Glaciers in the Grand Canyon of Mars?
2014-09-29
Boulder, Colo., USA – For decades, planetary geologists have speculated that glaciers might once have crept through Valles Marineris, the 2000-mile-long chasm that constitutes the Grand Canyon of Mars. Using satellite images, researchers have identified features that might have been carved by past glaciers as they flowed through the canyons; however, these observations have remained highly controversial and contested.
Now, a joint team from Bryn Mawr College and the Freie Universitaet Berlin has identified what could be the first mineralogical evidence of past glaciers ...
At the interface of math and science
2014-09-29
In popular culture, mathematics is often deemed inaccessible or esoteric. Yet in the modern world, it plays an ever more important role in our daily lives and a decisive role in the discovery and development of new ideas — often behind the scenes.
UC Santa Barbara's Paul Atzberger, a professor in the Department of Mathematics and an assistant professor of mechanical engineering, often works in areas where science and math intersect. Some of his recent research published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science (PNAS) and featured on the cover of the journal ...
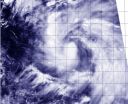
Newborn Tropical Storm Phanfone triggers warnings in Northwestern Pacific
2014-09-29
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over newborn Tropical Storm Phanfone on Sept. 29 and captured a picture of the storm that showed thunderstorms wrapped tightly around the storm's center, and a large band of thunderstorms spiraling into the center from the east. Phanfone is now a threat to various islands and warnings are in effect.
A tropical storm Warning is in effect for Saipan, Tinian, Pagan and Alamagan. In addition, a typhoon watch is in effect for the northern Marianas Islands, including Pagan and Alamagan.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) ...
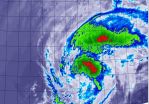
NASA sees Tropical Storm Kammuri winding down over open ocean
2014-09-29
Tropical Storm Kammuri continues to appear more like a cold front on satellite imagery as it transitions into an extra-tropical storm over the Northwestern Pacific Ocean.
When NASA's Terra satellite passed over Kammuri on Sept. 29 at 7:40 a.m. EDT (11:40 UTC), the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument captured an infrared look at the storm. MODIS showed that the bulk of strong storms elongated from southwest to northeast.
On Sept. 29, 2014 at 0300 UTC (Sept. 28 at 11 p.m. EDT) Tropical Storm Kammuri had maximum sustained winds near 45 knots ...
NASA's Aqua satellite sees Rachel before losing hurricane status
2014-09-29
Tropical Storm Rachel strengthened into a hurricane over the weekend of Sept. 27 and 28, only to weaken back into a tropical storm by Sept. 29. NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Rachel before it weakened and took a visible picture of the storm off Baja California's coast.
Rachel became the Eastern Pacific Ocean's twelfth hurricane on Saturday, Sept. 27 at 5 p.m. EDT when maximum sustained winds reached 75 mph (120 kph). When NASA's Aqua satellite saw Rachel, the maximum sustained winds were at the same strength. At that time, Rachel's center was 485 miles (780 km) west ...
MaxBin: Automated sorting through metagenomes
2014-09-29
Microbes – the single-celled organisms that dominate every ecosystem on Earth - have an amazing ability to feed on plant biomass and convert it into other chemical products. Tapping into this talent has the potential to revolutionize energy, medicine, environmental remediation and many other fields. The success of this effort hinges in part on metagenomics, the emerging technology that enables researchers to read all the individual genomes of a sample microbial community at once. However, given that even a teaspoon of soil can contain billions of microbes, there is a great ...
Adding uncertainty to improve mathematical models
2014-09-29
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Mathematicians from Brown University have introduced a new element of uncertainty into an equation used to describe the behavior of fluid flows. While being as certain as possible is generally the stock and trade of mathematics, the researchers hope this new formulation might ultimately lead to mathematical models that better reflect the inherent uncertainties of the natural world.
The research, published in Proceedings of the Royal Society A, deals with Burgers' equation, which is used to describe turbulence and shocks in fluid flows. ...
New ways to treat anemia could evolve from acetate supplement research
2014-09-29
DALLAS – Sept. 29, 2014 – UT Southwestern Medical Center researchers seeking novel treatments for anemia found that giving acetate, the major component of household vinegar, to anemic mice stimulated the formation of new red blood cells.
Currently, the hormone erythropoietin is administered to treat anemia, but this treatment carries with it side effects such as hypertension and thrombosis (blood clotting). The new research, which was performed in mice, suggests that acetate supplements could eventually be a suitable supplement or possibly even an alternative to administration ...
