Viruses impaired if their targets have diverse genes
2014-11-18
SALT LAKE CITY, Nov. 18, 2014 - When a viral infection spread through five genetically identical mice in a row, the virus replicated faster and became more virulent or severe. But when the infection spread one-by-one through five genetically diverse mice, the virus had trouble adapting and became less virulent.
By showing this long-suspected mechanism holds true within a single species of vertebrate animal, namely, mice, the University of Utah study suggests that increased genetic diversity should be promoted in livestock and in captive-bred endangered species so as to ...
Verbal abuse in the workplace: Are men or women most at risk?
2014-11-18
This news release is available in French. There is no significant difference in the prevalence of verbal abuse in the workplace between men and women, according to a systematic review of the literature conducted by researchers at the Institut universitaire de santé mentale de Montréal and the University of Montreal.
Verbal abuse is the most common form of workplace violence. It can lead to many consequences, particularly at the psychological and organizational levels. Several studies underline the importance of taking into account sociodemographic variables ...
A noncoding RNA promotes pediatric bone cancer
2014-11-18
Ewing sarcoma is a cancer of bone or its surrounding soft tissue that primarily affects children and young adults. A hallmark of Ewing sarcoma is a translocation event that results in the fusion of an RNA binding protein, known as EWS, with a transcription factor, such as FLI1. Previous work suggested that the fusion protein EWS-FLI1 promoted cancer by changing gene expression; however, the gene targets were unknown. A new study in the Journal of Clinical Investigation indicates that a long noncoding RNA named Ewing sarcoma-associated transcript 1 (EWSAT1) is a critical ...
Understanding adverse blood vessel remodeling following stenting
2014-11-18
Atherosclerosis is a leading cause of heart attacks and stroke. The narrowing of blood vessels that is caused by atherosclerosis can be treated with angioplasty or stenting to improve blood flow. However, the stenting process induces deleterious remodeling of the blood vessel that can increase thrombosis risk, limiting the use of this strategy. In an article published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, a research team led by Ziad Ali of the Columbia University Medical Center now provides new insights into the pathological remodeling that occurs following blood ...
Physicians prescribe less brand name drugs when EHR default settings show generics first
2014-11-18
PHILADELPHIA - Programming electronic health records to make generic drugs the default choice when physicians write prescriptions may offer one way to reduce unnecessary spending and improve health care value in the face of spiraling U.S. health expenditures, according to a new study from researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine, The Wharton School and the Center for Health Incentives and Behavioral Economics (CHIBE) at the University of Pennsylvania, and the Philadelphia VA Medical Center. The study is published in a special issue of Annals of Internal Medicine featuring ...
Antibiotics get a 'time-out'
2014-11-18
This news release is available in French.
Montreal, November 17, 2014 - Resistance to antibiotics is an important health concern that affects both the spread of infections, like Clostridium difficile, and the medication budget. Researchers at the McGill University Health Centre (MUHC) examined the effectiveness of adopting an antibiotic "time-out" during treatment, which involves regularly re-evaluating the treatment strategy as the clinical situation evolves. The study, published in this month's issue of the Annals of Internal Medicine, showed that structured time-outs, ...
The implications of new cholesterol guidelines on a rural Midwest community
2014-11-17
Minneapolis, MN - November 17, 2014 - At the 2014 American Heart Association Scientific Sessions in Chicago, Ill., Minneapolis Heart Institute Foundation Research Cardiologist Dr. Michael Miedema gave a presentation entitled "The Implications of the Recent American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Guidelines for the Treatment of Blood Cholesterol on a Rural Community: The Heart of New Ulm Project."
"The recently released cholesterol guidelines appear to have significantly increased the number of middle-aged adults who qualify for a cholesterol-lowering ...
Fat around the heart may cause irregular heartbeat
2014-11-17
MAYWOOD, Ill. - Obesity is a known risk factor for atrial fibrillation, the most common heart rhythm disorder.
Obesity is commonly measured as a person's body mass index (BMI). But a Loyola University Medical Center study has found that the layer of fat around the outside of the heart is more closely associated with atrial fibrillation than BMI.
"Many people who would not be considered obese by their BMI nevertheless have high volumes of fat around their hearts, which could put them at risk for atrial fibrillation. Simple measures such as BMI may fail to completely ...
Penn study examines patients' perspectives on deactivation of ICDs in end-of-life
2014-11-17
CHICAGO - Most patients with implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs)--small devices placed in a person's chest to help treat irregular heartbeats with electrical pulses, or shocks--haven't thought about device deactivation if they were to develop a serious illness from which they were not expected to recover. But given changes in healthcare, there may be a new reason to do so. A new study led by researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, which was presented today at the 2014 Scientific Sessions of the American Heart Association, ...
