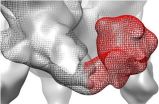
Symmetrical knees linked to Jamaican sprinting prowess
2014-11-17
Why is Jamaica, with a population smaller than that of Los Angeles, home to so many of the world's elite sprinters - runners who compete in the 100, 200, 400 and 800-meter races?
Robert Trivers, an evolutionary biologist and professor of anthropology and biology in the School of Arts and Sciences, set out with his colleagues to find out if there was something about the symmetry of their knees that might partly explain this phenomenon. They already knew from their earlier research that the symmetry of children's knees at age 8 predicts how fast a person runs 14 years later ...
NASA's SDO sees returning sunspot produce mid-level flare
2014-11-17
The sun emitted a mid-level solar flare, peaking at 12:48 p.m. EST on Nov. 16, 2014. NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, which watches the sun constantly, captured an image of the event. Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation. Harmful radiation from a flare cannot pass through Earth's atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground, however -- when intense enough -- they can disturb the atmosphere in the layer where GPS and communications signals travel.
To see how this event may affect Earth, please visit NOAA's Space Weather Prediction Center at http://spaceweather.gov, ...
As temperatures rise, soil will relinquish less carbon to the atmosphere than predicted
2014-11-17
Here's another reason to pay close attention to microbes: Current climate models probably overestimate the amount of carbon that will be released from soil into the atmosphere as global temperatures rise, according to research from the US Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab).
The findings are from a new computer model that explores the feedbacks between soil carbon and climate change. It's the first such model to include several physiologically realistic representations of how soil microbes break down organic matter, a process that ...
Fruit flies learn from others
2014-11-17
Fruit flies do not always conform to the norm. When female fruit flies have to decide where to lay their eggs, they take their lead from what they see most others in their group do. However, some do take their personal preferences into account. So says Marine Battesti of the Université Paris-Sud in France, lead author of a study in Springer's journal Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology.
The site on which an insect chooses to lay her eggs is very important for the development and survival of future generations. Such choices are not fixed, but are influenced by the ...
Advances in electron microscopy reveal secrets of HIV and other viruses
2014-11-17
UC Davis researchers are getting a new look at the workings of HIV and other viruses thanks to new techniques in electron microscopy developed on campus.
The envelope (or Env) protein of HIV is a key target for vaccine makers: it is a key component in RV144, an experimental vaccine that is so far the only candidate to show promise in clinical trials. Also called gp120, the Env protein associates with another protein called gp41 and three gp120/gp41 units associate to form the final trimeric structure. The gp120 trimer is the machine that allows HIV to enter and attack ...
The chemistry of cats: On catnip, pheromones and kitty litter (video)
2014-11-17
WASHINGTON, Nov. 17, 2014 -- They are seemingly the most popular thing on the Internet, the subject of millions of videos and hundreds of memes: cats. This week Reactions answers some of the biggest kitty questions out there: Why does catnip make most cats go crazy? What does it mean when your cat rubs against your leg? How does kitty litter clump? Check out the nearly purr-fect video here: http://youtu.be/6_C9i-2QGeU.
Subscribe to the series at Reactions YouTube, and follow us on Twitter @ACSreactions to be the first to see our latest videos.
INFORMATION:
The American ...
People with COPD who received nutrition treatment in the hospital had better health outcomes
2014-11-17
ABBOTT PARK, Ill., Nov. 17, 2014 - People aged 65 and older, who were being treated for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in the hospital and received nutrition treatment (oral nutrition supplements) had reduced lengths of stay, hospital costs and chances of returning to the hospital within 30-days, according to a study published in CHEST.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) -- which includes conditions like chronic bronchitis and emphysema -- is a lung disease that compromises breathing. As COPD often occurs among seniors, it is one of the leading ...
EARTH Magazine: How much natural hazard mitigation is enough?
2014-11-17
Alexandria, Va. -- Hurricane Sandy struck the U.S. East Coast in October 2012, leaving about $65 billion of damage in its wake and raising the question of how to mitigate the damage from future storms. It's a question that arises in the wake of most natural disasters: What steps can society take to protect itself from storms, floods, landslides, earthquakes, tsunamis or volcanic eruptions? But the question itself illustrates the complexity of preparing for natural disasters.
Our first instincts might be to protect ourselves as well as possible, but reality sets in quickly: ...
New advance in cryopreservation could change management of world blood supplies
2014-11-17
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Engineers at Oregon State University have identified a method to rapidly prepare frozen red blood cells for transfusions, which may offer an important new way to manage the world's blood supply.
