Evolutionary analysis improves ability to predict the spread of flu
2012-10-01
BETHESDA, MD – October 1, 2012 – With flu season around the corner, getting a seasonal vaccine might be one of the best ways to prevent people from getting sick. These vaccines only work, however, if their developers have accurately predicted which strains of the virus are likely to be active in the coming season because vaccines must be developed in advance of the upcoming flu season. Recently, a team of scientists from Germany and the United Kingdom have improved the prediction methods used to determine which strains of the flu virus to include in the current season's ...
First large scale trial of whole-genome cancer testing for clinical decision-making reported
2012-10-01
VIENNA, Austria, 1 October 2012 – For the first time, researchers have conducted a large trial in which they tested the entire genome of individual breast cancers to help personalize treatment. They released their findings at the ESMO 2012 Congress of the European Society for Medical Oncology in Vienna.
In recent years, a number of drugs have been developed that target specific genetic alterations in cancer. To choose which of these drugs are suitable for individual patients, some genetic testing is performed. "In most of these cases, these genetic testing approaches ...
New findings on optimal duration of trastuzumab therapy for women with HER2+ early breast cancer
2012-10-01
VIENNA, Austria, 1 October 2012 – New studies that advance understanding of the optimal duration of therapy with the targeted cancer drug trastuzumab were released today at the ESMO 2012 Congress of the European Society for Medical Oncology in Vienna.
"These long awaited results constitute a further milestone in the treatment of patients with early breast cancer over-expressing HER2/neu, corresponding to a population of about 12-15% of all cases of breast cancer," commented Prof Christoph Zielinski, Chairman of the Clinical Division of Oncology, at Medical University ...
Phase III data in treatment of renal cell carcinoma reported
2012-10-01
Vienna, Austria, 1 October 2012 – New results from phase III trials exploring treatment options for patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma were released at the ESMO 2012 Congress of the European Society for Medical Oncology in Vienna.
Renal cell carcinoma is a type of kidney cancer that starts in the lining of very small tubes (tubules) in the kidney.
Prof Maria De Santis from Kaiser Franz Josef-Spital, Vienna, Chair of the ESMO 2012 Genitourinary program track (who was not involved in the studies) commented: "At this year's ESMO congress, three urgently awaited ...
New findings highlight the challenges of managing blood clotting in cancer patients
2012-10-01
VIENNA, Austria, 1 October 2012 – New findings that highlight the challenges of managing thromboembolic events in patients being treated for cancer were released at the ESMO 2012 Congress of the European Society for Medical Oncology in Vienna.
Venous thromboembolism causes symptoms in about 3 to 4% of cancer patients whose chemotherapy drugs are delivered via a central venous catheter, comments Dr. Fausto Roila, from Medical Oncology Department, Terni, Italy, Chair of the ESMO 2012 Supportive Care Track. "When asymptomatic patients are considered, these events affect ...
Should aspirin be used to prevent cancer?
2012-10-01
VIENNA, Austria, 1 October 2012 – Aspirin, the everyday drug taken by countless people around the world to ward off pain and reduce their risk of developing heart disease, may have a new trick up its sleeve –-preventing cancer.
A growing body of evidence suggests that taking aspirin may reduce an individual's chances of developing colorectal cancer and perhaps other malignancies, but whether that evidence is strong enough to outweigh the risks of prescribing it to millions of healthy people is the subject of debate.
At the ESMO 2012 Congress in Vienna, both sides of ...
Putting a 'HEX' on muscle regeneration
2012-10-01
A complex genetic regulatory network mediates the regeneration of adult skeletal muscles. In this issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation, researchers at the State University of New York Downstate Medical Center in Brooklyn report that HEXIM1, a protein that regulates gene transcription, is important for skeletal muscle regeneration in mice. M.A.Q. Saddiqui and colleagues found that HEXIM1 blocks gene expression that is required for muscle regeneration after injury. Mice with a 50% reduction in HEXIM1 exhibited greater muscle mass and function after injury compared ...
JCI early table of contents for October 1, 2012
2012-10-01
Sphingolipid metabolism contributes to diabetes-associated heart disease
Patients with type 2 diabetes are subject to a number of major health risks, including a greatly increased risk of heart failure. This is due in part to the development of diabetic cardiomyopathy (DbCM), a condition that significantly impairs heart function. In this issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation, Ashley Cowart and colleagues at the Medical University of South Carolina report that an increase in specific types of saturated fatty acids (SFAs) and fatty acid metabolic pathways cause ...
