Trafalgar Hosts Special Vancouver Presentation by Best-Selling Travel Author, Patricia Schultz
2013-03-01
After last year's sponsorship of Patricia Schultz's highly successful North America and London, UK travel presentation series, Trafalgar (www.trafalgar.com), the Insider of guided vacations is thrilled to welcome back the New York Times best-selling author of 1,000 Places to See Before You Die to Canadian soil for another special speaking engagement. Due to overwhelming consumer response from the previous events, the award-winning travel company is once again sponsoring this year's free travel presentation, which will take place in Vancouver on March 7th.
Trafalgar invites ...
Seeking to Save Lives, Author Supports Giving Away 5,000 Copies of Her Own Book
2013-03-01
What would cause an author to support giving away 5,000 copies of her own book through personal donations and by declining all royalty payments? These aren't just any books - they share the author's message of hope, encouragement and truth for women facing the fears of an unplanned pregnancy. These books are being offered free as an outreach effort to save lives by Elizabeth Ministry International working in conjunction with Christian author and pro-life speaker, Sheila M. Luck, and her publisher, Life Sentence Publishing.
Jeannie Hannemann, Founder and Executive Director ...
Kennedy Engineers Designing Plant Habitat For Space Station
2013-03-01
Some of the research on the International Space Station focuses on meeting the needs of long-term spaceflight to destinations such as asteroids or Mars. A group of engineers at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida is developing a plant habitat with a large growth chamber to learn the effects of long-duration microgravity exposure to plants in space.
Through most of Kennedy's history, the space center has focused on receiving, processing and launching vehicles developed at other centers. Design projects such as the plant habitat give people at the Florida spaceport ...
Neutron scattering provides data on adsorption of ions in microporous materials
2013-02-28
The adsorption of ions in microporous materials governs the operation of technologies as diverse as water desalination, energy storage, sensing and mechanical actuation. Until now, however, researchers attempting to improve the performance of these technologies haven't been able to directly and unambiguously identify how factors such as pore size, pore surface chemistry and electrolyte properties affect the concentration of ions in these materials as a function of the applied potential.
To provide the needed information, researchers at the Georgia Institute of Technology ...
Physicists demonstrate the acceleration of electrons by a laser in a vacuum
2013-02-28
Accelerating a free electron with a laser has been a longtime goal of solid-state physicists.
David Cline, a distinguished professor in the UCLA Department of Physics and Astronomy, and Xiaoping Ding, an assistant researcher at UCLA, have conducted research at Brookhaven National Laboratory in New York and have established that an electron beam can be accelerated by a laser in free space.
This has never been done before at high energies and represents a significant breakthrough, Cline said, adding that it also may have implications for fusion as a new energy source. ...
New protein quality method provides important information on sustainable diet
2013-02-28
Rosemont, IL (February 27, 2013) – A groundbreaking report by an Expert Consultation of the Food and Agriculture Organization of United Nations (FAO) has recommended a new, advanced method for assessing the quality of dietary proteins.
The report, "Dietary protein quality evaluation in human nutrition", recommends that the Digestible Indispensable Amino Acid Score (DIAAS) replace the Protein Digestibility Corrected Amino Acid Score (PDCAAS) as the preferred method of measuring protein quality. The report recommends that more data be developed to support full implementation, ...
Mutation location is the key to prognosis
2013-02-28
HOUSTON – (Feb. 28, 2013) – The three most important factors in real estate are location, location, location, and the same might be said for mutations in the gene MECP2, said researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute (NRI) at Texas Children's Hospital in a report in the journal Cell.
"Where a mutation occurs can affect the severity of the symptoms of the disease," said Dr. Huda Zoghbi, professor of molecular and human genetics at BCM and director of the NRI. Zoghbi, corresponding author of the report, found the ...
UCLA study could explain why some people get zits and others don't
2013-02-28
The bacteria that cause acne live on everyone's skin, yet one in five people is lucky enough to develop only an occasional pimple over a lifetime. What's their secret?
In a boon for teenagers everywhere, a UCLA study conducted with researchers at Washington University in St. Louis and the Los Angeles Biomedical Research Institute has discovered that acne bacteria contain "bad" strains associated with pimples and "good" strains that may protect the skin.
The findings, published in the Feb. 28 edition of the Journal of Investigative Dermatology, could lead to a myriad ...