It's already possible to cryopreserve human red blood cells in the presence of 40 percent glycerol, but is rarely done because of the time-consuming process to thaw and remove the glycerol from the blood. This can take an hour or more and makes it logistically difficult to use frozen blood.
However, some initial experiments and computer modeling of a proposed ...
Hiding in plain sight: Elusive dark matter may be detected with GPS satellites
2014-11-17
RENO, Nev. - The everyday use of a GPS device might be to find your way around town or even navigate a hiking trail, but for two physicists, the Global Positioning System might be a tool in directly detecting and measuring dark matter, so far an elusive but ubiquitous form of matter responsible for the formation of galaxies.
Andrei Derevianko, of the University of Nevada, Reno, and his colleague Maxim Pospelov, of the University of Victoria and the Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics in Canada, have proposed a method for a dark-matter search with GPS satellites ...
Lawrence Livermore develops method to measure residual stress in 3-D printed metal parts
2014-11-17
LIVERMORE, Calif. - Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory researchers have developed an efficient method to measure residual stress in metal parts produced by powder-bed fusion additive manufacturing.
This 3D printing process produces metal parts layer by layer using a high-energy laser beam to fuse metal powder particles. When each layer is complete, the build platform moves downward by the thickness of one layer, and a new powder layer is spread on the previous layer.
While this process is able to produce quality parts and components, residual stress is a major ...
Penn engineers efficiently 'mix' light at the nanoscale
2014-11-17
The race to make computer components smaller and faster and use less power is pushing the limits of the properties of electrons in a material. Photonic systems could eventually replace electronic ones, but the fundamentals of computation, mixing two inputs into a single output, currently require too much space and power when done with light.
Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania have engineered a nanowire system that could pave the way for this ability, combining two light waves to produce a third with a different frequency and using an optical cavity to amplify ...
Graphene/nanotube hybrid benefits flexible solar cells
2014-11-17
Rice University scientists have invented a novel cathode that may make cheap, flexible dye-sensitized solar cells practical.
The Rice lab of materials scientist Jun Lou created the new cathode, one of the two electrodes in batteries, from nanotubes that are seamlessly bonded to graphene and replaces the expensive and brittle platinum-based materials often used in earlier versions.
The discovery was reported online in the Royal Society of Chemistry's Journal of Materials Chemistry A.
Dye-sensitized solar cells have been in development since 1988 and have been the subject ...
'Probiotics' for plants boost detox abilities; untreated plants overdose and die
2014-11-17
Scientists using a microbe that occurs naturally in eastern cottonwood trees have boosted the ability of two other plants - willow and lawn grass - to withstand the withering effects of the nasty industrial pollutant phenanthrene and take up 25 to 40 percent more of the pollutant than untreated plants.
The approach could avoid the regulatory hurdles imposed on transgenic plants - plants with genes inserted from or exchanged with other plant or animal species - that have shown promise in phytoremediation, the process of using plants to remove toxins from contaminated sites, ...
Researchers present highly anticipated IMPROVE-IT results
2014-11-17
More than a decade ago, researchers from Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) demonstrated that a high dose statin, which lowered cholesterol further than a regular dose statin, provided better clinical outcomes. But questions remained about whether further reducing cholesterol would be even more effective in reducing cardiovascular-related events.
Now, results of the highly anticipated IMProved Reduction of Outcomes: Vytorin Efficacy International Trial (IMPROVE-IT), co-led by researchers at BWH and Duke Medicine, indicate that adding a second drug, ezetimibe, that blocks ...
Ten ways remote sensing can contribute to conservation
2014-11-17
WCS, NASA, And other conservation and remote sensing agencies, universities and NGOs focus on top 10 conservation questions for satellite technology
Remote sensing has and can continue to play a critical role in conserving Earth's biological diversity
Protected area management is a key use of remote sensing data
Newly formed Conservation Remote Sensing Network to apply remote sensing data to conservation challenges
NEW YORK (November 17, 2014)--Scientists from the WCS (Wildlife Conservation Society), NASA, and other organizations have partnered to focus global attention ...
Reprogramming cells, long term
2014-11-17
Harvard Stem Cell Institute (HSCI) researchers, representing five Harvard departments and affiliated institutions as well as the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), have demonstrated that adult cells, reprogrammed into another cell type in a living animal, can remain functional over a long period.
The work by Joe Zhou, an associate professor in Harvard's Department of Stem Cell and Regenerative Biology, and his collaborators is an important advance in the effort to develop cell-based therapies for tissue repair, and specifically in the effort to develop improved ...
