model that has been built has already sparked interest among international mining companies.
"The planning of international investments with the help of more detailed models can save tens of millions ...
VTT sensor detects spoilage of food
2015-05-06
VTT has developed a sensor that detects ethanol in the headspace of a food package. Ethanol is formed as a result of food spoilage. The sensor signal is wirelessly readable, for instance, by a mobile phone. VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland Ltd is searching for a partner so as to commercialise the sensor.
The sensor monitors ethanol emitted from the spoilage of foods into the headspace of a package. Ethanol, in addition to carbon dioxide, was found to be the main volatile spoilage metabolite in fresh-cut fruit. The information given by the sensor is transmitted ...
Supercycles in subduction zones
2015-05-06
This news release is available in German. On 11 March 2011, a massive release of stress between two overlapping tectonic plates occurred beneath the ocean floor off the coast of Japan, triggering a giant tsunami. The Tohoku quake resulted in the death of more than 15,000 people, the partial or total destruction of nearly 400,000 buildings, and major damage to the Fukushima nuclear power plant. This "superquake" may have been the largest in a series of earthquakes, thus marking the end of what's known as a supercycle: a sequence of several large earthquakes.
A research ...
Blood markers could help predict outcome of infant heart surgery
2015-05-06
The study, published today in the journal Critical Care Medicine and carried out at Royal Brompton Hospital, followed children undergoing surgery for congenital heart disease, and found that by analysing metabolites in the blood -- molecules created as a result of metabolism -- it was possible to predict a child's clinical outcome.
Congenital heart disease is relatively common, affecting between 4 and 14 babies in every 1,000 live births. Around one third of affected children require surgery during early childhood. However, surgery itself can cause complications, affecting ...
Bacteria research opens way for new antibiotics
2015-05-06
University of Adelaide researchers have discovered a target for the development of completely new antibiotics against disease-causing bacteria.
Published online ahead of print in the leading microbiology journal Molecular Microbiology, the researchers have identified a building block common to many types of bacterial 'virulence factors' (the bacterial proteins which act as weapons to cause disease, such as toxins or degrading enzymes).
The building block, called the Passenger-associated Transport Repeat (PATR), has been found in virulence factors of many major harmful ...
UCSF team proposes new clinical model
2015-05-06
Recognizing that patients' experiences of childhood and adult trauma are common and have a direct impact on their health, UCSF clinical researchers and Positive Women's Network-USA have developed and are reporting a new primary care model.
"In our clinic where we treat women with HIV, we are able to deliver lifesaving anti-HIV medications, but we still lose patients far too often. Looking back over the last ten years, only 16 percent of our patient deaths were due to HIV/AIDS. Most deaths were due to events such as depression, suicide, murder, drug overdoses and lung ...
[1] ... [2996]
[2997]
[2998]
[2999]
[3000]
[3001]
[3002]
[3003]
3004
[3005]
[3006]
[3007]
[3008]
[3009]
[3010]
[3011]
[3012]
... [8827]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.