Saddam Hussein -- a sincere dictator?
2014-08-28
Are political speeches manipulative and strategic? They could be – when politicians say one thing in public, and privately believe something else, political scientists say. Saddam Hussein's legacy of recording private discussions offers researchers a fascinating insight: both into the consistency of this controversial leader's public and private rhetoric and into the bigger picture of conflict and national security during his regime. New research into the similarity between political leaders' public statements and private beliefs, using Saddam Hussein's transcripts, appeared ...
Ontario has one of the highest rates of IBD in the world
2014-08-28
OTTAWA, August 28, 2014 – One in every 200 Ontarians has been diagnosed with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), with the number of people living with the disease increasing by 64 per cent between 1999 and 2008, according to a study by researchers at the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences (ICES), the Children's Hospital of Eastern Ontario (CHEO), and the Ottawa Hospital Research Institute. That puts Ontario in the 90th percentile for IBD prevalence in the world.
The study, published this week in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, is the first and largest Canadian study ...
How does it feel to be old in different societies?
2014-08-28
People aged 70 and over who identify themselves as 'old' feel worse about their own health in societies where they perceive they have lower value than younger age groups.
New research from psychologists at the University of Kent, titled 'Being old and ill' across different countries: social status, age identification and older people's subjective health, used data from the European Social Survey. Respondents, who were all aged 70 and over, were asked to self-rate their health.
The researchers found that those living in societies where older people have lower status were ...
Arthritis patients failing to take expensive medication, according to new research
2014-08-28
Twenty seven per cent of rheumatoid arthritis patients in the study who were on a class of drugs known as anti-TNF therapies did not take them as prescribed in the first six months. Patients from Manchester Royal Infirmary were among those from 60 hospitals around the UK involved in the study.
Researchers from the Arthritis Research UK Centre for Genetics and Genomics at The University of Manchester, who led the study, warned that failure to take the drugs correctly, known as 'non-adherence', reduced their effectiveness and may lead to a worsening of patients' disease. ...
Research demonstrates potential method to better control lung cancer using radiotherapy
2014-08-28
Manchester scientists are working out how to safely increase the radiotherapy dose given to lung cancer patients – potentially offering improved local control and survival.
Standard treatment for locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer is a combination of radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Traditionally this is planned in a one-size-fits-all manner but the radiation dose may not always be enough to stop tumour growth.
The potential to increase the radiation dose to the cancerous tissue varies between patients and depends on the size and location of the tumour in relation ...
Dyslexic readers have disrupted network connections in the brain
2014-08-28
Philadelphia, PA, August 28, 2014 – Dyslexia, the most commonly diagnosed learning disability in the United States, is a neurological reading disability that occurs when the regions of the brain that process written language don't function normally.
The use of non-invasive functional neuroimaging tools has helped characterize how brain activity is disrupted in dyslexia. However, most prior work has focused on only a small number of brain regions, leaving a gap in our understanding of how multiple brain regions communicate with one another through networks, called functional ...
Study shows where on the planet new roads should and should not go
2014-08-28
More than 25 million kilometres of new roads will be built worldwide by 2050. Many of these roads will slice into Earth's last wildernesses, where they bring an influx of destructive loggers, hunters and illegal miners.
Now, an ambitious study has created a 'global roadmap' for prioritising road building across the planet, to try to balance the competing demands of development and environmental protection.
The map has two components: an 'environmental-values' layer that estimates that natural importance of ecosystems and a 'road-benefits' layer that estimates the potential ...
Nanoscale assembly line
2014-08-28
This news release is available in German. Cars, planes and many electronic products are now built with the help of sophisticated assembly lines. Mobile assembly carriers, on to which the objects are fixed, are an important part of these assembly lines. In the case of a car body, the assembly components are attached in various work stages arranged in a precise spatial and chronological sequence, resulting in a complete vehicle at the end of the line.
The creation of such an assembly line at molecular level has been a long-held dream of many nanoscientists. "It would ...
Paleontology: Oldest representative of a weird arthropod group
2014-08-28
Biologists at Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich have assigned a number of 435-million-year-old fossils to a new genus of predatory arthropods. These animals lived in shallow marine habitats and were far less eye-catching than related forms found in Jurassic strata.
Before they sank to the bottom of their shallow marine habitat and were fossilized some 435 million years ago, these arthropods preyed on other denizens of the Silurian seas – although they were not exactly inconspicuous, possessing a bivalved carapace and multiple abdominal limbs. A group of ...
