Corcentric to Exhibit at the TMC's 2013 Annual Meeting in Nashville, Tennessee
2013-03-06
Corcentric, a leading provider of financial process automation solutions for the trucking industry, today announced they will host booth #259 at the 2013 Technology & Maintenance Council's Annual Meeting, which will take place March 11-14 at the Gaylord Opryland Hotel & Conference Center, Nashville, TN.
Corcentric is a leader in financial process automation, specializing in Centralized Billing solutions, and Accounts Payable automation for the transportation industry. By creating a paperless conduit between procurement, Accounts Payable, Accounts Receivable, ...
Genki USA Introduces Shirataki Rice: 0 Calories, 0 Fat, 0 Net Carbs
2013-03-06
Genki USA, Inc., maker of America's Skinny Noodles brand shirataki products, is pleased to announce the newest waist- and diabetic-friendly innovation: Skinny Rice Shirataki. Like increasingly popular shirataki noodles, this all natural, pre-cooked, rice-shaped shirataki is gluten-free with no calories, no fat, and no net carbs.
Shirataki (Japanese for "white waterfall") is made from the root of the Asian konnyaku or konjac plant, which consists primarily of a dietary fiber called glucomannan. Food products made from the unique root have been consumed in Japan ...
Ubiquity Global Services Announces Ray Iglesias as CEO
2013-03-06
Ubiquity Global Services, an innovative Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) organization, today announced that Ray Iglesias has joined as CEO.
The announcement speaks to the aggressive expansion of the business in 2013. Iglesias brings a recognized track record in growing a number of successful companies, and most recently helped manage the integration of payments technology company TxVia into Google.
"One of my strengths is recognizing great talent and people who can really lead. When I saw this team and they invited me to join as chief executive officer, it ...
Author of "Broken Mask: My Struggle to Forgive" Gives First Interview to Help Women in Crisis
2013-03-06
"Broken Mask: My struggle to forgive" was introduced Saturday, March 2, 2013 on station 1680 AM Winter Garden, Florida by Reverend Bryan on his radio show. Kristina Wetzel gave a preview for the next show, Saturday, March 9, to share the purpose of her book aimed at helping struggling girls and women. The interview will stream live on http://tunein.com/radio/WOKB-1680-s23142/ at 6:00 a.m.
Wetzel wrote her autobiography to explain how events throughout her life, from childhood circumstances to rape, to workplace sexual engagement with a superior to poor relationship ...
All-New SEAT Leon Goes on Sale in Ireland
2013-03-06
SEAT Ireland has launched the new SEAT Leon on to the Irish market with a 12 model line-up which includes a choice of 1.2-litre TSI petrol (86bhp and 105bhp), 1.6-litre TDI diesel (90bhp and 105bhp), 1.8-litre TSI petrol (180bhp) and 2.0-litre TDI (150bhp and 184bhp) engines. These engines boast low emissions and outstanding efficiency.
The model that is expected to be the volume seller, the 1.6 TDI, has emissions of just 99g/km placing it in motor tax band A2 and can return fuel economy of just 3.8 l/100km. making this one of the most fuel efficient cars in its class.
The ...
Corcentric's Automated Billing Solution for Daimler Trucks North America Goes Live
2013-03-06
Corcentric has partnered with Daimler Trucks North America (DTNA) to provide an automated centralized billing solution for Daimler Trucks North America's customers. Daimler Trucks North America sells and services a full product line of parts and service through a network of more than 600 franchised dealers and distributors across the U.S. Corcentric is a leading provider of workflow automation solutions, specializing in fleet solutions.
Developed for DTNA's Pinnacle Fleet Solutions Parts and Service Program, Corcentric's solution supports DTNA's ability to provide complete ...
Admiral Reveals Cars Targeted by Thieves and Vandals
2013-03-06
Admiral has revealed owners of Smarts, BMWs or Maseratis are the most likely to be targeted by thieves and vandals but Bentley drivers might also want to pay special attention to the safety of their vehicles too.
Car insurance specialist Admiral looked at over 700,000 claims and found that Smarts were the make of car most likely to have something stolen from them, BMWs were the most likely to be stolen and Maseratis the most likely to be vandalised.* But Bentleys appear to be a risk across the board, appearing in the top five on the lists for having something stolen, ...
Materials Science Research Rack Heats Up For Valuable Space Station Science
2013-03-06
Have you ever wondered how we develop new materials or find out what properties we can change in existing materials to improve them? Scientists and researchers at NASA are doing just that through materials science research using the Materials Science Research Rack (MSRR) aboard the International Space Station.
Materials science research is the applied study of the properties of matter and substances. This type of research in space benefits from the microgravity environment, and it allows researchers to isolate chemical and thermal properties of materials from the effects ...
