To improve oral health of adults with developmental disabilities, support caregivers
2014-10-01
BOSTON (October 1, 2014) — Despite a policy focus on expanding access to care for adults with developmental disabilities, this vulnerable population continues to have significant dental disease. In this month's issue of The Journal of the American Dental Association, researchers from Tufts University School of Medicine and Tufts University School of Dental Medicine report on the first large-scale survey to investigate factors influencing at-home oral care provided by caregivers to adults with developmental disabilities. The study findings suggest that, in addition to addressing ...
Keeping your eyes on the prize can help with exercise, NYU study finds
2014-10-01
New research suggests the adage that encourages people to keep their "eyes on the prize" may be on target when it comes to exercise. When walking, staying focused on a specific target ahead can make the distance to it appear shorter and help people walk there faster, psychology researchers have found. Their study, which compares this technique to walking while looking around the environment naturally, offers a new strategy to improve the quality of exercise.
"People are less interested in exercise if physical activity seems daunting, which can happen when distances to ...
Study offers insight into challenges facing college athletes
2014-10-01
A new study from North Carolina State University sheds light on how some collegiate student-athletes deal with uncertainties ranging from excelling in both school and sports to their career prospects outside of athletics, and urges university athletic programs to adopt new efforts to support student-athletes.
"We wanted to explore how student-athletes at top-tier universities cope with the dual challenges of meeting the expectations of their teams while simultaneously complying with their responsibilities as university students," says Dr. Lynsey Romo, an assistant professor ...
Novel approach to magnetic measurements atom-by-atom
2014-10-01
Having the possibility to measure magnetic properties of materials at atomic precision is one of the important goals of today's experimental physics. Such measurement technique would give engineers and physicists an ultimate handle over magnetic properties of nano-structures for future applications. In an article published in Physical Review Letters researchers propose a new method, utilizing properties of the quantum world – the phase of the electron beam – to detect magnetism with atom-by-atom precision.
The electron microscope is a fascinating instrument. It uses a ...
Platinum meets its match in quantum dots from coal
2014-10-01
Graphene quantum dots created at Rice University grab onto graphene platelets like barnacles attach themselves to the hull of a boat. But these dots enhance the properties of the mothership, making them better than platinum catalysts for certain reactions within fuel cells.
The Rice lab of chemist James Tour created dots known as GQDs from coal last year and have now combined these nanoscale dots with microscopic sheets of graphene, the one-atom-thick form of carbon, to create a hybrid that could greatly cut the cost of generating energy with fuel cells.
The research ...
Predicting the future course of psychotic illness
2014-10-01
Psychiatry researchers from the University of Adelaide have developed a model that could help to predict a patient's likelihood of a good outcome from treatment - from their very first psychotic episode.
The model is based on a range of factors, including clinical symptoms, cognitive abilities, MRI scans of the brain's structure, and biomarkers in the patient's blood.
Speaking in the lead up to World Mental Health Day (10 October), the University's Head of Psychiatry, Professor Bernhard Baune, says the model is a revolutionary idea for psychiatric care, and is aimed ...
Fat chats: The good, the bad and the ugly comments
2014-10-01
Cyberbullying and hurtful 'fat jokes' are disturbingly prevalent in the social media environment, especially on Twitter, says Wen-ying Sylvia Chou of the National Institutes of Health in the US. Chou is lead author of a study in Springer's journal Translational Behavioral Medicine which analyzed well over a million social media posts and comments about weight matters. However, the researchers were also happy to find that the news was not all bad: many instances of support and advice were also observed, especially on blogs and forums.
The study is one of the first to analyze ...
Fall in monsoon rains driven by rise in air pollution, study shows
2014-10-01
Emissions produced by human activity have caused annual monsoon rainfall to decline over the past 50 years, a study suggests.
In the second half of the 20th century, the levels of rain recorded during the Northern Hemisphere's summer monsoon fell by as much as 10 per cent, researchers say. Changes to global rainfall patterns can have serious consequences for human health and agriculture.
Scientists found that emissions of tiny air particles from man-made sources – known as anthropogenic aerosols – were the cause. High levels of aerosols in the atmosphere cause heat ...
Wild ducks take flight in open cluster
2014-10-01
Messier 11 is an open cluster, sometimes referred to as a galactic cluster, located around 6000 light-years away in the constellation of Scutum (The Shield). It was first discovered by German astronomer Gottfried Kirch in 1681 at the Berlin Observatory, appearing as nothing more than a fuzzy blob through the telescope. It wasn't until 1733 that the blob was first resolved into separate stars by the Reverend William Derham in England, and Charles Messier added it to his famous catalogue in 1764.
