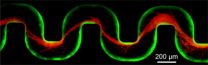
Study confirms safety of colonoscopy
2013-03-01
Colon cancer develops slowly. Precancerous lesions usually need many years to turn into a dangerous carcinoma. They are well detectable in an endoscopic examination of the colon called colonoscopy and can be removed during the same examination. Therefore, regular screening can prevent colon cancer much better than other types of cancer. Since 2002, colonoscopy is part of the national statutory cancer screening program in Germany for all insured persons aged 55 or older.
However, only one fifth of those eligible actually make use of the screening program. The reasons ...
Towards more sustainable construction
2013-03-01
This press release is available in French.
Montreal, March 1, 2013 – Construction in Montreal is under a microscope. Now more than ever, municipal builders need to comply with long-term urban planning goals. The difficulties surrounding massive projects like the Turcot interchange lead Montrealers to wonder if construction in this city is headed in the right direction. New research from Concordia University gives us hope that this could soon be the case if sufficient effort is made.
A team of graduate students from Concordia's Department of Geography, Planning and Environment ...
How do bacteria clog medical devices? Very quickly.
2013-03-01
A new study has examined how bacteria clog medical devices, and the result isn't pretty. The microbes join to create slimy ribbons that tangle and trap other passing bacteria, creating a full blockage in a startlingly short period of time.
The finding could help shape strategies for preventing clogging of devices such as stents — which are implanted in the body to keep open blood vessels and passages — as well as water filters and other items that are susceptible to contamination. The research was published in Proceedings of the National ...
New study could explain why some people get zits and others don't
2013-03-01
The bacteria that cause acne live on everyone's skin, yet one in five people is lucky enough to develop only an occasional pimple over a lifetime.
In a boon for teenagers everywhere, a UCLA study conducted with researchers at Washington University in St. Louis and the Los Angeles Biomedical Research Institute has discovered that acne bacteria contain "bad" strains associated with pimples and "good" strains that may protect the skin.
The findings, published in the Feb. 28 edition of the Journal of Investigative Dermatology, could lead to a myriad of new therapies to ...
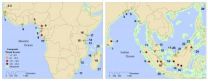
Where the wild things go… when there's nowhere else
2013-03-01
Ecologists have evidence that some endangered primates and large cats faced with relentless human encroachment will seek sanctuary in the sultry thickets of mangrove and peat swamp forests. These harsh coastal biomes are characterized by thick vegetation — particularly clusters of salt-loving mangrove trees — and poor soil in the form of highly acidic peat, which is the waterlogged remains of partially decomposed leaves and wood. As such, swamp forests are among the few areas in many African and Asian countries that humans are relatively less interested in exploiting (though ...
Thyroid hormones reduce damage and improve heart function after myocardial infarction in rats
2013-03-01
Thyroid hormone treatment administered to rats at the time of a heart attack (myocardial infarction) led to significant reduction in the loss of heart muscle cells and improvement in heart function, according to a study published by a team of researchers led by A. Martin Gerdes and Yue-Feng Chen from New York Institute of Technology College of Osteopathic Medicine.
The findings, published in the Journal of Translational Medicine, have bolstered the researchers' contention that thyroid hormones may help reduce heart damage in humans with cardiac diseases.
"I am extremely ...
Groundbreaking UK study shows key enzyme missing from aggressive form of breast cancer
2013-03-01
LEXINGTON, Ky. (Feb. 28, 2013) – A groundbreaking new study led by the University of Kentucky Markey Cancer Center's Dr. Peter Zhou found that triple-negative breast cancer cells are missing a key enzyme that other cancer cells contain — providing insight into potential therapeutic targets to treat the aggressive cancer. Zhou's study is unique in that his lab is the only one in the country to specifically study the metabolic process of triple-negative breast cancer cells.
Normally, all cells — including cancerous cells — use glucose to initiate the process of making Adenosine-5'-triphosphate ...
Lost in translation: HMO enrollees with poor health have hardest time communicating with doctors
2013-03-01
In the nation's most diverse state, some of the sickest Californians often have the hardest time communicating with their doctors. So say the authors of a new study from the UCLA Center for Health Policy Research that found that residents with limited English skills who reported the poorest health and were enrolled in commercial HMO plans were more likely to have difficulty understanding their doctors, placing this already vulnerable population at even greater risk.
The findings are significant given that, in 2009, nearly one in eight HMO enrollees in California was ...
Study shows need for improved empathic communication between hospice teams and caregivers
2013-03-01
LEXINGTON, Ky. (Feb. 26, 2013) — A new study authored by University of Kentucky researcher Elaine Wittenberg-Lyles shows that more empathic communication is needed between caregivers and hospice team members.
