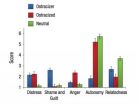
'Mean girls' be warned: Ostracism cuts both ways
2013-03-05
If you think giving someone the cold shoulder inflicts pain only on them, beware. A new study shows that individuals who deliberately shun another person are equally distressed by the experience.
"In real life and in academic studies, we tend to focus on the harm done to victims in cases of social aggression," says co-author Richard Ryan, professor of clinical and social psychology at the University of Rochester. "This study shows that when people bend to pressure to exclude others, they also pay a steep personal cost. Their distress is different from the person excluded, ...
Domestic violence in New Jersey
2013-03-05
Domestic violence in New Jersey
Article provided by Keith, Winters & Wenning, L.L.C.
Visit us at http://www.kwwlawfirm.com
Everyone thought the story was over. In 2009 pop sensation Rihanna was brutally assaulted by her then boyfriend Chris Brown. The singer stated that she ended the relationship and the media applauded her brave move. She became a role model for domestic violence victims around the world.
That is, until January of 2013 when the star publicly announced that she had rekindled her relationship with her convicted abuser. Unfortunately, Rihanna's ...
Revocable living trust: Is it right for you?
2013-03-05
Revocable living trust: Is it right for you?
Article provided by Anderson and Associates, P.C.
Visit us at http://www.davidandersonlaw.com/
Most people consider wills for estate planning; however, this is not the only option. In addition to avoiding probate, a revocable living trust may offer you significant before-death and after-death advantages.
In general, a trust involves three parties: the creator, the trustee or trustees (who agree to manage the assets according to the terms of the trust) and the beneficiary or beneficiaries. Something as miniscule as ...
Why borrowing against your 401(k) may be a bad idea
2013-03-05
Why borrowing against your 401(k) may be a bad idea
Article provided by Law Offices of Brian Barta
Visit us at http://www.brianbartalaw.com
Twenty-five percent of Americans have made early withdrawals from their retirement plans using a 401(k) loan, according to a recent report by online financial guidance service HelloWallet. However, many people who tap into their retirement funds may do so without being fully aware of the risks involved in doing so.
Particularly in the aftermath of the recent recession, people who borrow against their retirement savings often ...
Changes for teen distracted driving laws in California?
2013-03-05
Changes for teen distracted driving laws in California?
Article provided by Law Offices of Joshua Katz and Bozman-Moss & Watson
Visit us at http://www.sonomalegal.com
One of the most highly-anticipated moments for any teen is when he or she finally receives a driver's license. Once licensed, these drivers no longer have to rely upon mom or dad for transportation. They can go where they want to go, when they want to go there.
However, the freedom that a new driver's license provides requires that teens practice safe driving habits. Even after passing the test, ...
Obamacare may curb health care spending, lead to more investigations
2013-03-05
Obamacare may curb health care spending, lead to more investigations
Article provided by Rivas Goldstein LLP
Visit us at http://www.rivasgoldstein.com/
A new government report states the massive increases in health care costs are starting to slow. In fact, according to Susan Dentzer, an expert with the well respected journal Health Affairs, 2009 and 2010 showed the slowest increase in health care spending in 51 years.
The motivator for this change is a controversial topic in Washington. According to some, the change is due to the economic downtown. People simply ...
NY appeals court: Protection order not always a bar to child custody
2013-03-05
NY appeals court: Protection order not always a bar to child custody
Article provided by DeRoberts Law Firm
Visit us at http://www.derobertslaw.com/
According to a recent decision by a New York appellate court, parents in New York may be granted child custody even if a criminal court has barred them from having contact with their children.
On December 26, 2012, the New York Appellate Division, Second Department, ruled unanimously that judges in the state's family courts may override a criminal order of protection against a child's parent as long as the protection ...
Almost half of Americans near financial collapse, report says
2013-03-05
Almost half of Americans near financial collapse, report says
Article provided by Law Offices of Scott R. Schneider
Visit us at http://www.scott-schneider.com
The recent economic recession has been hard on many Americans. However, according to a new report, it may be worse than previously thought. According to the report from the Corporation for Enterprise Development, about 43.9 percent of U.S. households are nearing financial collapse.
The report found that in event of a health crisis, job loss or other financial emergency, this percentage of Americans lack ...
Florida criminal law: major St. Augustine marijuana cultivation bust
2013-03-05
Florida criminal law: major St. Augustine marijuana cultivation bust
Article provided by The Law Office of Donald A. Lykkebak
Visit us at http://www.donaldlykkebak.com
The state of Florida has very tough drug laws with steep penalties and is not a good place to be arrested for narcotic-related criminal charges. As common as marijuana has become in our society and despite the beginning of a national trend to decriminalize some uses, modern Florida criminal laws treat marijuana possession harshly.
On January 31, 2013, law enforcement arrested a middle-aged St. ...
