Research and development found to be most prevalent in a small number of regions across the country
2012-09-12
Businesses perform a large share of their research and development in a small number of geographic areas, two of the largest being the San Jose-San Francisco-Oakland area and the New York-Newark-Bridgeport area. In these two areas alone, designated as combined statistical areas (CSAs) by the Office of Management and Budget, companies performed at least $29.3 billion of R&D, according to a recent National Science Foundation report.
Data are from the 2008 Business R&D and Innovation Survey (BRDIS). These new BRDIS data allow policymakers and researchers to explore patterns ...
Insecticide resistance caused by recombination of 2 genes
2012-09-12
Helicoverpa armigera: a global pest
Larvae of the cotton bollworm (Helicoverpa armigera) are dreaded pests all over the world. They have a very wide host range: About 200 different plant species are known as potential food for the voracious insect. The herbivore attacks crops in Africa, South Europe, India, Central Asia, New Zealand, and Australia. Nearly 30% of all globally used insecticides − Bt toxins as well as pyrethroids − are applied to protect cotton and other crops against the bollworm.
Resistance to pyrethroids
Pyrethroids are synthetic substances ...
Nationwide Children's Hospital develops prototype for safer, child-resistant spray bottle
2012-09-12
VIDEO:
Studies show that when it comes to household cleaners, the spray bottle is the most common source of exposure to injury among children in the US Not only have children...
Click here for more information.
Researchers at The Research Institute at Nationwide Children's Hospital, in partnership with The Ohio State University have developed a prototype for child-resistant spray bottles for household cleaning products. If produced, the prototype would provide an alternative ...
Forensic science on trial
2012-09-12
The key player in a movement challenging improper use of DNA testing and other elements of forensic science is the topic of a compelling cover story in this week's edition of Chemical & Engineering News. The story in the weekly newsmagazine of the American Chemical Society (ACS) — the world's largest scientific society — features the Innocence Project, which, in the last two decades, has helped free nearly 300 wrongfully convicted prisoners.
C&EN Senior Editor Carmen Drahl uses a symposium on the Innocence Project held at ACS' Fall National Meeting & Exposition to discuss ...
An advance toward a flu-fighting nasal spray
2012-09-12
In an advance toward development of a nasal spray that protects against infection with influenza and spread of the disease, scientists are reporting identification of a substance that activates the first-line defense system against infection inside the nose. They describe effects of a synthetic form of a natural substance found in bacterial cell walls in ACS' journal Molecular Pharmaceutics.
David C. Jackson and colleagues explain that the body's so-called innate immune system forms a first-line defense system against respiratory diseases like influenza A — which causes ...
Record 4.02 billion prescriptions in United States in 2011
2012-09-12
People in the United States took more prescription drugs than ever last year, with the number of prescriptions increasing from 3.99 billion (with a cost of $308.6 billion) in 2010 to 4.02 billion (with a cost of $319.9 billion) in 2011. Those numbers and others appear in an annual profile of top prescription medicines published in the journal ACS Chemical Neuroscience.
Journal Editor-in-Chief Craig W. Lindsley analyzed data on 2011 drugs with a focus on medications for central nervous system (CNS) disorders. So-called antipsychotic medicines — including those used to ...
New analysis of drinking water-related gastrointestinal illness
2012-09-12
The distribution system piping in U.S. public water systems that rely on non-disinfected well water or "ground water" may be a largely unrecognized cause of up to 1.1 million annual cases of acute gastrointestinal illness (AGI), involving nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, scientists are reporting. Their study in ACS' journal Environmental Science & Technology concludes that such illnesses may become more of a problem as much of the nation's drinking water supply system continues to age and deteriorate.
Frank J. Loge, Mark A. Borchardt and colleagues explain that more than ...
Russia fails to grasp democratic ideals
2012-09-12
EAST LANSING, Mich. — The brutally repressive Soviet Union Vladimir Shlapentokh left behind 33 years ago may have opened its borders to the world, but today's Russia has become wracked with greed, corruption and mass emigration that threaten the nation's future.
So argues Shlapentokh, a Michigan State University sociologist, in the academic journal Communist and Post-Communist Studies.
"As Russia's plight shows, the assumption that openness and liberalization automatically promote democracy and guarantee it will function turned out to be wrong," Shlapentokh said. "It ...
Himalayan glaciers retreating at accelerated rate in some regions but not others
2012-09-12
WASHINGTON -- Glaciers in the eastern and central regions of the Himalayas appear to be retreating at accelerating rates, similar to those in other areas of the world, while glaciers in the western Himalayas are more stable and could be growing, says a new report from the National Research Council.