Imperfect system is all that protects you from genetic parasites out to destroy your genes
2014-11-17
We like to think of evolution as a fine-tuning process, one that whittles away genetic redundancies. The only problem is, we are not fine-tuned machines. Our bodies are chock-full of parts that either don't work anymore or are so buggy that our biology has Macgyvered a way to make it work.
Take our DNA. No, seriously, take our DNA. It's mostly garbage anyways. Fifty percent of our genome is comprised of genetic parasites, called transposable elements or transposons, that usually lie dormant. When they are allowed to move around the genome, they can wreak havoc on our ...
Race, hospital, insurance status all factors in how lung cancer is treated
2014-11-17
African Americans, Hispanics, and those who receive care at a community hospital are all significantly less likely than other patients to receive treatment for early stage non-small cell lung cancer, according to a report in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology.
"We found significant disparities for treatment of a curable cancer based on race, insurance status, and whether or not treatment was at an academic or community hospital," said Dr. Matthew Koshy, a physician in the department of radiation oncology at the University of Illinois at Chicago College of Medicine, and ...
U-M-led study adds to understanding of how phthalate exposure impacts pregnancy
2014-11-17
ANN ARBOR--In recent years, scientists have linked chemicals known as phthalates with complications of pregnancy and fetal development.
Now, a study led by researchers at the University of Michigan School of Public Health sheds light on the mechanism that may be to blame.
Phthalates are chemicals used to make plastic materials more flexible and can also be found in personal care products such as perfumes, deodorants and lotions. They can enter the human body by being ingested, inhaled or through the skin. Most often phthalates are metabolized and excreted quickly, but ...
Nothing fishy about health benefits of plant-based omega-3 fatty acid
2014-11-17
Increasing the amount of omega-3s in your diet, whether from fish or flax, will likely decrease your risk of getting heart disease, according to Penn State nutritionists.
A substantial amount of evidence exists supporting the heart-health benefits of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid (EPA and DHA), marine-derived omega-3 fatty acids. However, much less evidence exists to demonstrate the positive effects of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a plant-based omega-3 fatty acid.
"The benefits reported for EPA and DHA are stronger because supplements of EPA and DHA ...
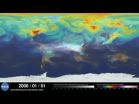
NASA computer model provides a new portrait of carbon dioxide
2014-11-17
VIDEO:
An ultra-high-resolution NASA computer model has given scientists a stunning new look at how carbon dioxide in the atmosphere travels around the globe. Plumes of carbon dioxide in the simulation...
Click here for more information.
An ultra-high-resolution NASA computer model has given scientists a stunning new look at how carbon dioxide in the atmosphere travels around the globe.
Plumes of carbon dioxide in the simulation swirl and shift as winds disperse the greenhouse ...
Geologic mapping of asteroid Vesta reveals history of large impacts
2014-11-17
A team of 14 scientists led by David Williams of Arizona State University's School of Earth and Space Exploration has completed the first global geologic and tectonic map of the asteroid Vesta. The work reveals that Vesta's history has been dominated by impacts from large meteorites.
The mapping was carried out using images from NASA's Dawn spacecraft, which orbited Vesta between June 2011 and September 2012. The images let scientists create high-resolution geological maps, revealing the variety of Vesta's surface features in unprecedented detail.
"The geologic mapping ...
Catering to needs of in-store, online customers boosts marketing effectiveness, revenue
2014-11-17
COLUMBIA, Mo. - Online retail sales totaled $75 billion in the second quarter of 2014, according to data from the U.S. Census Bureau. As consumers shop more using the Internet and cell phones, retailers must adjust their marketing strategies to reach these consumers. In a recently published study, a University of Missouri researcher found that consumers' preferences differ when they are shopping in a physical store compared to shopping online. Catering to shoppers' online and in-store preferences can increase the effectiveness of traditional marketing tactics such as direct ...
Growth factor regenerates damaged nerves without sprouting new blood vessels
2014-11-17
Researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago College of Medicine have found that a growth factor can regenerate damaged peripheral nerves without causing the growth of new blood vessels -- making it a unique candidate to treat nerve damage in areas of the body where the proliferation of blood vessels would be a drawback.
"One example would be in the cornea, which has a requirement for dense innervation but where the formation of new blood vessels would block vision," said Dr. Mark Rosenblatt, professor and head of ophthalmology and visual sciences at UIC and corresponding ...