Florida criminal law: retired sheriff's deputy arrested for embezzlement
2013-03-05
Florida criminal law: retired sheriff's deputy arrested for embezzlement
Article provided by The Law Office of Donald A. Lykkebak
Visit us at http://www.donaldlykkebak.com
In January 2013, a retired 22-year Broward County sheriff's deputy in her 70s was in Florida state court for allegedly embezzling about $40,000 over a five-year period from her local Fraternal Order of Police Lodge, which she served as president, according to the Sun Sentinel.
The Fraternal Order of Police, or FOP, says on its website that it is the "world's largest organization of sworn ...
Come Up For a Breath of Fresh Aer!
2013-03-05
Elevate yourself to Melbourne's newest rooftop bar and lounge that has reworked the standards of substance and style. Aer Bar is spectacular - unquestionably one of the best spots in the city for open-air drinking and dining. And being a haven for style and sophistication, Aer Bar supplies nothing but premium beverages, with a select range of draught beers and cider along with Moët & Chandon Champagne and the super premium Belvedere Vodka.
A sophisticated urban playground for grownups, Aer Bar is built to entertain. During the day enjoy the chilled-out atmosphere ...
Austin Healthy Living and Good Eating Expo Adds Speakers Series with American Diabetes Association Speakers
2013-03-05
The Healthy Living and Good Eating Expo, an event from My City Shows an Austin, TX based Event Management Company, has announced the addition of Educational Sessions to the Healthy Living and Good Eating Expo which will be held in Austin on May 4, 2013 on the St. Louis School grounds at 7601 Burnet Rd. The show will feature Healthy and Natural Products, Services, Food, Snacks, and activities. The educational sessions will be offered throughout the day from 10 AM to 5 PM with initial speakers including: Maryum Mitchell, M.Ed. and BS, Associate Manager, Administration, American ...
Insomnia Studies Show a Cooler Body Temperature and Natural Sleep Aids Help Sleep
2013-03-05
A cooler body temperature may help people to fall asleep. According to a study in the Journal "Sleep", making a special effort to cool down before bedtime may be of particular benefit to insomniacs. Sleep specialists have long debated whether the regular nighttime drop in temperature induces sleep or follows it. To investigate this question, Doctors Murphy and Campbell of the New York Hospital's Cornell Medical Center in White Plains, recruited 21 men and 23 women, aged 19 to 82.
The researchers identified the time at which the subjects' body temperature fell ...
H2 Golf to Distribute High Performance Sports Drink, BioSteel to the Golf Market
2013-03-05
H2 Golf Company LLC., a golf corporation that distributes premium golf brands and accessories, announced today that the company has agreed to distribute BioSteel, a high performance sports drink developed to meet the needs of professional athletes, exercise enthusiasts, and golfers of all levels.
According to Taylor Herber, H2 Golf Vice President of Sales and Marketing, "H2Golf and Bio-Steel are a great match. We look forward to bringing this revolutionary sports drink to all of our loyal customers and see huge potential in this new relationship."
BioSteel ...
Figue Mediterranean Restaurant to Host Desert Smash Player's Party on March 5
2013-03-05
The 9th Annual K-Swiss Desert Smash Charity Tennis Event will conclude with a flourish on Tuesday evening, March 5, 2013, as the Player's Party is hosted by the much-anticipated new restaurant, Figue Mediterranean, in La Quinta (47-474 Washington St.; 760-698-9040). The Player Party is the annual post-tournament charitable extravaganza attended by the event's roster of professional tennis players as well as a prestigious guest list of Hollywood celebrities and VIPs. Doors open at 7:30 p.m., Tuesday, March 5, 2013 at Figue. Tickets to the event are $125 per person; the public ...
Southern Breeze Home Design Center Opens at the Avenue
2013-03-05
Southern Breeze Home Design Center is a locally-owned and operated business. While the retail location at the Avenue between Michael's and Petco, is a new facet of the business, Southern Breeze has been serving Rutherford County and the surrounding area for 15 years. Owners Daniel and Brittany Gammon are both Middle Tennessee State University graduates and actively involved in the community.
Southern Breeze Home Design Center is Murfreesboro's premier home remodeling destination. The showroom features cabinetry, countertops, ceramic & porcelain tile, flooring, blinds ...
Multiple Sclerosis Foundation Announces "Full Moon Party" Benefit
2013-03-05
On Friday, March 29th, from 7:00pm - 10:00pm, The Full Moon Party will be held on the beautiful pool deck of the iconic Ritz-Carlton, Ft. Lauderdale to benefit the Multiple Sclerosis Foundation.
With a $10 donation, guests will receive complimentary cocktails and an issue of the glossy and vibrant Lifestyles Magazine. Also on site will be a beautiful display of Fiora Charms , the first to combine jewelry and perfume in a stunning filigree bead, emanating a captivating scent.Additional information about the Full Moon Party and other events, as well as the Multiple Sclerosis ...