Public health messages can influence infectious disease stigmas
2012-10-01
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Crafting public health messages about a disease may create stigmas that influence how likely people are to endorse certain interventions, such as isolating infected persons, forcing treatment on them and mapping their location, according to a Penn State researcher.
Rachel Smith, associate professor of communication arts and sciences and investigator with the University's Center for Infectious Disease Dynamics, used a hypothetical disease -- a virus carried by rodents -- to develop 16 different health alerts describing the virus and those who were ...
Preoperative needle breast biopsies can lead to improved treatment outcomes
2012-10-01
Chicago: Women suspected of having breast cancer now have more reasons to be diagnosed with a needle biopsy instead of a traditional open surgical biopsy. Besides avoiding the risks and discomfort of an open surgical procedure, needle biopsies can also lead to improved treatment outcomes according to findings from a new study published in the October issue of the Journal of the American College of Surgeons.
Breast cancer is the number one form of cancer diagnosed in women in the United States, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. [1] In ...
Researchers identify a Dance Dance Revolution in kids' physical activity
2012-10-01
A study published in Pediatrics this morning by researchers at the University of Montreal offers positive news for Wii-loving teenagers and their parents: games such as Wii Sports and Dance Dance Revolution can bring them closer to recommended physical activity levels. The study is the first of its kind. "Teenage exergamers – people who play video games that require physical activity – are most likely females who are stressed about their weight. On average, they play two 50 minute sessions per week," said study author Jennifer O'Loughlin of the university's Department of ...
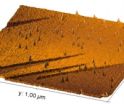
Nano-hillocks: Of mountains and craters
2012-10-01
In the field of nanotechnology, electrically-charged particles are frequently used as tools for surface modification. Researchers at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) and the TU Vienna were at last able to reconcile important issues concerning the effects of highly charged ions on surfaces.
Ion beams have been used for some time now for surface modification as ions are capable of carrying such high energies that a single particle alone can induce drastic changes to the surface under bombardment. Following careful examination, an international team of researchers ...
Study reveals how memory load leaves us 'blind' to new visual information
2012-10-01
Trying to keep an image we've just seen in memory can leave us blind to things we are 'looking' at, according to the results of a new study supported by the Wellcome Trust.
It's been known for some time that when our brains are focused on a task, we can fail to see other things that are in plain sight. This phenomenon, known as 'inattentional blindness', is exemplified by the famous 'invisible gorilla' experiment in which people watching a video of players passing around a basketball and counting the number of passes fail to observe a man in a gorilla suit walking across ...
Physiological role of a novel hormone FNDC5/irisin revealed in humans
2012-10-01
Oxford, October 1, 2012 - A research team led by Dr. Christos Mantzoros, MD, PhD, at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, has published new findings elucidating the molecular and clinical role of FNDC5/irisin in humans.
Irisin is a recently identified hormone secreted from muscle cells that has been found to serve as a chemical messenger providing key exercise-induced health benefits in mice. In these earlier studies, irisin showed direct effects on 'browning' of white fat which would lead to burning of excess calories. Discovery of irisin therefore ...
Computerized osteoporosis detection
2012-10-01
A computerized approach to examining patient bone X-rays for diagnosis of osteoporosis could side-step the subjectivity associated with visual examination, according to a new research paper in the International Journal of Biomedical Engineering and Technology published in October.
Neelesh Kumar of the Central Scientific Instruments Organisation in Chandigarh, India, and colleagues recognized that the bone disorder osteoporosis is on the increase but that diagnosis using X-ray images of the patient's skeleton often lead to false positives and false negatives because visual ...
The chemical memory of seawater
2012-10-01
Water does not forget, says Prof. Boris Koch, a chemist at the Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research in the Helmholtz Association. Irrespective of what happens in the sea: whether the sun shines, algae bloom or a school of dolphins swims through a marine area – everything and everyone leaves biomolecular tracks. With the help of a combination of new techniques, Boris Koch and colleagues can now identify and retrace some of these. In a special volume of the open access journal Biogeosciences, these scientists report on how these analyses work and which ...
First images of Landau levels revealed
2012-10-01
Physicists have directly imaged Landau Levels – the quantum levels that determine electron behaviour in a strong magnetic field – for the first time since they were theoretically conceived of by Nobel prize winner Lev Landau in 1930.
Using scanning tunnelling spectroscopy - a spatially resolved probe that interacts directly with the electrons - scientists at institutions including the University of Warwick and Tohoku University have revealed the internal ring-like structure of these Landau Levels at the surface of a semiconductor.