Bioplanet Reinvented the Bicycle with the Bike
2013-03-06
Bioplanet today introduced Bike, combining several products into one - a uniquely designed bicycle, an e-bike with a bottom bracket integrated electric motor and pedelec as electric bicycle with power assistance - into one lightweight and distinct electric bicycle. The Bioplanet Bike introduces a new bicycle frame design with integrated electric components which completely redefines what riders can do with their bikes.
Bioplanet Bike is a revolutionary product that sets a new era and trends in bicycle and light electric powered vehicles design. "Our Bike is the ...
Neighborhood poverty and health insurance figure in late-stage diagnosis of breast cancer
2013-03-05
Springfield, Ill., February 7, 2013 – Home may be where the heart is, but where you live could affect your health.
"Regardless of geographic location, women who live in high poverty areas or are uninsured are at greatest risk of being diagnosed with breast cancer at a later stage," said lead author Kevin Henry, Department of Geography, University of Utah.
A team of scientists was assembled by the North American Association of Central Cancer Registries (NAACCR) to examine breast cancer stage at diagnosis among 161,619 women aged 40 years and older diagnosed in ten participating ...
Pregnant mothers with strong family support less likely to have postpartum depression, study finds
2013-03-05
Women who receive strong social support from their families during pregnancy appear to be protected from sharp increases in a particular stress hormone, making them less likely to experience depression after giving birth, a new study by UCLA life scientists indicates.
"Now we have some clue as to how support might 'get under the skin' in pregnancy, dampening down a mother's stress hormone and thereby helping to reduce her risk for postpartum depression," said Jennifer Hahn-Holbrook, a UCLA National Institute of Mental Health postdoctoral scholar in psychology, a fellow ...
For birds, red means 'go'
2013-03-05
New research has shown that certain Australian native flowers have shifted away from using insects as pollinators and evolved their flower colour to the red hues favoured by birds.
In a study published in New Phytologist, biologists from Monash University and RMIT University have shown for the first time that Australian native flowers exclusively pollinated by birds have evolved colour spectral signatures that are best discriminated by those birds.
Dr Adrian Dyer of Monash and RMIT said previous studies had shown that flower colour evolved to attract bees as pollinators.
"We ...
Genetics Society of America's Genetics journal highlights for March 2013
2013-03-05
Bethesda, MD—March 5, 2013 – Listed below are the selected highlights for the March 2013 issue of the Genetics Society of America's journal, Genetics. The March issue is available online at www.genetics.org/content/current. Please credit Genetics, Vol. 193, MARCH 2013, Copyright © 2013.
Please feel free to forward to colleagues who may be interested in these articles on cellular genetics; population and evolutionary genetics; genome integrity and transmission; and genome and systems biology.
ISSUE HIGHLIGHTS
Cellular Genetics:
Systems genetics implicates cytoskeletal ...
New gene variant may explain psychotic features in bipolar disorder
2013-03-05
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have found an explanation for why the level of kynurenic acid (KYNA) is higher in the brains of people with schizophrenia or bipolar disease with psychosis. The study, which is published in the scientific periodical Molecular Psychiatry, identifies a gene variant associated with an increased production of KYNA. The discovery contributes to the further understanding of the link between inflammation and psychosis – and might pave the way for improved therapies.
Kynurenic acid (KYNA) is a substance that affects several signalling ...
Discovery of human genetic mutation could lead to new treatments for type 1 diabetes
2013-03-05
In type 1 diabetes, the immune system destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, but the precise cause has not been clear. A study published by Cell Press on March 5th in Cell Metabolism reveals that a single mutation in the "longevity gene" SIRT1 can cause type 1 diabetes in humans. The findings unearth the role this gene plays in human autoimmunity and disease and also offer new avenues for treating a range of autoimmune disorders.
"We describe one of the first single gene defects leading to type 1 diabetes, as well as the first human mutation in the SIRT1 gene," ...
Molecular coordination in evolution: A review in 'Nature Reviews Genetics'
2013-03-05
Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) researchers Alfonso Valencia, Director of the Structural Biology and Biocomputing Programme and David de Juan, jointly with Florencio Pazos, from the Spanish National Centre for Biotechnology (CNB-CSIC), publish a review on the latest computational methods that, based on evolutionary principles, are revolutionising the field of analysis and prediction of protein structure, function and protein-protein interactions, as well as the short- and long-term expectations for the field.
"The computational and mathematical analysis ...
How cells optimize the functioning of their power plants
2013-03-05
Mitochondria, which are probably derived from distant bacterial ancestors incorporated into our cells, have their own DNA. However, we know little about how these organelles, which convert oxygen and consumed nutrients into energy, regulate the expression of their own genes. Jean-Claude Martinou, professor at the University of Geneva (UNIGE), Switzerland, and his team, have discovered the existence of compartments at the heart of mitochondria, consisting of hundreds of different proteins. It is here that RNA molecules (the many copies made from DNA) come together to be ...