Lunabrite Light Technology Offers up to 20% in Savings on its Popular Glow Ribbon Line
2013-03-05
Lunabrite, known for its high performance glow materials including patented glow rope and ribbon trim is offering a special Winter Sale. Savings of 20% off of regular prices are available on all of the company's signature Glow Ribbon items including popular sample packs. All items are available directly through the company's online Shop or by calling Lunabrite Customer Support at 973-794-1062.
The company, known for its innovation with high performance glow materials, created Glow Ribbon, a flexible, glow material in order to enhance the creative options of designers, ...
Edealeo LLC New And Innovative Daily Deals Website Launch in Western Massachusetts
2013-03-05
Edealeo LLC is a new and innovative advancement to the Massachusetts world of online shopping to have its very own daily deals website, when the website launches officially in Western Massachusetts on April 1, 2013. Visitors to the website will be able to snap up amazing daily deals at the lowest prices, while businesses will be able to advertise their deals at rates that leave current deal sites in the dust.
Andrew Dunn, manager and owner of Edealeo.com, believes in building strong and lasting relationships with their customers and businesses, with continuous communication ...
Book Marketing Announcements: The Authors Show Lineup for the Week of March 4, 2013
2013-03-05
Don McCauley of the Free Publicity Focus Group and Danielle Hampson of eBroadcastMedia.com, founders of Book Marketing, announced today The Authors Show radio and TV weekly broadcast schedule.
Book Marketing, branded as 'The Authors Marketing Powerhouse', allows authors and publishers the opportunity to upload photos, bios, book covers, video and book videos. The site also offers discussion forums, segmented special interest groups and allows for event listings. Each author can develop a personalized page. In addition the site allows for integration with Facebook and ...
Environmental Hygienists Announce Expansion to Serve Property Owners, Managers, and Tenants in Southeast Asia
2013-03-05
The Environmental Hygienists Association announces that it now has two experienced Certified Environmental Hygienists in Southeast Asia to serve property owners, managers, and tenants in the Philippines, Hong Kong, Thailand, Malaysia, and Singapore.
The Philippines-based environmental hygienists are Hank Taylor and Merley Martinez Taylor, both of whom are Certified Environmental Hygienists, Professional Industrial Hygienists, Certified Mold Inspectors, Certified Mold Remediators, and Certified Ozone Professionals. Hank Taylor has 25 years of mold and environmental inspection ...
Elite Ayrshire Business Circle Holds Successful Meeting at West Sound Radio
2013-03-05
The Elite Ayrshire Business Circle held its latest business breakfast networking meeting last week in the boardroom of independent local radio station West Sound Radio in Holmston Road, Ayr.
The meeting was hosted by station director Brenda Ritchie and her team, and attended by John Scott, MSP for Ayr, Provost Helen Moonie, Councillor Brian Connolly, and Tricia Irving, Senior Enterprise & Tourism Officer, South Ayrshire Council.
Elite Ayrshire Business Circle executive chairman and Frazer Coogans Commercial Solicitors managing partner Norman Geddes opened the ...
Leesburg VA Author, Veteran, and Speaker Deborah L. Parker Presents on Personal and Family History's "Greatest Generation" at Balch Library on Sunday March 10, 2013 at 2pm
2013-03-05
One's own history can be the greatest educator. A passion for understanding what each generation brings can lead to greatly helping others through writing, teaching, and inspiring.
This is Leesburg resident and author Deborah L. Parker's story. Join her as she maps her family and personal narratives beginning with her pre-civil rights era upbringing in Waverly, Virginia, located in Sussex County 'peanut country.' Raised by a determined single mother in the home of wise maternal grandparents and surrounded by encouraging extended family that instilled in her a strong ...
Simple and Affordable MICR Check Writing Software for Any Businesses
2013-03-05
Check printing software allows user to print bank checks with Laser or MICR enabled printer and produce checks. One check printing software that is simple, affordable and risk-free for even the smallest businesses is the new edition of ezCheckprinting from halfpricesoft.com. The improved graphic interface is so straight-forward and user-friendly. Even the first time check writer customers can figure out how to use it quickly once they install this software.
ezCheckPrinting is designed for use by non-accountants with minimal computer skills. New users can download the ...
Salvador Scores First for the 2014 World Cup
2013-03-05
Victor Mooney of Queens, New York and executive director of South African Arts International, Ltd. (USA) ended his two week visit to Brazil on Sunday with the launch of the One Million Score A Goal for an AIDS-free generation campaign in the City of Salvador, a host city for the 2014 World Cup.
In the Historic Centre (known in Portuguese as The Pelourinho), Victor Hugo Poria Nasicmento, ten years old, scored the first goal out of 1,000,000 on Friday. The campaign will spread throughout the other host cities before and during the championship series matches in Belo Horizonte, ...
[1] ... [5106]
[5107]
[5108]
[5109]
[5110]
[5111]
[5112]
[5113]
5114
[5115]
[5116]
[5117]
[5118]
[5119]
[5120]
[5121]
[5122]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.