Messier was a comet hunter and the catalogue came into being as he was frustrated ...
Gene interacts with stress and leads to heart disease in some people
2014-10-01
DURHAM, N.C. – A new genetic finding from Duke Medicine suggests that some people who are prone to hostility, anxiety and depression might also be hard-wired to gain weight when exposed to chronic stress, leading to diabetes and heart disease.
An estimated 13 percent of people, all of whom are Caucasian, might carry the genetic susceptibility, and knowing this could help them reduce heart disease with simple interventions such as a healthy diet, exercise and stress management.
"Genetic susceptibility, psychosocial stress and metabolic factors act in combination to increase ...
Results of large-scale roll out of combination treatment for kala-azar in Eastern Africa
2014-10-01
Today in Bahir Dar, Ethiopia, at the occasion of the Leishmaniasis East Africa Platform meeting, which has gathered some 150 African and international leishmaniasis experts, results of a pharmacovigilance – or large-scale treatment safety and efficacy monitoring – plan, carried out by MSF, DNDi, and national partners in Kenya, Sudan, Uganda, and Ethiopia, were presented to key decision makers in order to boost patient access to treatment of kala-azar with the combination of Sodium Stibogluconate and Paromomycin (SSG&PM) in the region. In this large cohort of patients, treated ...
Long-acting insulin is safer, more effective for patients with Type 1 diabetes
2014-10-01
TORONTO, Oct. 1, 2014 – Long-acting insulin is safer and more effective than intermediate-acting insulin for patients with Type 1 diabetes, according to new research published in the BMJ.
Researchers looked at once-daily and twice-daily doses of both long- and intermediate-acting insulin, ranking their effectiveness, safety and cost-effectiveness.
"In patients with Type 1 diabetes, we found that long-acting insulin is superior to intermediate-acting insulin when it came to controlling blood sugar, preventing weight gain and treating severe hypoglycemia," said Dr. ...
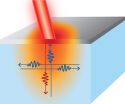
All directions are not created equal for nanoscale heat sources
2014-10-01
Thermal considerations are rapidly becoming one of the most serious design constraints in microelectronics, especially on submicron scale lengths. A study by researchers from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign has shown that standard thermal models will lead to the wrong answer in a three-dimensional heat-transfer problem if the dimensions of the heating element are on the order of one micron or smaller.
"As materials shrink, the rules governing heat transfer change as well," explained David Cahill, a professor of materials science and engineering at Illinois. ...
Microbes in Central Park soil: If they can make it there, they can make it anywhere
2014-10-01
Soil microbes that thrive in the deserts, rainforests, prairies and forests of the world can also be found living beneath New York City's Central Park, according to a surprising new study led by Colorado State University and the University of Colorado Boulder.
The research team analyzed 596 soil samples collected from across Central Park's 843 acres and discovered a stunning diversity of below-ground life, most of which had never been documented before.
Only 8.5 percent to 16.2 percent of the organisms discovered in the park soils, depending on their type, had been ...
Non-citizens face harsher sentencing than citizens in US criminal courts
2014-10-01
WASHINGTON, DC, September 29, 2014 — Non-Americans in the U.S. federal court system are more likely to be sentenced to prison and for longer terms compared to U.S. citizens, according to a new study.
"Much of the discussion in this area has centered around deportation, but increasing numbers of immigrants are being brought before criminal courts, and little is known about how they are treated once they are in the criminal justice system," said Michael T. Light, an assistant professor of sociology at Purdue University and the lead author of the study. "This is a major ...
Immunotherapy could stop resistance to radiotherapy
2014-10-01
Treating cancers with immunotherapy and radiotherapy at the same time could stop them from becoming resistant to treatment, according to a study published in Cancer Research* today (Wednesday).
The researchers, based at The University of Manchester and funded by MedImmune, the global biologics research and development arm of AstraZeneca, and Cancer Research UK, found that combining the two treatments helped the immune system hunt down and destroy cancer cells that weren't killed by the initial radiotherapy in mice with breast, skin and bowel cancers.
Radiotherapy ...
Is Australia prepared for Ebola?
2014-10-01
Australia needs to be proactive about potential disease outbreaks like Ebola and establish a national centre for disease control.
In an Editorial in the October issue of Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health, Allen Cheng from Monash University and Heath Kelly from the Australian National University question Australia's preparation for public health crises.
