Drug helps women who stop smoking keep weight off
2012-12-11
A medication being tested to help smokers kick the habit also may help avoid the weight gain that is common after quitting but only in women, according to a study published in the December issue of Biological Psychiatry. This is the first medication shown to reduce weight gain for up to one year in women smokers who quit.
Naltrexone — an opioid blocker that can dampen the desire for alcohol, heroin and nicotine, as well as the pleasures of eating — helped men quit smoking. It improved their quit rates after three months of treatment in a large controlled trial, from 17 ...
A new tool for secret agents -- and the rest of us
2012-12-11
PASADENA, Calif.—A secret agent is racing against time. He knows a bomb is nearby. He rounds a corner, spots a pile of suspicious boxes in the alleyway, and pulls out his cell phone. As he scans it over the packages, their contents appear onscreen. In the nick of time, his handy smartphone application reveals an explosive device, and the agent saves the day.
Sound far-fetched? In fact it is a real possibility, thanks to tiny inexpensive silicon microchips developed by a pair of electrical engineers at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech). The chips generate ...
Researcher finds gender differences in seasonal auditory changes
2012-12-11
ATLANTA – Auditory systems differ between sexes in sparrows depending on the season, a Georgia State University neuroscientist has found. The work adds to our knowledge of how the parts of the nervous system, including that of humans, are able to change.
Megan Gall, a post-doctoral researcher with Georgia State's Neuroscience Institute, tested the peripheral auditory systems of male and female house sparrows, comparing the hearing of each gender during non-breeding seasons and breeding seasons.
Gall measured frequency selectivity – the ability to tell sounds that are ...
Pharmacy researcher finds most popular weight-loss drug strongly alters other drug therapies
2012-12-11
KINGSTON, R.I.— December 10, 2012 – A University of Rhode Island researcher has discovered that the weight-loss drug orlistat, known by the brand names Xenical and Alli, inhibits a key enzyme that may lead to "severe toxicity of internal organs such as the liver and kidney." The inhibition is irreversible and can be caused by a low level of the drug.
Professor Bingfang Yan's study funded by the National Institutes of Health, also found that the drug alters efficacy of medicines, and particularly limits the effectiveness of some anti-cancer drugs.
Part of the research ...
Novel drug therapy targets aggressive form of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
2012-12-11
NEW YORK (Dec. 10, 2012) -- Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common subtype of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and the seventh most frequently diagnosed cancer. The most chemotherapy resistant form of DLBCL, called activated B-cell – DLBCL (ABC-DLBCL), remains a major therapeutic challenge. An international research team, led by two laboratories from Weill Cornell Medical College, has developed a new experimental drug therapy to target this aggressive form of lymphoma.
In the journal Cancer Cell, researchers report the discovery of an experimental small molecule ...
Quantifying corn rootworm damage
2012-12-11
URBANA – Every year farmers spend a lot of money trying to control corn rootworm larvae, which are a significant threat to maize production in the United States and, more recently, in Europe. University of Illinois researchers have been working on validating a model for estimating damage functions.
Nicholas Tinsley, a doctoral candidate in crop sciences, has refined a model developed in 2009 by researchers at the University of Wisconsin and in Brescia, Italy, to describe the relationship between root injury caused by these pests and yield loss. He used the equivalent ...
Wayne State researcher finds possible clue to children's early antisocial behavior
2012-12-11
DETROIT - Both nature and nurture appear to be significant factors in early antisocial behaviors of adopted children, a Wayne State University researcher believes.
Christopher Trentacosta, Ph.D., assistant professor of psychology in the College of Liberal Arts and Sciences, recently examined data from 361 linked triads (birth mother, adoptive parents, adopted child) in order to assess externalizing behavioral problems such as aggression and defiance when children were 18, 27 and 54 months of age.
The triads were part of the Early Growth and Development Study (EGDS), ...
The dark side of kerosene lamps: High black-carbon emissions
2012-12-11
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — The small kerosene lamps that light millions of homes in developing countries have a dark side: black carbon – fine particles of soot released into the atmosphere.
New measurements show that kerosene wick lamps release 20 times more black carbon than previously thought, say researchers at the University of Illinois and the University of California, Berkeley. The group published its findings in the journal Environmental Science and Technology.
Black carbon is a hazard for human health and the environment, affecting air quality both indoors and out. ...
Intensified chemotherapy shows promise for children with very high risk form of leukemia
2012-12-11
Young patients with an aggressive form of leukemia who are likely to relapse after chemotherapy treatment can significantly reduce those odds by receiving additional courses of chemotherapy, suggest the findings of a clinical trial led by investigators at Dana-Farber/Children's Hospital Cancer Center in Boston.
