Scanning babies' fingerprints could save lives
2014-09-26
Each year 2.5 million children die worldwide because they do not receive life-saving vaccinations at the appropriate time.
Anil Jain, Michigan State University professor, is developing a fingerprint-based recognition method to track vaccination schedules for infants and toddlers, which will increase immunization coverage and save lives.
To increase coverage, the vaccines must be recorded and tracked. The traditional tracking method is for parents to keep a paper document. But in developing countries, keeping track of a baby's vaccine schedule on paper is largely ineffective, ...
Decision analysis can help women make choices about breast reconstruction
2014-09-26
September 26, 2014 – Decision analysis techniques can help surgeons and patients evaluate alternatives for breast reconstruction—leading to a "good decision" that reflects the woman's preferences and values, according to an article in the October issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS).
The special topic article by Mia K. Markey, PhD, and colleagues of The University of Texas at Austin and The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, introduces plastic surgeons to the ...
New tool assesses skill development in robotic microsurgery, reports Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
2014-09-26
September 26, 2014 – A new standardized assessment provides a useful tool for tracking surgeons' progress as they develop the skills needed to perform robot-assisted microsurgery, reports a study in the October issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS).
"The Structured Assessment of Robotic Microsurgical Skills (SARMS) is the first validated instrument for assessing robotic microsurgical skills," according to the report by ASPS Member Surgeon Dr Jesse C. Selber of the University of Texas ...
Disease without borders
2014-09-26
In a paper published this week online in Global Society, researchers with University of California, San Diego School of Medicine and the Urban Studies and Planning Program, also at UC San Diego, present a bioregional guide that merges place-based (territorial) city planning and ecosystem management along the United States-Mexico border as way to improve human and environmental health.
Issues like climate change, economic crisis, natural disasters and disease outbreaks do not stop at national borders, compelling public health officials, academics and researchers to think ...
Cardiology leaders call for global prevention of heart disease, stroke
2014-09-26
WASHINGTON (Sept. 29, 2014) — Heart disease and stroke contribute to 30 percent of global deaths, more than all infectious and parasitic diseases combined, and 11 cardiovascular organizations are calling for the United Nations to address prevention of heart disease and other non-communicable diseases.
In a statement published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and other cardiology journals, the World Heart Federation's Global Cardiovascular Disease Taskforce—which is comprised of cardiologists and health advocates from the World Heart Federation, African ...
Progress in materials science
2014-09-26
RESEARCHERS at the University of Huddersfield have collaborated with a colleague at a leading Chinese university to produce a detailed appraisal of a complex new welding technique that could be increasingly valuable to modern industry.
‌Professor Andrew Ball (pictured below) and his colleague Dr Fengshou Gu, of the University of Huddersfield's Centre for Efficiency and Performance Engineering, teamed up with Professor Xiaocong He of Kunming University of Science and Technology's (KUST) Innovative Manufacturing Research Centre in order to investigate the technique ...
Severe periodontitis: Sixth most prevalent health condition in the world
2014-09-26
Alexandria, Va., USA – The International and American Associations for Dental Research (IADR/AADR) have published a paper titled "Global Burden of Periodontitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Regression." The manuscript, by lead researcher Wagner Marcenes (Queen Mary University of London, Institute of Dentistry, Barts and The London School) is published in the OnlineFirst portion of the IADR/AADR Journal of Dental Research (JDR).
The purpose of this study was to consolidate all epidemiological data about severe periodontitis and subsequently to generate internally consistent ...
Morphed images of Hollywood celebrities reveal how neurons make up your mind
2014-09-26
An international team of scientists, involving Professor Rodrigo Quian Quiroga, director of the Centre for Systems Neuroscience and Head of Bioengineering at the University of Leicester, has shown how individual neurons in the human brain react to ambiguous morphed faces.
For this, the researchers used images of celebrities, such as Angelina Jolie and Halle Berry, morphed together to create an ambiguous face which test subjects were asked to identify.
The study found that for the same ambiguous images, the neurons fired according to the subjective perception by the ...
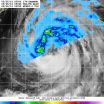
NASA sees Tropical Storm Kammuri's spiral bands of soaking thunderstorms
2014-09-26
Tropical Storm Kammuri continues to strengthen on its north-northwestern track through the Northwestern Pacific Ocean and NASA's TRMM satellite identified a band of thunderstorms containing heavy rainfall northwest of the storm's center. Meanwhile NASA's Aqua satellite got a look at the entire storm and saw that those bands of storms circled the entire storm.