Action video games boost reading skills
2013-02-28
Much to the chagrin of parents who think their kids should spend less time playing video games and more time studying, time spent playing action video games can actually make dyslexic children read better. In fact, 12 hours of video game play did more for reading skills than is normally achieved with a year of spontaneous reading development or demanding traditional reading treatments.
The evidence, appearing in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on February 28, follows from earlier work by the same team linking dyslexia to early problems with visual attention rather ...
Fighting GM crop vandalism with a government-protected research site
2013-02-28
Genetically modified (GM) crops have been a source of great controversy—particularly in Europe—but acts of vandalism and associated security costs have made scientific evidence about the health and ecological impacts of those crops hard to come by. A Swiss government-protected field site dedicated for use in GM crop studies could serve as an example to other European countries interested in pursuing crop biotechnology, according to an article published in Trends in Biotechnology, a Cell Press publication, on February 28.
The protected field site will now enable research ...
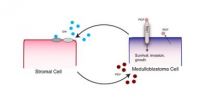
Study identifies growth factor essential to the most common malignant pediatric brain tumor
2013-02-28
A multi-institutional team led by Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) researchers has identified a molecular pathway that appears to be essential for the growth and spread of medulloblastoma, the most common malignant brain tumor in children. In their report in the Feb. 28 issue of Cell, they show that blocking this pathway – which involves interactions between tumor cells and the surrounding tissues – leads to regression of all four molecular subtypes of medulloblastoma in several mouse models.
"Our finding that a pathway carrying signals from host cells to tumor cells ...
How did early primordial cells evolve?
2013-02-28
VIDEO:
L-form bacteria undergoes cell division. The time scale is in minutes.
Click here for more information.
Four billion years ago, soon after the planet cooled enough for life to begin, primordial cells may have replicated and divided without protein machinery or cell walls, relying instead on just a flimsy lipid membrane. New research on bacteria examines exactly how these primitive cells could have evolved without such crucial structures. While the vast majority of bacteria ...
Animas' development of a first-generation closed loop insulin delivery system progresses
2013-02-28
WEST CHESTER, Pa., February 28, 2013 – Animas Corporation announced today positive results from the second phase of human clinical trials of a first-generation, closed-loop insulin delivery system in development, designed to predict a rise or fall in blood glucose and correspondingly increase, decrease, suspend and resume insulin delivery. The data were presented at the Advanced Technologies & Treatments for Diabetes (ATTD) Conference in Paris, France.
The feasibility study of the predictive Hypoglycemia-Hyperglycemia Minimizer (HHM) System* in development was conducted ...
The birth of a giant planet?
2013-02-28
An international team led by Sascha Quanz (ETH Zurich, Switzerland) has studied the disc of gas and dust that surrounds the young star HD 100546, a relatively nearby neighbour located 335 light-years from Earth. They were surprised to find what seems to be a planet in the process of being formed, still embedded in the disc of material around the young star. The candidate planet would be a gas giant similar to Jupiter.
"So far, planet formation has mostly been a topic tackled by computer simulations," says Sascha Quanz. "If our discovery is indeed a forming planet, then ...
Secondary facelift achieves good results, reports plastic and reconstructive surgery
2013-02-28
Philadelphia, Pa. (February 28, 2013) – Performed an average of a decade after initial facelift surgery, a "secondary" facelift can achieve similarly lasting results with a low complication rate, according to a paper in the March issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS).
Dr. Rod J. Rohrich and colleagues of University of Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, report their 20-year experience with secondary facelift surgery, or "rhytidectomy." The researchers conclude that, with attention ...
Round or 'shaped,' implants yield good results in breast reconstruction
2013-02-28
Philadelphia, Pa. (February 28, 2013) –For women undergoing breast reconstruction using implants, most patient-reported outcomes are similar with two different shapes of silicone gel-filled implants, reports a study in the March issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS).
Assessment of key areas of quality of life after breast reconstruction shows few significant differences with conventional round implants versus newer "shaped" implants, according to the new research, led by Dr. Sheina ...
Progesterone may be why pregnant women are more vulnerable to certain infections
2013-02-28
Bethesda, MD—Women who are pregnant or using synthetic progesterone birth control injections have a conspicuous vulnerability to certain infections including malaria, Listeria, HIV, and herpes simplex virus. A new research report appearing in the March 2013 issue of the Journal of Leukocyte Biology offers strong evidence for a possible explanation: the progesterone receptor, a pregnancy hormone sensor, targets a part of the immune system responsible for protection against these and other invaders. In addition to helping explain why some women are more vulnerable to certain ...