The report examines how changes to glaciers in the Hindu Kush-Himalayan region, which covers eight countries across Asia, could affect the area's river systems, water supplies, and the South Asian population. The mountains in the region form the headwaters of several major ...
Math anxiety causes trouble for students as early as first grade
2012-09-12
Many high-achieving students experience math anxiety at a young age — a problem that can follow them throughout their lives, new research at the University of Chicago shows.
In a study of first- and second-graders, Sian Beilock, professor in psychology, found that students report worry and fear about doing math as early as first grade. Most surprisingly math anxiety harmed the highest-achieving students, who typically have the most working memory, Beilock and her colleagues found.
"You can think of working memory as a kind of 'mental scratchpad' that allows us to 'work' ...
Stress hormones: Good or bad for posttraumatic stress disorder risk?
2012-09-12
Philadelphia, PA, September 12, 2012 – Glucocorticoids, a group of hormones that includes cortisol, are considered stress hormones because their levels increase following stress. When their relationship to stress was first identified, it was shown that the release of cortisol prepared the body to cope with the physical demands of stress. Subsequently, high levels of cortisol were linked to depression and other stress-related disorders, giving rise to the hypothesis that high levels of cortisol on a long-term basis may impair the psychological capacity to cope with stress. ...
New model could help fill data gap in predicting historical air pollution exposure
2012-09-12
MEDFORD/SOMERVILLE, MASS. – In a study that analyzed relationships between air quality and unemployment levels, a Tufts University researcher has developed a new statistical model that retrospectively estimates air pollution exposure for previous time periods where such information is not available.
Mary Davis, an associate professor of urban and environmental policy and planning at Tufts University School of Arts and Sciences, analyzed traffic-related air pollution levels and unemployment rates in four separate regions of California for which extensive air monitoring ...
Amazing diversity documented in national park
2012-09-12
JEJU, REPUBLIC OF KOREA (September 12, 2012) – A remote park in northwest Bolivia may be the most biologically diverse place on earth, according to the Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS), which helped put together a comprehensive list of species found there. The announcement was released at the IUCN World Conservation Congress, an international gathering of conservationists meeting through Sept. 13 in Jeju, South Korea.
The list, published in a compendium by the Bolivian Park Service (SERNAP) and funded by WCS, shows that Madidi National Park contains 11 percent of ...
Popular pain-relieving medicines linked to hearing loss in women
2012-09-12
BOSTON, MA—Headache? Back pain? At the first sign of pain, you might reach for a pain-relieving medicine to sooth your bodily woes.
Analgesics are the most frequently used medications in the United States and are commonly used to treat a variety of medical conditions.
But although popping a pill may make the pain go away, it may do some damage to your ears.
According to a study by researchers at Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH), women who took ibuprofen or acetaminophen two or more days per week had an increased risk of hearing loss. The more often a woman took ...
GPs using unreliable websites for tinnitus information, study finds
2012-09-12
GPs are not always using the most comprehensive and reliable online resources to support them in treating patients with the debilitating hearing condition tinnitus, researchers have found.
The study looked at the 10 main websites used by GPs to get information on clinical practice and found that the two best websites for assessing or managing tinnitus — Map of Medicine and the British Tinnitus Association (BTA) — were rarely used by family doctors, with only two per cent logging on to access their pages.
The research, which involved a team of experts from The University ...
Study examines thoughts and feelings that foster collaboration across cultures
2012-09-12
NEW YORK -- September 12, 2012 -- The musician Paul Simon came to fame collaborating with his childhood friend Art Garfunkel, yet launched another chapter with his Graceland album, collaborating with musicians from Soweto. Ratan Tata made his name expanding his family's firms in India, yet in recent decades has reached even greater success helping foreign firms such as Daewoo and Jaguar find new markets.
Whether artists, entrepreneurs, or executives, some individuals are especially able to bridge cultural gaps and leverage foreign ideas and opportunities. Why can some ...
Self-control may not be a limited resource after all
2012-09-12
So many acts in our daily lives – refusing that second slice of cake, walking past the store with the latest gadgets, working on your tax forms when you'd rather watch TV – seem to boil down to one essential ingredient: self-control. Self-control is what enables us to maintain healthy habits, save for a rainy day, and get important things done.
But what is self-control, really? And how does it work?
In a new article in the September 2012 issue of Perspectives on Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science, researchers Michael Inzlicht ...
How is grief unique to young adults with cancer?