"Australia would do well to heed the lessons learned in other countries and be proactive in co-ordinating a consistent and outward looking response," the authors said.
"Australia needs a national disease ...
Targeted treatment could halt womb cancer growth
2014-10-01
A drug which targets a key gene fault could halt an aggressive womb cancer and shrink tumours, according to research published in the British Journal of Cancer*.
The scientists, from the Division of Gynaecologic Oncology at Yale School of Medicine funded by the National Institutes of Health, showed that the drug afatinib not only killed off uterine serous cancer cells after stopping their growth but also caused tumours to shrink.
The drug, a type of personalised medicine, attacks faults in the HER2 gene which lie at the heart of the cancer cells. This stops the disease ...
Third of countries struggling to meet the needs of aging population
2014-10-01
People around the world are living longer, but social policies to support their wellbeing in later life are lagging behind in many countries. This is according a new report by HelpAge International, developed in partnership with the University of Southampton.
More than a third of countries are falling significantly behind those at the top of the Global AgeWatch Index. It ranks 96 nations on the basis of the quality of life and social and economic wellbeing of older people (over 60s). The Index can also help governments to identify policies and institutional contexts that ...
Developing countries should enroll medical and nursing students from rural areas
2014-10-01
Nearly one third of medical and nursing students in developing countries may have no intention of working in their own countries after graduation, while less than one fifth of them intend to work in rural areas where they are needed most, according to a new study.
Health workforce shortages have been a major factor driving the current outbreak of Ebola in western Africa. The disease initially spread rapidly in rural parts of three of the world's poorest countries (Guinea, Sierra Leone and Liberia), where health workers are scarcest.
The study, which was published in ...
Minimum alcohol pricing would be up to 50 times more effective than below cost selling ban
2014-10-01
The previous policy of setting a minimum unit price would have had a 40-50 times greater effect, particularly among harmful drinkers, say researchers.
Increasing the price of alcohol has been shown to be effective in reducing both consumption levels and harms, and the UK government has been considering different policy options for price regulation in England and Wales.
In 2010, the government announced a ban on "below cost selling" to target drinks which are currently sold so cheaply that their price is below the cost of the tax (duty and VAT) payable on the product. ...
Healthy lifestyle could prevent nearly half of all diabetic pregnancies
2014-10-01
Gestational diabetes is a common pregnancy complication that has long-term adverse health implications for both mothers and babies.
Several modifiable risk factors before pregnancy have been identified over the past decade. These include maintaining a healthy weight, consuming a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and not smoking.
So a team of researchers based in the United States set out to examine the effect of these "low risk" lifestyle factors on the risk of gestational diabetes – and measure the portion of the condition that may be preventable through adhering ...
The Lancet: Latest estimates show that preterm birth complications and pneumonia are the leading causes of death in children under 5 years
2014-10-01
Complications from preterm (premature) births and pneumonia are now the leading causes of death in children under five years, together responsible for nearly 2 million deaths in 2013, according to the latest estimates, published today [Tuesday 30 September] in The Lancet.
Researchers led by Professor Robert Black, of Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, USA, used the latest available data and modelling methods to examine what caused an estimated 6•3 million deaths of newborn babies (neonates) and children under five years in 2013.
They found that ...
The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology: Genetic study casts further doubt that vitamin D prevents the development of type 2 diabetes
2014-10-01
A large genetic study, published today in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology journal, has concluded there is no evidence of a causal link between a person's vitamin D levels [1], and whether they develop type 2 diabetes.
The findings of the study, conducted by scientists at the University of Cambridge, challenge evidence from earlier observational studies which suggest that higher concentrations of circulating vitamin D might prevent type 2 diabetes. This evidence led to speculation that the development of type 2 diabetes is associated with vitamin D insufficiency. ...
Improving babies' language skills before they're even old enough to speak
2014-10-01
In the first months of life, when babies begin to distinguish sounds that make up language from all the other sounds in the world, they can be trained to more effectively recognize which sounds "might" be language, accelerating the development of the brain maps which are critical to language acquisition and processing, according to new Rutgers research.
The study by April Benasich and colleagues of Rutgers University-Newark is published in the October 1 issue of the Journal of Neuroscience. The researchers found that when 4-month-old babies learned to pay attention to ...
[1] ... [3300]
[3301]
[3302]
[3303]
[3304]
[3305]
[3306]
[3307]
3308
[3309]
[3310]
[3311]
[3312]
[3313]
[3314]
[3315]
[3316]
... [8827]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.