The trial leaders will present the results of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute ALL Consortium study, which involved nearly 500 patients under age 18 with B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology ...
As Amazon urbanizes, rural fires burn unchecked
2012-12-11
Over past decades, many areas of the forested Amazon basin have become a patchwork of farms, pastures and second-growth forest as people have moved in and cleared land--but now many are moving out, in search of economic opportunities in newly booming Amazonian cities. The resulting depopulation of rural areas, along with spreading road networks and increased drought are causing more and bigger fires to ravage vast stretches, say researchers in a new study. The study, focusing on the Peruvian Amazon, is the latest to suggest that land-use changes and other factors, including ...
Blood levels of immune protein predict risk in Hodgkin disease
2012-12-11
Blood levels of an immunity-related protein, galectin-1, in patients with newly diagnosed Hodgkin lymphoma reflected the extent of their cancer and correlated with other predictors of outcome, scientists reported at the American Society of Hematology annual meeting.
In a study of 315 patients from a German database, researchers from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute found that serum galectin-1 levels "are significantly associated with tumor burden and additional adverse clinical characteristics in newly diagnosed Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) patients."
The measurements were made ...
Conservatives can be persuaded to care more about the environment
2012-12-11
When it comes to climate change, deforestation and toxic waste, the assumption has been that conservative views on these topics are intractable. But new research from the University of California, Berkeley, suggests that such viewpoints can be changed after all, when the messages about the need to be better stewards of the land are couched in terms of fending off threats to the "purity" and "sanctity" of Earth and our bodies.
A UC Berkeley study has found that while people who identified themselves as conservatives tend to be less concerned about the environment than ...
Before 'Skyfall': 46 years of violence in James Bond movies
2012-12-11
Violent acts in James Bond films were more than twice as common in Quantum of Solace (2008) than in the original 1962 movie Dr No, researchers from New Zealand's University of Otago have found.
The researchers analysed 22 official franchise films, which span 46 years, to test the hypothesis that popular movies are becoming more violent (The latest Bond film, Skyfall, was not included as it was unreleased at the time of the study).
They found that rates of violence increased significantly over the period studied and there was an even bigger increase in portrayals of ...
NASA satellites see Typhoon Bopha fizzle over weekend
2012-12-11
Infrared data from NASA's Aqua satellite have watched the strong thunderstorms in Typhoon Bopha fizzle and shrink in area over the weekend as wind shear increased. Bopha has now dissipated in the South China Sea, just west of Luzon, Philippines.
NASA's Aqua satellite has been providing data on Bopha since the day it formed on Nov. 26. In the storm's last days, Aqua's Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured infrared data of the storm and showed that cloud top temperatures warmed from Dec. 8 through Dec. 9 as cloud heights fell and thunderstorms lost their ...
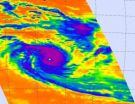
NASA gets eyeballed from Cyclone Claudia
2012-12-11
NASA's Aqua satellite got "eyeballed" from Cyclone Claudia in the Southern Indian Ocean when two instruments captured the storm's eye in infrared and visible light. Satellite data indicates that Claudia's eye is about 10 nautical miles wide.
On Dec. 10 at 0841 UTC (3:41 a.m. EST), NASA's Aqua satellite's Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured an infrared view of Cyclone Claudia which showed a clear eye surrounded by powerful thunderstorms. The thunderstorms that surrounded the eye were high in the troposphere and cloud top temperatures topped -63 Fahrenheit ...
Experimental graft-vs.-host disease treatment equivalent to standard care in Phase 3 trial
2012-12-11
An experimental drug combination for preventing graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) was not significantly better than the standard regimen on key endpoints, according to a report of a phase 3 trial at the American Society of Hematology annual meeting.
The combination of two immunosuppressive compounds -- tacrolimus plus sirolimus -- did not provide a statistically significant, GVHD-free survival benefit over the long-used standard of care, tacrolimus plus methotrexate, said researchers from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute who led the multi-center trial.
However, there were ...
Messages that speak to conservatives' morals narrow partisan gap on environment
2012-12-11
Public opinion on environmental issues such as climate change, deforestation, and toxic waste seems to fall along increasingly partisan lines. But new research suggests that environmental messages framed in terms of conservative morals — describing environmental stewardship in terms of fending off threats to the "purity" and "sanctity" of Earth and our bodies — may help to narrow the partisan gap.
A study from researchers at UC Berkeley has found that while people who identified themselves as conservatives tend to be less concerned about the environment than their liberal ...