Single gene might explain dramatic differences among people with schizophrenia
2013-03-05
March 5, 2013 (Toronto) – Some of the dramatic differences seen among patients with schizophrenia may be explained by a single gene that regulates a group of other schizophrenia risk genes. These findings appear in a new imaging-genetics study from the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health (CAMH).
The study revealed that people with schizophrenia who had a particular version of the microRNA-137 gene (or MIR137), tended to develop the illness at a younger age and had distinct brain features – both associated with poorer outcomes – compared to patients who did not have ...
Viruses: More survival tricks than previously thought
2013-03-05
Among eukaryotes with modified nuclear genetic codes, viruses are unknown. Until now it had been believed that the modifications to the genetic code effectively prevented new viral infections. However, researchers have now reported the first example of a virus that can be shown to have crossed the boundary from organisms using the standard genetic code to those with an alternate genetic code.
"The finding is significant because it means that virus-host co-evolution after a genetic code shift can be more extensive than previously thought", said researcher Derek J. Taylor, ...
West Nile virus passes from female to eggs, but less so from larvae to adults
2013-03-05
In California Culex mosquitoes are considered to be the principle vectors of West Nile virus (WNV), which infects birds, humans, and other mammals during the summer. In addition, these mosquitoes may also serve as overwintering reservoir hosts as the virus is passed "vertically" from female mosquito to egg, then larva, and then adult.
To find out how often this happens, California researchers monitored WNV in mosquitoes in the field and in the lab, and observed how the virus is transmitted between generations and between insect stages. The results are published in the ...
Remains of extinct giant camel discovered in High Arctic by Canadian Museum of Nature
2013-03-05
Ottawa, Canada, March 5, 2013 - A research team led by the Canadian Museum of Nature has identified the first evidence for an extinct giant camel in Canada's High Arctic. The discovery is based on 30 fossil fragments of a leg bone found on Ellesmere Island, Nunavut and represents the most northerly record for early camels, whose ancestors are known to have originated in North America some 45 million years ago.
The fossils were collected over three summer field seasons (2006, 2008 and 2010) and are about three-and-a-half million years old, dating from the mid-Pliocene ...
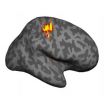
Amputee phantom pain linked to brain retaining picture of missing limb
2013-03-05
Changes in the brain following amputation have been linked to pain arising from the missing limb, called 'phantom pain', in an Oxford University brain imaging study.
Arm amputees experiencing the most phantom limb pain were found to maintain stronger representation of the missing hand in the brain – to the point where it was indistinguishable from people with both hands.
The researchers hope their identification of brain responses correlated with the level of phantom pain can aid the development of treatment approaches, as well as increase understanding of how the brain ...
Ancient DNA solves 320-year-old mystery
2013-03-05
University of Adelaide researchers have found the answer to one of natural history's most intriguing puzzles – the origins of the now extinct Falkland Islands wolf and how it came to be the only land-based mammal on the isolated islands – 460km from the nearest land, Argentina.
Previous theories have suggested the wolf somehow rafted on ice or vegetation, crossed via a now-submerged land bridge or was even semi-domesticated and transported by early South American humans.
The 320-year-old mystery was first recorded by early British explorers in 1690 and raised again ...
Mental picture of others can be seen using fMRI, finds new study
2013-03-05
ITHACA, N.Y. – It is possible to tell who a person is thinking about by analyzing images of his or her brain. Our mental models of people produce unique patterns of brain activation, which can be detected using advanced imaging techniques according to a study by Cornell University neuroscientist Nathan Spreng and his colleagues.
"When we looked at our data, we were shocked that we could successfully decode who our participants were thinking about based on their brain activity," said Spreng, assistant professor of human development in Cornell's College of Human Ecology.
Understanding ...
Children of divorced parents more likely to switch, pull away from religions, Baylor study finds
2013-03-05
Adults whose parents were divorced are more likely to switch religions or disassociate themselves from institutional religions altogether — but growing up in a single-parent family does not have any effect on private religious life, including praying, according to a study by a Baylor University sociologist.
The findings also suggest that being a child of divorced parents is not in itself as important a factor in a person's religious life as previous research has indicated, according to Jeremy Uecker, Ph.D., an assistant professor of sociology in Baylor's College of Arts ...
[1] ... [5114]
[5115]
[5116]
[5117]
[5118]
[5119]
[5120]
[5121]
5122
[5123]
[5124]
[5125]
[5126]
[5127]
[5128]
[5129]
[5130]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.