Better classification to improve treatments for breast cancer
2014-08-28
Breast cancer can be classified into ten different subtypes, and scientists have developed a tool to identify which is which. The research, published in the journal Genome Biology, could improve treatments and targeting of treatments for the disease.
Cancer arises due to genetic changes which cause normal cells to develop into tumors. As we learn more about breast cancer, we are seeing that it is not one single disease – the mutations in the genes that cause different cancers are not alike, and this is why tumors respond differently to treatment and grow at different ...
New study charts the global invasion of crop pests
2014-08-28
Many of the world's most important crop-producing countries will be fully saturated with pests by the middle of the century if current trends continue, according to a new study led by the University of Exeter.
More than one-in-ten pest types can already be found in around half the countries that grow their host crops. If this spread advances at its current rate, scientists fear that a significant proportion of global crop-producing countries will be overwhelmed by pests within the next 30 years.
Crop pests include fungi, bacteria, viruses, insects, nematodes, viroids ...
The Lancet journals: Three-quarters of depressed cancer patients do not receive treatment for depression but a new approach could transform their care
2014-08-28
Three papers published in The Lancet Psychiatry, The Lancet, and The Lancet Oncology reveal that around three-quarters of cancer patients who have major depression are not currently receiving treatment for depression, and that a new integrated treatment programme is strikingly more effective at reducing depression and improving quality of life than current care.
An analysis of data from more than 21 000 patients attending cancer clinics in Scotland, UK, published in The Lancet Psychiatry, found that major depression is substantially more common in cancer patients than ...
Better health care as important as controlling risk factors for heart health
2014-08-28
Hamilton, ON (August 27, 2014) – Keeping a healthy heart may have as much to do with the quality of health care you have available as it does you avoiding risk factors such as smoking, bad diet and little exercise.
A large international study led by researchers at the Population Health Research Institute at McMaster University and Hamilton Health Sciences has found a that low-income countries which have people with the lowest risk factors for cardiovascular problems have the highest rates of cardiovascular events and death, while the high-income countries of people with ...
Researchers investigating new treatment for multiple sclerosis
2014-08-27
MINNEAPOLIS – A new treatment under investigation for multiple sclerosis (MS) is safe and tolerable in phase I clinical trials, according to a study published August 27, 2014, in Neurology® Neuroimmunology & Neuroinflammation, a new online-only, freely accessible, specialty medical journal. The publication is part of the Neurology® family of journals, published by the American Academy of Neurology.
The phase I studies were the first to test the drug candidate in humans. Studies with animals showed that the drug, which is called anti-LINGO-1, or BIIB033, may be able to ...
Bundled approach to reduce surgical site infections in colorectal surgery
2014-08-27
Bottom Line: A multidisciplinary program (called a "bundle") that spanned the phases of perioperative care helped reduce surgical site infections (SSIs) in patients undergoing colorectal surgery (CRS) at an academic medical center.
Author: Jeffrey E. Keenan, M.D., of the Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., and colleagues.
Background: SSIs are associated with increased complications, length of hospital stay, readmission rates and health care costs. Efforts that have used systematic approaches, called bundles, that aim to incorporate best practices across the ...
Photodynamic therapy vs. cryotherapy for actinic keratoses
2014-08-27
Bottom Line: Photodynamic therapy (PDT, which uses topical agents and light to kill tissue) appears to better clear actinic keratoses (AKs, a common skin lesion caused by sun damage) at three months after treatment than cryotherapy (which uses liquid nitrogen to freeze lesions).
Author: Gayatri Patel, M.D., M.P.H., of the University of California Davis Medical Center, in Sacramento, and colleagues.
Background: AKs are rough, scaly lesions on the skin typically found on individuals with fair complexions who have had lots of sun exposure. The lesions have the potential ...
APOE, diagnostic accuracy of CSF biomarkers for Alzheimer disease
2014-08-27
Bottom Line: Cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) levels of β-amyloid 42(Aβ42) are associated with the diagnosis of Alzheimer disease (AD) and (Aβ) accumulation in the brain independent of apolipoprotein E (APOE) gene makeup.
Authors: Ronald Lautner, M.D., of Sahlgrenska University Hospital, Sweden, and colleagues.
Background: With the emergence of biomarker dementia diagnostics, interest in CSF biomarkers associated with AD, including Aβ42 and tau proteins, is increasing. The APOE gene is the most prominent susceptibility gene for late-onset AD. For the ...