Health-care practitioners must cooperate to reduce medication mismanagement, MU expert says
2012-12-11
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Medication reconciliation is a safety practice in which health care professionals review patients' medication regimens when patients transition between settings to reduce the likelihood of adverse drug effects. It is among the most complex clinical tasks required of physicians, nurses and pharmacists, who must work cooperatively to minimize discrepancies and inappropriate medication orders. Now, a University of Missouri gerontologiccal nursing expert suggests that acknowledging practitioners' varying perspectives on the purpose of medication reconciliation ...
Drug combination acts against aggressive chronic lymphocytic leukemia
2012-12-11
ATLANTA - A two-prong approach combining ibrutinib and rituximab (Rituxin®) to treat aggressive chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) produced profound responses with minor side effects in a Phase 2 clinical trial at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
Researchers presented the results today at the 54th annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology (ASH).
"This is a patient population with a great need for more targeted therapies," said Jan Burger, M.D., Ph.D., associate professor in MD Anderson's Department of Leukemia. Burger was lead author of ...
Grateful patient philanthropy and the doctor-patient relationship
2012-12-11
Physicians associated with "patient philanthropy" – financial donations from grateful patients to a medical institution – are concerned with how these contributions might affect their own behavior and attitudes, and how they might impact the doctor-patient relationship. A new study¹ by Scott Wright, MD and Joseph A. Carrese, MD, MPH of Johns Hopkins University, and colleagues, explores this topic. The paper considers the perspectives of internal medicine physicians working in an academic medical center who have had experiences with these situations. Their findings appear ...
Brain angioplasty and stents found safe and effective for stroke patients
2012-12-11
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Some stroke patients may benefit from cerebral angioplasty and stent placement, according to a new study published online in the journal Radiology.
"As many as 70 percent of ischemic stroke patients could have positive clinical outcomes with the additional use of intra-arterial revascularization using stents," said Martin Roubec, M.D., Ph.D., a neurologist in the Comprehensive Stroke Center at the University Hospital Ostrava in the Czech Republic.
Ischemic stroke, the most common form of stroke, occurs when blockage in an artery—often from a blood ...
Combination of imaging exams improves Alzheimer's diagnosis
2012-12-11
OAK BROOK, Ill. – A combination of diagnostic tests, including imaging and cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers can improve prediction of conversion from mild cognitive impairment (MCI) to Alzheimer's disease, according to a new study published online in the journal Radiology.
"Because new treatments are likely to be most effective at the earliest stages of Alzheimer's disease, there is great urgency to develop sensitive markers that facilitate detection and monitoring of early brain changes in individuals at risk," said Jeffrey R. Petrella, M.D., associate professor of radiology, ...
Combining diagnostic tests more accurate at predicting Alzheimer's
2012-12-11
DURHAM, N.C. -- Employing a combination of imaging and biomarker tests improves the ability of doctors to predict Alzheimer's in patients with mild cognitive impairment, according to researchers at Duke Medicine.
The findings, which appear Tuesday, Dec. 11, 2012, in the journal Radiology, provide new insight into how to accurately detect Alzheimer's before the full onset of the disease.
Duke researchers studied three tests – magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), fluorine 18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET), and cerebrospinal fluid analysis – to ...
Bedroom TV viewing increases risk of obesity in children
2012-12-11
San Diego, CA, December 11, 2012 – The average American child from age 8 to 18 watches about 4.5 hours of TV each day. Seventy percent have a TV in the bedroom and about one-third of youth aged 6-19 is considered obese. Previous studies have shown that TV viewing time during childhood and adolescence continues into adulthood, resulting in overweight and elevated total cholesterol. An investigative team from the Pennington Biomedical Research Center in Baton Rouge, LA reports new study findings, establishing the relationship between having and watching TV in the bedroom ...
New coronavirus has many potential hosts, could pass from animals to humans repeatedly
2012-12-11
The SARS epidemic of 2002-2003 was short-lived, but a novel type of human coronavirus that is alarming public health authorities can infect cells from humans and bats alike, a fact that could make the animals a continuing source of infection, according to a study to be published in in mBio®, the online open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology, on December 11. The new coronavirus, called hCoV-EMC, is blamed for five deaths and several other cases of severe disease originating in countries in the Middle East. According to the new results, hCoV-EMC uses ...
[1] ... [5510]
[5511]
[5512]
[5513]
[5514]
[5515]
[5516]
[5517]
5518
[5519]
[5520]
[5521]
[5522]
[5523]
[5524]
[5525]
[5526]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.