The study, published in Patient Education and Counseling, was done in collaboration with Debra Parker Oliver, professor in the University of Missouri Department of Family and Community Medicine. The team enrolled hospice family caregivers and interdisciplinary team members at two hospice agencies in the Midwestern United States.
Researchers analyzed the bi-weekly ...
New method for researching understudied malaria-spreading mosquitoes
2013-03-01
Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Malaria Research Institute have developed a new method for studying the complex molecular workings of Anopheles albimanus, an important but less studied spreader of human malaria. An. albimanus carries Plasmodium vivax, the primary cause of malaria in humans in South America and regions outside of Africa. Unlike Anopheles gambiae, the genome of the An. albimanus mosquito has not been sequenced and since these two species are evolutionarily divergent, the genome sequence of An. gambiae cannot serve as an appropriate reference. The researcher's ...
Nearly 1 in 4 women newly diagnosed with breast cancer
2013-03-01
A study by researchers at the Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center (HICCC) at NewYork-Presbyterian/Columbia University Medical Center, has found that nearly one in four women (23 percent) newly diagnosed with breast cancer reported symptoms consistent with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) shortly after diagnosis, with increased risk among black and Asian women. The research has been e-published ahead of print in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
"This study is one of the first to evaluate the course of PTSD after a diagnosis of breast cancer," said ...
British Columbia traffic deaths could be cut in half
2013-03-01
A study by a Simon Fraser University researcher shows British Columbia has much higher traffic death rates than most northern European countries. Comparisons to the safest country, the Netherlands, suggest B.C. could reduce the number of traffic deaths by more than 200 per year.
It also found that fatality and injury risks varied by travel mode.
"Many studies have shown that overall, considering both potential physical activity benefits and injury risks, cycling and walking are on the whole very healthy travel activities," says SFU health sciences assistant professor ...
Mineral diversity clue to early Earth chemistry
2013-03-01
Washington, D.C.— Mineral evolution is a new way to look at our planet's history. It's the study of the increasing diversity and characteristics of Earth's near-surface minerals, from the dozen that arrived on interstellar dust particles when the Solar System was formed to the more than 4,700 types existing today. New research on a mineral called molybdenite by a team led by Robert Hazen at Carnegie's Geophysical Laboratory provides important new insights about the changing chemistry of our planet as a result of geological and biological processes.
The work is published ...
CETS offers new method to help simplify the study of brain pathologies
2013-03-01
Scientists from the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, MD have developed a new way to identify heterogeneous brain cells by looking at epigenetic variation (the heritable alterations in gene expression caused by mechanisms other than changes in DNA sequence). With this publicly available new method (named "CETS"), it will be possible to generate neuronal profiles from DNA methylation data, which will simplify the study of several brain pathologies, including depression and age-associated disorders. The study, titled "A cell epigenotype specific model ...
Third radiation belt discovered with UNH-led instrument suite
2013-03-01
DURHAM, N.H. – Although scientists involved in NASA's Van Allen Probes mission were confident they would eventually be able to rewrite the textbook on Earth's twin radiation belts, getting material for the new edition just two days after launch was surprising, momentous, and gratifying.
The Radiation Belt Storm Probes mission, subsequently renamed in honor of the belts' discoverer, astrophysicist James Van Allen, was launched in the pre-dawn hours of August 30, 2012. Shortly thereafter, and well ahead of schedule in normal operational protocol, mission scientists turned ...
Adult sleepwalking is serious condition that impacts health-related quality of life
2013-03-01
DARIEN, IL – A new study found that adult sleepwalking is a potentially serious condition that may induce violent behaviors and affect health-related quality of life.
"We found a higher frequency of daytime sleepiness, fatigue, insomnia, depressive and anxiety symptoms and altered quality of life in patients with sleepwalking compared to the control group," said Yves Dauvilliers, MD, PhD, the study's principal investigator and lead author. Dr. Dauvilliers is professor of physiology and neurology and director of the sleep lab at Gui-de-Chauliac Hospital in Montpellier, ...
Elephants are vanishing from DRC's best-run reserve
2013-03-01
NEW YORK (Feb. 28, 2013) — The Democratic Republic of Congo's (DRC) largest remaining forest elephant population, located in the Okapi Faunal Reserve (OFR), has declined by 37 percent in the last five years, with only 1,700 elephants now remaining, according to wildlife surveys by WCS and DRC officials. WCS scientists warn that if poaching of forest elephants in DRC continues unabated, the species could be nearly extinguished from Africa's second largest country within ten years.