First genetic-based tool to detect circulating cancer cells in blood
2014-11-17
Metastasis is bad news for cancer patients. Northwestern University scientists now have demonstrated a simple but powerful tool that can detect live cancer cells in the bloodstream, potentially long before the cells could settle somewhere in the body and form a dangerous tumor.
The NanoFlare technology is the first genetic-based approach that is able to detect live circulating tumor cells out of the complex matrix that is human blood -- no easy feat. In a breast cancer study, the NanoFlares easily entered cells and lit up the cell if a biomarker target was present, even ...
Why lizards have bird breath
2014-11-17
SALT LAKE CITY, Nov. 17, 2014 - Whether birds are breathing in or out, air flows in a one-directional loop through their lungs. This pattern was unexpected and for decades, biologists assumed it was unique to birds, a special adaptation driven by the intense energy demands of flight.
But that view is wrong, according to University of Utah scientists who now have shown that bird-like breathing also developed in green iguanas - reptiles not known for high-capacity aerobic fitness. The finding bolsters the case that unidirectional bird-like flow evolved long before the first ...
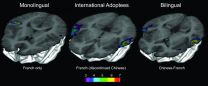
Finding 'lost' languages in the brain
2014-11-17
MONTREAL: An infant's mother tongue creates neural patterns that the unconscious brain retains years later even if the child totally stops using the language, (as can happen in cases of international adoption) according to a new joint study by scientists at the Montreal Neurological Institute and Hospital - The Neuro and McGill University's Department of Psychology. The study offers the first neural evidence that traces of the "lost" language remain in the brain.
"The infant brain forms representations of language sounds, but we wanted to see whether the brain maintains ...
New paper identifies virus devastating sea stars on Pacific Coast
2014-11-17
November 17, 2014--Museum biological collections are the records of life on Earth and as such, they are frequently used to investigate serious environmental issues. When public health officials were concerned about the levels of mercury in fish and birds, for example, scientists studied museum specimens to assess historical changes in mercury contamination. Eggs in museum collections were analyzed to establish the connection between DDT, thinning eggshells, and the decline in bird populations. And now, specimens from the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County (NHM) ...
No racial disparities in development of atrial fibrillation among heart failure patients
2014-11-17
CHICAGO - Black patients who have been diagnosed with heart failure are no less likely than white patients to get atrial fibrillation (an irregular heartbeat, or arrhythmia), according to a new study led by researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, which was presented today at the 2014 Scientific Sessions of the American Heart Association. These findings run counter to previous studies, which have found that black patients with heart failure tend to have less atrial fibrillation problems than white patients.
"Even though ...
Investigational oral drug combo shows promise for newly diagnosed multiple myeloma
2014-11-17
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- The investigational drug ixazomib taken orally in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone shows promise in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma, according to the results of a phase 1/2 study published in the journal Lancet Oncology.
"Ixazomib is an investigational, oral proteasome inhibitor with promising anti-myeloma effects and low rates of peripheral neuropathy," says Shaji Kumar, M.D., a hematologist at Mayo Clinic and lead author of the study. "While it is well known that a combination of bortezomib, lenalidomide and dexamethasone ...
New study demonstrates high burden of AFib is associated with lower cognitive function
2014-11-17
iRhythm Technologies, Inc. announced today that study results presented during the American Heart Association (AHA) Scientific Sessions showed an association between a high burden of atrial fibrillation (AFib) and lower cognitive function, specifically executive and verbal function. Previous studies have shown a relationship between AFib, cognitive decline and increased risk of dementia. However, this study, which was led by researchers at the University of Minnesota, demonstrates for the first time a correlation between high AFib burden - the percent of time a person has ...
Simple clinical tests help differentiate Parkinson's disease from atypical parkinsonism
2014-11-17
Amsterdam, NL, 17 November 2014 - Two simple tests conducted during the neurological exam can help clinicians differentiate between early-stage Parkinson's disease (PD) and atypical parkinsonism. By asking patients to perform a tandem gait test and inquiring whether they are still able to ride a bicycle, clinicians can ascertain whether medio-lateral balance is impaired, a defining characteristic of atypical parkinsonism. These findings are published in the Journal of Parkinson's Disease.
This issue of the Journal of Parkinson's Disease also marks the inauguration of ...
[1] ... [3190]
[3191]
[3192]
[3193]
[3194]
[3195]
[3196]
[3197]
3198
[3199]
[3200]
[3201]
[3202]
[3203]
[3204]
[3205]
[3206]
... [8825]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.