2012-09-12
New Rochelle, NY, September 12, 2012—The life disruption and losses experienced by young adults battling advanced cancer can result in a unique burden of grief that is too often overlooked, as described in an article in Journal of Adolescent and Young Adult Oncology (JAYAO), (http://www.liebertpub.com/JAYAO) a multidisciplinary peer-reviewed publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. (http://www.liebertpub.com) JAYAO is the Official Journal of the Society for Adolescent and Young Adult Oncology. The article is available free online at the JAYAO (http://www.liebertpub.com/JAYAO) ...
New clinical guidelines for managing hypothyroid disease presented in Thyroid Journal
2012-09-12
New Rochelle, NY, September 12, 2012—New evidence-based guidelines have been released for the diagnosis and treatment of hypothyroidism, a complex disease caused by an underactive thyroid gland that cannot produce enough thyroid hormone. These updated clinical recommendations are published in Thyroid (http://www.liebertpub.com/thy), a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers (http://www.liebertpub.com). The new guidelines (http://online.liebertpub.com/doi/pdfplus/10.1089/thy.2012.0205), developed jointly by the American Thyroid Association (ATA) (http://www.thyroid.org) ...
With food insecurity rising in US, SNAP benefits should be left alone
2012-09-12
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — In a time of record-high food insecurity rates in the U.S., cutting the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (the former Food Stamp Program) is the wrong approach to fighting hunger, says a University of Illinois economist who studies the efficacy of food assistance programs on public health.
Whether it's some Republicans who have proposed modifying funding, or some Democrats who have proposed restricting what kind of food beneficiaries are allowed to buy, restructuring SNAP would likely only lead to more food insecurity, says Craig Gundersen, a ...
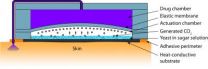
Body heat, fermentation drive new drug-delivery 'micropump'
2012-09-12
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – Researchers have created a new type of miniature pump activated by body heat that could be used in drug-delivery patches powered by fermentation.
The micropump contains bakers yeast and sugar in a small chamber. When water is added and the patch is placed on the skin, the body heat and the added water causes the yeast and sugar to ferment, generating a small amount of carbon dioxide gas. The gas pushes against a membrane and has been shown to continually pump for several hours, said Babak Ziaie, a Purdue University professor of electrical and computer ...
Hearing impaired ears hear differently in noisy environments
2012-09-12
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - The world continues to be a noisy place, and Purdue University researchers have found that all that background chatter causes the ears of those with hearing impairments to work differently.
"When immersed in the noise, the neurons of the inner ear must work harder because they are spread too thin," said Kenneth S. Henry, a postdoctoral researcher in Purdue's Department of Speech, Language and Hearing Sciences. "It's comparable to turning on a dozen television screens and asking someone to focus on one program. The result can be fuzzy because these ...
Planets can form in the galactic center
2012-09-12
At first glance, the center of the Milky Way seems like a very inhospitable place to try to form a planet. Stars crowd each other as they whiz through space like cars on a rush-hour freeway. Supernova explosions blast out shock waves and bathe the region in intense radiation. Powerful gravitational forces from a supermassive black hole twist and warp the fabric of space itself.
Yet new research by astronomers at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics shows that planets still can form in this cosmic maelstrom. For proof, they point to the recent discovery of a ...
Improved nanoparticles deliver drugs into brain
2012-09-12
The brain is a notoriously difficult organ to treat, but Johns Hopkins researchers report they are one step closer to having a drug-delivery system flexible enough to overcome some key challenges posed by brain cancer and perhaps other maladies affecting that organ.
In a report published online on August 29 in Science Translational Medicine, the Johns Hopkins team says its bioengineers have designed nanoparticles that can safely and predictably infiltrate deep into the brain when tested in rodent and human tissue.
"We are pleased to have found a way to prevent drug-embedded ...
Newly discovered letters and translated German ode expand Texas link to infamous Bone Wars
2012-09-12
In the late 1800s, a flurry of fossil speculation across the American West escalated into a high-profile national feud called the Bone Wars.
Drawn into the spectacle were two scientists from the Lone Star State: geologist Robert T. Hill, now acclaimed as the Father of Texas Geology, and naturalist Jacob Boll, who made many of the state's earliest fossil discoveries.
Hill and Boll had supporting roles in the Bone Wars through their work for one of the feud's antagonists, Edward Drinker Cope. A new study by vertebrate paleontologist Louis L. Jacobs at Southern Methodist ...
[1] ... [5989]
[5990]
[5991]
[5992]
[5993]
[5994]
[5995]
[5996]
5997
[5998]
[5999]
[6000]
[6001]
[6002]
[6003]
[6004]
[6005]
... [8807]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.