According to the latest survey, 5,100, or 75 percent, of the reserve's elephants have been ...
New model could lead to improved treatment for early stage Alzheimer's
2013-03-01
GAINESVILLE, Fla. — Researchers at the University of Florida and The Johns Hopkins University have developed a line of genetically altered mice that model the earliest stages of Alzheimer's disease. This model may help scientists identify new therapies to provide relief to patients who are beginning to experience symptoms.
The researchers report their findings in the current issue of The Journal of Neuroscience.
"The development of this model could help scientists identify new ways to enhance brain function in patients in the early stages of the disease," said David ...
Research unearths new dinosaur species
2013-03-01
RAPID CITY, S.D. (Feb. 28, 2013) – A South Dakota School of Mines & Technology assistant professor and his team have discovered a new species of herbivorous dinosaur and published the first fossil evidence of prehistoric crocodyliforms feeding on small dinosaurs.
Research by Clint Boyd, Ph.D., provides the first definitive evidence that plant-eating baby ornithopod dinosaurs were a food of choice for the crocodyliform, a now extinct relative of the crocodile family. While conducting their research, the team also discovered that this dinosaur prey was a previously unrecognized ...
ACC/HRS release appropriate use criteria for ICDs and CRT
2013-03-01
WASHINGTON (Feb. 28, 2013) –The American College of Cardiology and the Heart Rhythm Society, along with key specialty societies, today released appropriate use criteria for implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) and cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT). The document provides assessed levels of appropriateness for implanting the devices in 369 real-life clinical scenarios, with the goal of enhancing physician and patient decision making and improving care and health outcomes.
Implantable cardioverter-defibrillators are devices that monitor the heart's rhythms ...
Sea lamprey genome mapped with help from scientists at OU
2013-03-01
Beginning in 2004, a group of scientists from around the globe, including two University of Oklahoma faculty members, set out to map the genome of the sea lamprey. The secrets of how this jawless vertebrate separated from the jawed vertebrates early in the evolutionary process will give insight to the ancestry of vertebrate characters and may help investigators more fully understand neurodegenerative diseases in humans.
David McCauley, associate professor in the Biology Department in the OU College of Arts and Sciences, and Sandra W. Clifton, with the OU Center for Advanced ...
Pour, shake and stir
2013-03-01
TORONTO, Ontario (Feb. 28, 2013) - A diagnostic "cocktail" containing a single drop of blood, a dribble of water, and a dose of DNA powder with gold particles could mean rapid diagnosis and treatment of the world's leading diseases in the near future. The cocktail diagnostic is a homegrown brew being developed by University of Toronto's Institute of Biomaterials and Biomedical Engineering (IBBME) PhD student Kyryl Zagorovsky and Professor Warren Chan that could change the way infectious diseases, from HPV and HIV to malaria, are diagnosed.
And it involves the same technology ...
NOAA and NASA's next generation weather satellite may provide earlier warnings
2013-03-01
A new satellite that will detect the lightning inside storm clouds may lead to valuable improvements in tornado detection. The GOES-R satellite is currently being built with new technology that may help provide earlier warnings for severe weather. The national average is a 14-minute lead time to warn residents of a tornado, but NASA and NOAA scientists are looking to improve severe weather detection to save lives and property. They are developing the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-R Series, or GOES-R, to observe thunderstorm development with much greater ...
NASA's Van Allen Probes discover a surprise circling Earth
2013-03-01
After most NASA science spacecraft launches, researchers wait patiently for months as instruments on board are turned on one at a time, slowly ramped up to full power, and tested to make sure they work at full capacity. It's a rite of passage for any new satellite in space, and such a schedule was in place for the Van Allen Probes when they launched on Aug. 30, 2012, to study two giant belts of radiation that surround Earth.
But a group of scientists on the mission made a case for changing the plan. They asked that the Relativistic Electron Proton Telescope (REPT) be ...
Zeroing in on heart disease
2013-03-01
Studies screening the genome of hundreds of thousands of individuals (known as Genome-wide association studies or GWAS) have linked more than 100 regions in the genome to the risk of developing cardiovascular disease. Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and the University of Heidelberg, through the joint Molecular Medicine Partnership Unit (MMPU), are taking these results one step further by pinpointing the exact genes that could have a role in the onset of the disease. Their findings are published today in the Public Library of Science (PLoS) ...
[1] ... [5131]
[5132]
[5133]
[5134]
[5135]
[5136]
[5137]
[5138]
5139
[5140]
[5141]
[5142]
[5143]
[5144]
[5145]
[5146]
[5147]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.