Brown unveils novel wireless brain sensor
2013-02-28
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — A team of neuroengineers based at Brown University has developed a fully implantable and rechargeable wireless brain sensor capable of relaying real-time broadband signals from up to 100 neurons in freely moving subjects. Several copies of the novel low-power device, described in the Journal of Neural Engineering, have been performing well in animal models for more than year, a first in the brain-computer interface field. Brain-computer interfaces coud help people with severe paralysis control devces with their thoughts.
Arto Nurmikko, ...
Brain-to-brain interface allows transmission of tactile and motor information between rats
2013-02-28
DURHAM, N.C. -- Researchers have electronically linked the brains of pairs of rats for the first time, enabling them to communicate directly to solve simple behavioral puzzles. A further test of this work successfully linked the brains of two animals thousands of miles apart—one in Durham, N.C., and one in Natal, Brazil.
The results of these projects suggest the future potential for linking multiple brains to form what the research team is calling an "organic computer," which could allow sharing of motor and sensory information among groups of animals. The study was published ...
Replacing soybean meal in pig diets
2013-02-28
Canola, cottonseed, and sunflower products can replace soybean meal in diets fed to pigs, but they contain less protein and energy. To determine if it makes economic sense to use them, producers need to know the concentrations and digestibility of the nutrients they contain. To help them make the decision, University of Illinois researchers examined amino acid digestibility for these products.
"Soybean is by far the biggest oilseed crop in the world," said Hans Stein, professor of animal sciences. "But canola, cottonseed, and sunflowers are grown in areas where soybeans ...
After the human genome project: The human microbiome project
2013-02-28
Bethesda, MD—Earth Day may be more than a month away, but another, more personal, ecosystem has been shown to also be worth protecting—within our bodies are communities of microbes that affect the behavior of human cells hosting them. These communities, called the "microbiome," are so crucial to our health that some consider it to be a complex "second genome." Understanding the interaction of these microbes among one another and their human hosts has the potential to yield insights into numerous diseases and complex human disorders from obesity to susceptibility to infection. ...
Physical activity does not protect against in situ breast cancer
2013-02-28
A European study published in the 'Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention' journal has analysed the association between physical activities and in situ or non-invasive breast cancer, or, in other words, cancer that has not yet invaded cells within or outside of the breast.
Headed by researchers from ten European countries including Spain, the work carried out under the framework of the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) concludes that physical activity has no relation with the risk of developing this type of non-invasive cancer. ...
Eating junk food while pregnant may make your child a junk food addict
2013-02-28
Bethesda, MD—Here's another reason why a healthy diet during pregnancy is critical to the future health of your children: New research published in the March 2013 issue of The FASEB Journal, suggests that pregnant mothers who consume junk food actually cause changes in the development of the opioid signaling pathway in the brains of their unborn children. This change results in the babies being less sensitive to opioids, which are released upon consumption of foods that are high in fat and sugar. In turn, these children, born with a higher "tolerance" to junk food need ...
Global tipping point not backed by science: Study
2013-02-28
A group of international ecological scientists led by the University of Adelaide have rejected a doomsday-like scenario of sudden, irreversible change to the Earth's ecology.
In a paper published today in the journal Trends in Ecology and Evolution, the scientists from Australia, US and UK argue that global-scale ecological tipping points are unlikely and that ecological change over large areas seem to follow a more gradual, smooth pattern.
This opposes recent efforts to define 'planetary tipping points' ‒ critical levels of biodiversity loss or land-use change ...
The giant cockroach genus Pseudophoraspis expands to the north with 3 new species
2013-02-28
Cockroaches (Blattodea) are an insect order remarkable in their biodiversity and distribution, with more than 4500 species known and great geographical reach. Cockroach fossils date back around 400 million years, which testifies to their great adaptability and endurance that puts them among the planet's great survivors.
The cockroach genus Pseudophoraspism has has been reported from China for the first time thanks to the discovery of three new species: Pseudophoraspis clavellata, Pseudophoraspis recurvata and Pseudophoraspis incurvata, alongside the first regional record ...
[1] ... [5124]
[5125]
[5126]
[5127]
[5128]
[5129]
[5130]
[5131]
5132
[5133]
[5134]
[5135]
[5136]
[5137]
[5138]
[5139]
[5140]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.