The experimental challenge in the work ...
UK-led project unravels the structures of membrane proteins
2012-10-01
The European Drug Initiative on Channels and Transporters (EDICT), which comes to an end this year, focused on membrane proteins. They make up a third of all proteins in every organism and play a key role in many human diseases.
Membrane proteins are difficult to study and poorly understood, but the four-year EDICT project has enabled a major step forward in our understanding of the structures – and even more importantly the functions – of over 30 of these proteins. Bringing together over 100 researchers across 12 countries, the project has developed better and faster ...
'Green Brain' project to create an autonomous flying robot with a honey bee brain
2012-10-01
Scientists at the Universities of Sheffield and Sussex are embarking on an ambitious project to produce the first accurate computer models of a honey bee brain in a bid to advance our understanding of Artificial Intelligence (AI), and how animals think.
The team will build models of the systems in the brain that govern a honey bee's vision and sense of smell. Using this information, the researchers aim to create the first flying robot able to sense and act as autonomously as a bee, rather than just carry out a pre-programmed set of instructions.
If successful, this ...
Yearlong MAGIC climate study launches
2012-10-01
UPTON, NY - A Horizon Lines container ship outfitted with meteorological and atmospheric instruments installed by U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) scientists from Argonne National Laboratory and Brookhaven National Laboratory will begin taking data today for a yearlong mission aimed at improving the representation of clouds in climate models. The study, a collaborative effort between DOE's Atmospheric Radiation Measurement (ARM) program Climate Research Facility and Horizon Lines, marks the first official marine deployment of the second ARM Mobile Facility, AMF2, and is ...
Nothing to sneeze at: Scientists find cheating ragweed behaves better with its kin
2012-10-01
Cheating. Conflict. Competition. It may sound like a soap opera but this is the complex life of the despised ragweed plant.
And in the highly competitive fight for nutrients, researchers have found ragweed will behave altruistically with its siblings, investing precious resources for the benefit of the group.
A growing body of work suggests plants recognize and respond to the presence and identity of their neighbours and the findings, published online in the journal PLOS ONE, provide further evidence of the importance of family in preserving cooperation within and ...
Evidence-based guidelines enable optimal treatment of common low-back pain
2012-10-01
AUGUSTA, Ga. – While scientific evidence suggests that less is typically more when it comes to diagnosing and treating low-back pain in the U.S., the number of expensive imaging exams and surgeries done on patients continues to rise, researchers say.
More than 25 percent of American adults report at least one episode of acute low-back pain in the past three months and the annual total price tag is about $100 billion, according to a study in an issue of the Journal of the American College of Radiology focusing on health care reform.
"For the great majority of patients, ...
Longest fiber-optic sensor network developed
2012-10-01
This press release is available in Spanish.Montserrat Fernández-Vallejo, a telecommunications engineer and graduate of the UPNA-Public University of Navarre, has experimentally developed various fibre-optic sensor networks for the remote monitoring of large infrastructures. Specifically, she has managed to develop the largest network so far in existence —measuring 250 km—, which is equipped with a multiplexing capability, (which enables two or more information channels to be combined within a single transmission medium).
This technological development in the field of ...
EARTH: Risky business: Modeling catastrophes
2012-10-01
Alexandria, VA – The probability that a given natural hazard could become a natural disaster is higher today than at any previous point in history, largely because of population growth putting more people and infrastructure in harm's way. Who pays for the damage and how is value and risk assessed? Much of it comes down to insurance and reinsurance agencies, which are relying more and more on sophisticated catastrophe modeling tools to help gauge when the next disaster will strike, and how much it will cost.
Catastrophe modeling has only been around for a couple of decades, ...
Baby communication gives clues to autism
2012-10-01
CORAL GABLES, FL -- Approximately 19 percent of children with a sibling diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) will develop Autism due to shared genetic and environmental vulnerabilities, according to previous studies. For that reason, University of Miami (UM) psychologists are developing ways to predict the occurrence of ASD in high-risk children, early in life, in hopes that early intervention will lead to better outcomes in the future. Their findings are published in the journal Infancy.
The study is one of the first to show that measures of non-verbal communication ...
[1] ... [5881]
[5882]
[5883]
[5884]
[5885]
[5886]
[5887]
[5888]
5889
[5890]
[5891]
[5892]
[5893]
[5894]
[5895]
[5896]
[5897]
... [8810]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.