Fires in Papua, Indonesia and New Guinea
2014-09-29
According to a NASA story from 2009, "human activities in this area of the world have contributed to the growing fire emissions issue. Palm oil is increasingly grown for use as a cooking oil and biofuel, while also replacing trans fats in processed foods. It has become the most widely produced edible oil in the world, and production has swelled in recent years to surpass that of soybean oil.
The environmental effects of such growth have been significant. Land has to be cleared to grow the crop, and the preferred method is fire. The clearing often occurs in drained peatlands ...
Modeling shockwaves through the brain
2014-09-29
Since the start of the military conflicts in Iraq and Afghanistan, more than 300,000 soldiers have returned to the United States with traumatic brain injury caused by exposure to bomb blasts — and in particular, exposure to improvised explosive devices, or IEDs. Symptoms of traumatic brain injury can range from the mild, such as lingering headaches and nausea, to more severe impairments in memory and cognition.
Since 2007, the U.S. Department of Defense has recognized the critical importance and complexity of this problem, and has made significant investments in traumatic ...
Self-compassion key to positive body image and coping
2014-09-29
Women who accept and tolerate their imperfections appear to have a more positive body image despite their body mass index (BMI) and are better able to handle personal disappointments and setbacks in their daily lives.
Research out of the Faculty of Arts at the University of Waterloo found that this self-compassion might be an important means to increase positive body image and protect girls and young women against unhealthy weight-control practices and eating disorders.
"Women may experience a more positive body image and better eating habits if they approach disappointments ...
Chefs move to schools can increase school meal participation and vegetable intake among students
2014-09-29
Gourmet pizza in school? According to a new Food and Brand Lab pilot study, published in Appetite, chef-made meals can increase participation in the National School Lunch Program (NSLP) by 9% and overall selection and consumption of vegetables by 16%!
Chefs Move to Schools (CMTS), an initiative of Michelle Obama's Let's Move campaign, pairs chefs with schools in order to provide nutrition instruction to students and culinary advice to interested school food service workers.
A CMTS event was held in an Upstate New York high school (of 370 students) and researchers David ...
Childhood asthma linked to lack of ventilation for gas stoves, OSU study shows
2014-09-29
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Parents with children at home should use ventilation when cooking with a gas stove, researchers from Oregon State University are recommending, after a new study showed an association between gas kitchen stove ventilation and asthma, asthma symptoms and chronic bronchitis.
"In homes where a gas stove was used without venting, the prevalence of asthma and wheezing is higher than in homes where a gas stove was used with ventilation," said Ellen Smit, an associate professor in the College of Public Health and Human Sciences at OSU and one of the study's ...
Transplant drug could boost the power of brain tumor treatments, U-M study finds
2014-09-29
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — Every day, organ transplant patients around the world take a drug called rapamycin to keep their immune systems from rejecting their new kidneys and hearts. New research suggests that the same drug could help brain tumor patients by boosting the effect of new immune-based therapies.
In experiments in animals, researchers from the University of Michigan Medical School showed that adding rapamycin to an immunotherapy approach strengthened the immune response against brain tumor cells.
What's more, the drug also increased the immune system's "memory" ...
UT Arlington researchers develop new transparent nanoscintillators for radiation detection
2014-09-29
A University of Texas at Arlington research team says recently identified radiation detection properties of a light-emitting nanostructure built in their lab could open doors for homeland security and medical advances.
In a paper to be published in the Oct. 1 issue of Optics Letters, UT Arlington Physics Professor Wei Chen and his co-authors describe a new method to fabricate transparent nanoscintillators by heating nanoparticles composed of lanthanum, yttrium and oxygen until a transparent ceramic is formed. A scintillator refers to a material that glows in response ...
'Deadly diarrhea' rates nearly doubled in 10 years: Study
2014-09-29
Washington, DC, September 29, 2014 – Infections with the intestinal superbug C. difficile nearly doubled from 2001 to 2010 in U.S. hospitals without noticeable improvement in patient mortality rates or hospital lengths of stay, according to a study of 2.2 million C. difficile infection (CDI) cases published in the October issue of the American Journal of Infection Control, the official publication of the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology (APIC).
In this retrospective study from The University of Texas College of Pharmacy, researchers ...
Sleep twitches light up the brain
2014-09-29
VIDEO:
Researchers record no brain activity when a baby rat vigorously moves its left hindlimb while awake.
Click here for more information.
A University of Iowa study has found twitches made during sleep activate the brains of mammals differently than movements made while awake.