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite flew over the northern half of Tropical Storm Kammuri on Sept. 26 at 1:44 a.m. EDT and the Precipitation Radar instrument saw a strong band of thunderstorms ...
UB study: COPD patients breathe easier with Lung Flute
2014-09-26
BUFFALO, N.Y. – Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) report improved symptoms and health status when they use a hand-held respiratory device called the Lung Flute®, according to a new study by the University at Buffalo. Usually caused by smoking, COPD, which includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema, is the third leading cause of death in the U.S.
The Lung Flute, manufactured by Medical Acoustics, (Buffalo), uses sound waves to break up mucus in the lungs. The device allows patients to clear lung mucus simply by blowing into the hand-held respiratory ...
Penn chemists observe key reaction for producing 'atmosphere's detergent'
2014-09-26
VIDEO:
Earth's atmosphere is a complicated dance of molecules. The chemical output of plants, animals and human industry rise into the air and pair off in sequences of chemical reactions. Such...
Click here for more information.
Earth's atmosphere is a complicated dance of molecules. The chemical output of plants, animals and human industry rise into the air and pair off in sequences of chemical reactions. Such processes help maintain the atmosphere's chemical balance; for ...
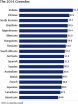
National Geographic/GlobeScan study reveals increased concern about environment
2014-09-26
WASHINGTON (Sept. 26, 2014)—A new global analysis released today by the National Geographic Society and GlobeScan finds that concern about environmental problems has increased in most countries surveyed, and that more people now expect global warming will negatively affect them during their lifetime than in 2012. Despite this, National Geographic's Greendex, a comprehensive measure of consumer behavior in 65 areas related to housing, transportation, food and consumer goods, shows that sustainable consumer behavior has only grown slowly.
Results of the 2014 Greendex, a ...
Strategy to reduce side effects in modern cancer therapy
2014-09-26
This news release is available in German. An interdisciplinary team of researchers from the University of Vienna (Institute of Inorganic Chemistry) and the Medical University of Vienna (Institute for Cancer Research) has successfully developed a new strategy for reducing the often serious side effects of an important class of modern anticancer drugs (tyrosine kinase inhibitors). The novel drug is supposed to restrict its activity with high selectivity to the malignant tumour.
The occurrence of severe side effects and the development of resistance are two of the biggest ...
Sensitive youngsters
2014-09-26
Young individuals of a species are often more sensitive towards environmental stress than their adult counterparts. Scientists from GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel now observed this effect in the sea star Asterias rubens from the Baltic Sea. In a long-term laboratory experiment that was conducted in the framework of the German research network BIOACID (Biological Impacts of Ocean Acidification), the researchers simulated three different levels of acidification that could be reached in the Baltic Sea by the uptake of additional carbon dioxide (CO2) within ...
Study identifies unexpected clue to peripheral neuropathies
2014-09-26
CINCINNATI – New research shows that disrupting the molecular function of a tumor suppressor causes improper formation of a protective insulating sheath on peripheral nerves – leading to neuropathy and muscle wasting in mice similar to that in human diabetes and neurodegeneration.
Scientists from Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center report their findings online Sept. 26 in Nature Communications. The study suggests that normal molecular function of the tumor suppressor gene Lkb1 is essential to an important metabolic transition in cells as peripheral nerves (called ...
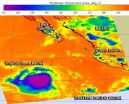
NASA identifies cold cloud tops in Tropical Storm Rachel
2014-09-26
NASA's Aqua satellite saw the area of strong thunderstorms with colder cloud tops had grown within the Eastern Pacific Ocean's Tropical Storm Rachel.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the large Tropical Storm Rachel on Sept. 25 at 4:41 p.m. EDT and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument, saw that the extent of colder cloud tops had increased, indicating thunderstorm heights were increasing and it was strengthening. The expansion of those stronger thunderstorms also suggests that the northeasterly wind shear may be relaxing a little. The strongest thunderstorms ...
Underwater robot for port security
2014-09-26
Last week, at the International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, MIT researchers unveiled an oval-shaped submersible robot, a little smaller than a football, with a flattened panel on one side that it can slide along an underwater surface to perform ultrasound scans.
Originally designed to look for cracks in nuclear reactors' water tanks, the robot could also inspect ships for the false hulls and propeller shafts that smugglers frequently use to hide contraband. Because of its small size and unique propulsion mechanism — which leaves no visible wake — the ...