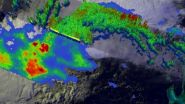
NASA's TRMM Satellite sees powerful towering storms in Cristobal
2014-08-27
VIDEO:
NASA's TRMM Satellite Sees Powerful Towering Storms in Cristobal On Aug. 26, NASA's TRMM Satellite saw a band of thunderstorms with heights of over 15km (about 9.3 miles) and was...
Click here for more information.
NASA's TRMM satellite identified areas of heavy rainfall occurring in Hurricane Cristobal as it continued strengthening on approach to Bermuda.
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite flew above Hurricane Cristobal on August 26 at 11:35 ...
Experiments explain why some liquids are 'fragile' and others are 'strong'
2014-08-27
Only recently has it become possible to accurately "see" the structure of a liquid. Using X-rays and a high-tech apparatus that holds liquids without a container, Kenneth Kelton, PhD, the Arthur Holly Compton Professor in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis, was able to compare the behavior of glass-forming liquids as they approach the glass transition.
The results, published in the August 6 issue of Nature Communications, are the strongest demonstration yet that bulk properties of glass-forming liquids, such as viscosity, are linked to microscopic ...
Novel 'butterfly' molecule could build new sensors, photoenergy conversion devices
2014-08-27
TALLAHASSEE, Fla. — Exciting new work by a Florida State University research team has led to a novel molecular system that can take your temperature, emit white light, and convert photon energy directly to mechanical motions.
And, the molecule looks like a butterfly.
Biwu Ma, associate professor in the Department of Chemical and Biomedical Engineering in the FAMU-FSU College of Engineering, created the molecule in a lab about a decade ago, but has continued to discover that his creation has many other unique capabilities.
For example, the molecular butterfly can flap ...
A touching story: The ancient conversation between plants, fungi and bacteria
2014-08-27
MADISON, Wis. — The mechanical force that a single fungal cell or bacterial colony exerts on a plant cell may seem vanishingly small, but it plays a heavy role in setting up some of the most fundamental symbiotic relationships in biology. In fact, it may not be too much of a stretch to say that plants may have never moved onto land without the ability to respond to the touch of beneficial fungi, according to a new study led by Jean-Michel Ané, a professor of agronomy at the University of Wisconsin-Madison.
"Many people have studied how roots progress through the soil, ...
Protein in 'good cholesterol' may be a key to treating pulmonary hypertension
2014-08-27
Oxidized lipids are known to play a key role in inflaming blood vessels and hardening arteries, which causes diseases like atherosclerosis. A new study at UCLA demonstrates that they may also contribute to pulmonary hypertension, a serious lung disease that narrows the small blood vessels in the lungs.
Using a rodent model, the researchers showed that a peptide mimicking part of the main protein in high-density lipoprotein (HDL), the so-called "good" cholesterol, may help reduce the production of oxidized lipids in pulmonary hypertension. They also found that reducing ...
Research geared to keep women from fleeing IT profession
2014-08-27
WACO, Texas (August 27, 2014) – For years, employers and experts have been trying to reverse the exodus of women from information technology positions.
They're failing.
Studies show that women are significantly underrepresented in the IT field, and the number of women who've graduated with degrees in computer and information science have plummeted from 37 percent in 1985 to 18 percent in 2011.
The failure to "stop the bleeding" stems, in part, from the industry's reliance on an oft-cited, outdated and under-studied research model, said Cindy Riemenschneider, Ph.D., ...
No cookie-cutter divorces, so what info should online co-parenting classes offer?
2014-08-27
URBANA, Ill. – Required online classes for divorcing couples who have children are good at teaching parents how to deal with children's needs and responses to their family's new situation. But co-parenting couples would benefit from content that helps adults cope with their own emotions and from unique tracks for families with special circumstances such as intimate partner violence or alcoholism, said a University of Illinois researcher in human and community development.
"There is no cookie-cutter divorcing couple, and with online programming, educators are able to supply ...
NASA telescopes uncover early construction of giant galaxy
2014-08-27
Astronomers have for the first time caught a glimpse of the earliest stages of massive galaxy construction. The building site, dubbed "Sparky," is a dense galactic core blazing with the light of millions of newborn stars that are forming at a ferocious rate.
The discovery was made possible through combined observations from NASA's Hubble and Spitzer space telescopes, the W.M. Keck Observatory in Mauna Kea, Hawaii, and the European Space Agency's Herschel space observatory, in which NASA plays an important role.
A fully developed elliptical galaxy is a gas-deficient ...
[1] ... [3381]
[3382]
[3383]
[3384]
[3385]
[3386]
[3387]
[3388]
3389
[3390]
[3391]
[3392]
[3393]
[3394]
[3395]
[3396]
[3397]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.