Researchers say the findings show twitches during rapid eye movement (REM) sleep comprise a different class of movement and provide further evidence that sleep twitches activate circuits throughout ...
Higher nurse-to-patient standard improves staff safety
2014-09-29
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) —A 2004 California law mandating specific nurse-to-patient staffing standards in acute care hospitals significantly lowered job-related injuries and illnesses for both registered nurses and licensed practical nurses, according to UC Davis research published online in the International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health. The study is believed to be the first to evaluate the effect of the law on occupational health.
"We were surprised to discover such a large reduction in injuries as a result of the California law," said study lead author ...
2013 Colorado front range flood: Debris-flow a major hazard
2014-09-29
Boulder, Colorado, USA – Massive flooding in Colorado in September 2013, and the concomitant landslides and debris flows, caused widespread damage across the Front Range. In the October issue of GSA Today, Jeffrey Coe, Jason Kean, Jonathan Godt, Rex Baum, and Eric Jones at the U.S. Geological Survey; David Gochis at the National Center for Atmospheric Research; and Gregory Anderson of the Boulder Mountain Fire Protection District present insights on hazard assessment gained from this extraordinary debris-flow event.
Between 9 and 13 September 2013, more than 1,100 debris ...
Tree killers, yes, fire starters, no: Mountain pine beetles get a bad rap, study says
2014-09-29
MADISON, Wis. — Mountain pine beetles get a bad rap, and understandably so. The grain-of-rice-sized insects are responsible for killing pine trees over tens of millions of acres in the Western U.S. and Canada over the last decade.
But contrary to popular belief, these pests may not be to blame for more severe wildfires like those that have recently swept through the region. Instead, weather and topography play a greater role in the ecological severity of fires than these bark-boring beetles.
New research led by the University of Wisconsin-Madison and the Washington ...
Brief depression questionnaires could lead to unnecessary antidepressant prescriptions
2014-09-29
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) —Short questionnaires used to identify patients at risk for depression are linked with antidepressant medications being prescribed when they may not be needed, according to new research from UC Davis Health System published in the September-October issue of the Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine.
Known as "brief depression symptom measures," the self-administered questionnaires are used in primary care settings to determine the frequency and severity of depression symptoms among patients. Several questionnaires have been developed to ...
Nitrogen fingerprint in biomolecules could be from early sun
2014-09-29
Chemical fingerprints of the element nitrogen vary by extremes in materials from the molecules of life to the solar wind to interstellar dust. Ideas for how this great variety came about have included alien molecules shuttled in by icy comets from beyond our solar system and complex chemical scenarios.
New experiments using a powerful source of ultraviolet light have shown that no extra-solar explanation is needed and the chemistry is straight forward, scientists from the University of California, San Diego, Hebrew University and UCLA report in the early online edition ...
Study reveals new clues to help understand brain stimulation
2014-09-29
BOSTON – Over the past several decades, brain stimulation has become an increasingly important treatment option for a number of psychiatric and neurological conditions.
Divided into two broad approaches, invasive and noninvasive, brain stimulation works by targeting specific sites to adjust brain activity. The most widely known invasive technique, deep brain stimulation (DBS), requires brain surgery to insert an electrode and is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of Parkinson's disease and essential tremor. Noninvasive techniques, ...
Research suggests new strategies for killing TB bacterium
2014-09-29
Over the past few years, a class of compounds called ADEPs (cyclic acyldepsipeptides) has emerged as a promising new weapon in the fight against drug-resistant bacteria. The compounds work by attaching themselves to a cellular enzyme called ClpP, which bacterial cells use to rid themselves of harmful proteins. With an ADEP attached, ClpP can't function properly, and the bacterial cell dies.
Now, scientists from Brown University and Massachusetts Institute of Technology have shown new details of how ADEPs bind to the ClpP complex in the bacterium that causes tuberculosis. ...
Viral infection might just be a phase... transition
2014-09-29
PITTSBURGH—Many double-stranded DNA viruses infect cells by ejecting their genetic information into a host cell. But how does the usually rigid DNA packaged inside a virus' shell flow from the virus to the cell?
In two separate studies, Carnegie Mellon University biophysicist Alex Evilevitch has shown that in viruses that infect both bacteria and humans, a phase transition at the temperature of infection allows the DNA to change from a rigid crystalline structure into a fluid-like structure that facilitates infection.
The findings, published in Nature Chemical Biology ...
[1] ... [3306]
[3307]
[3308]
[3309]
[3310]
[3311]
[3312]
[3313]
3314
[3315]
[3316]
[3317]
[3318]
[3319]
[3320]
[3321]
[3322]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.