UTHealth smoking study: Financial incentives double quit rates
2014-11-17
HOUSTON - (Nov. 17, 2014) - Offering small financial incentives doubles smoking cessation rates among socioeconomically disadvantaged smokers, according to research from The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth). The findings were published last week in the American Journal of Public Health.
Tobacco use is the leading cause of preventable death in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Thanks to public health efforts, smoking rates have declined to 18 percent among American adults. However, nearly 30 percent ...
Family ties that bind: Having the right surname sets you up for life
2014-11-17
If your surname reveals that you descended from the "in" crowd in the England of 1066--the Norman Conquerors--then even now you are more likely than the average Brit to be upper class. To a surprising degree, the social status of your ancestors many generations in the past still exerts an influence on your life chances, say Gregory Clark of the University of California, Davis, in the US and Neil Cummins of the London School of Economics in the UK. They used the Oxbridge attendance of people with rare English surnames (last names) to track social mobility from 1170 to 2012. ...
Behavioral flexibility impaired after exposure to oxycodone
2014-11-17
(NEW YORK - November 17) Brief usage of the painkiller oxycodone may impair behavioral flexibility even after that use ends, suggesting impaired decision-making as an enduring consequence of exposure, according to a study conducted at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and published November 17 in the journal Learning and Memory.
The Mount Sinai study investigated behavioral flexibility, the ability to select new responses when otherwise familiar circumstances change. In people and rodents exposed to drugs of addiction, repeated actions can become automated ...
Businesses can help preserve endangered species with small landscape changes
2014-11-17
Raptors, or birds of prey, some of which are endangered species, typically live in environments that provide natural land cover, such as forests and grasslands. Protecting endangered raptor species helps maintain food chain balance and prevents overpopulation of common raptor prey, such as snakes and rodents. As more businesses are built on the edges of urban areas, land where raptors once lived becomes industrialized, which raises concerns about the consequences of habitat destruction on raptor populations. Now, University of Missouri researchers have found that businesses ...
Newly discovered hormone with potential treatment for obesity, type 2 diabetes, liver disease
2014-11-17
ANN ARBOR -- Researchers at the University of Michigan have discovered how a previously unknown hormone serves as a messenger from fat cells to the liver and are investigating the potential of developing a new treatment for metabolic disorders.
Jiandie Lin of the Life Sciences Institute described how in mice the hormone, NRG4, is secreted by so-called brown fat cells and communicates with the liver to regulate the conversion of sugar into fat. Mice without NRG4 became obese and developed hallmarks of type 2 diabetes and fatty liver disease. When scientists genetically ...
NASA sees the Southern Indian Ocean cyclone season awaken
2014-11-17
The first tropical cyclone of the Southern Indian Ocean cyclone season has formed over 300 miles from Diego Garcia. When NASA-NOAA Suomi NPP satellite passed over Tropical Storm Adjali the VIIRS instrument aboard took a visible picture of the storm that showed bands of thunderstorms wrapped around its center.
NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite passed over Tropical Storm Adjali on Nov. 17 at 09:56 UTC (4:56 a.m. EDT) and the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) instrument aboard captured a visible picture of the storm. The VIIRS image showed that the storm ...
Middle managers and hermit crabs
2014-11-17
RIVERSIDE, Calif. (http://www.ucr.edu) -- Ideas from mid-level managers that can benefit an organization are less likely to be passed up to superiors as hierarchy in the organization increases, according to a just published paper by an assistant professor at the University of California, Riverside.
"I like to call this hermit crab syndrome," said Boris Maciejovsky, an assistant professor of management at UC Riverside's School of Business Administration. "When mid-level managers feel their ideas are not reflected in top management decisions they withdraw, like a hermit ...
New protocol for imaging patients with Ebola
2014-11-17
In a breakthrough that could substantially improve physicians' ability to rapidly evaluate patients with suspected Ebola, radiologists at Emory University Hospital have devised a protocol for obtaining chest radiographs using portable computed radiography. The protocol not only limits the exposure of personnel and equipment to body fluids, it also minimizes the risk of contaminants leaving the isolation unit by use of thorough decontamination procedures.
The step-by-step protocol is outlined in an article published ahead of print in the American Journal of Roentgenology ...
[1] ... [3191]
[3192]
[3193]
[3194]
[3195]
[3196]
[3197]
[3198]
3199
[3200]
[3201]
[3202]
[3203]
[3204]
[3205]
[3206]
[3207]
... [8825]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.