Penn team studies nanocrystals by passing them through tiny pores
2014-09-26
An interdisciplinary team of University of Pennsylvania researchers has now applied a cutting-edge technique for rapid gene sequencing toward measuring other nanoscopic structures. By passing nanoscale spheres and rods through a tiny hole in a membrane, the team was able to measure the electrical properties of those structures' surfaces.
Their findings suggest new ways of using this technique, known as "nanopore translocation," to analyze objects at the smallest scale.
The research was led by Marija Drndić, professor in the Department of Physics and Astronomy ...
Geisel researchers contribute to study of trained immunity
2014-09-26
Hanover, NH - A study published in the journal Science provides support for a new—and still controversial—understanding of the immune system. The research was conducted by collaborators in the U.S. and Europe, including Robert Cramer, PhD, an assistant professor of microbiology and immunology at the Geisel School of Medicine and member of the Dartmouth Lung Biology Center, and Kelly Shepherdson, PhD, at the time a graduate student in Cramer's lab.
Typically, scientists divide the immune system into two categories: the innate immune response and the adaptive immune response. ...
New UT Dallas technology may lead to prolonged power in mobile devices
2014-09-26
Researchers from The University of Texas at Dallas have created technology that could be the first step toward wearable computers with self-contained power sources or, more immediately, a smartphone that doesn't die after a few hours of heavy use.
This technology, published online in Nature Communications, taps into the power of a single electron to control energy consumption inside transistors, which are at the core of most modern electronic systems.
Researchers from the Erik Jonsson School of Engineering and Computer Science found that by adding a specific atomic ...
High-throughput cell-sorting method can separate 10 billion bacterial cells in 30 minutes
2014-09-26
University of Hawaii at Manoa College of Engineering mechanical engineer Yi Zuo has developed a new, high-throughput method for sorting cells capable of separating 10 billion bacterial cells in 30 minutes.
The finding has already proven useful for studying bacterial cells and microalgae, and could one day have direct applications for biomedical research and environmental science—basically any field in which a large quantity of microbial samples need to be processed.
The new method was described in a September 2014 publication in the scientific journal Analytical Chemistry, ...
New scientific review of genetically engineered feeds in livestock diets
2014-09-26
An article published in the peer-reviewed Journal of Animal Science concludes feeding livestock diets that contain genetically engineered (GE) crops has no impact on the health or productivity of those animals. In a thorough review of scientific literature and field data sets, the article documents evidence that the performance and health of food-producing animals fed GE crops are comparable with those of animals fed non-GE crops.
Since their introduction in 1996, GE feed crops have become an increasing component of livestock diets. Today, more than 95 percent of U.S. ...
Experts call for widening the debate on climate change
2014-09-26
Environmental scientists are being urged to broaden the advice they give on global climate change, say experts who are also frustrated that decision makers are not taking enough action.
Writing in the journal Nature Climate Change, The University of Manchester researchers argue that scientists are expressing a strong desire to fix the problems highlighted by their studies into human-induced climate change
The authors suggest there are problems with environmental scientists offering practical solutions that can help societies adapt to a fast-changing Earth - one where ...
How plankton gets jet lagged
2014-09-26
A hormone that governs sleep and jet lag in humans may also drive the mass migration of plankton in the ocean, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have found. The molecule in question, melatonin, is essential to maintain our daily rhythm, and the European scientists have now discovered that it governs the nightly migration of a plankton species from the surface to deeper waters. The findings, published online today in Cell, indicate that melatonin's role in controlling daily rhythms probably evolved early in the history ...
Green light for clever algae
2014-09-26
The researchers headed by Prof Dr Nicole Frankenberg-Dinkel have been the first ones to reveal similarities and differences in the assembly of the light-harvesting machinery of the cryptophyte Guillardia theta compared to cyanobacteria and red algae. The publication of their results in the current issue of "The Journal of Biological Chemistry" is among the two per cent of the publications that were selected as "Paper of the week".
Cryptophytes: Matryoshka dolls of the waters
Unlike traditional eukaryotic cells – i.e. all cells with a nucleus – cryptophyte cells resemble ...
[1] ... [3310]
[3311]
[3312]
[3313]
[3314]
[3315]
[3316]
[3317]
3318
[3319]
[3320]
[3321]
[3322]
[3323]
[3324]
[3325]
[3326]
... [8827]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.