Waterford Dentist Introduces New Dentist to His Practice
2012-08-08
Dr. Bruce Roach, Waterford, MI dentist, is excited to introduce Dr. Hyden Choi to his patients. Dr. Choi has joined the staff at Dental 1 and will work with Dr. Roach to provide the best possible care to their patients.
"I'm excited to welcome Dr. Choi to our practice. He is extremely well qualified and will fit in great with our staff here. In addition, he brings some skills in implant placement and periodontal surgery to our practice that we did not previously offer. I know all of our patients will be very happy with their experience with Dr. Choi," said ...
Fort Lauderdale Dentist Offers Mobile Version of Her Website
2012-08-08
Dr. Julia Neuls, cosmetic dentist in Fort Lauderdale, is excited that her practice is offering a mobile version her comprehensive dental website. The mobile site is designed to be viewed on smartphone and tablet devices.
"I'm very happy that we are able to offer a mobile version of our website. I know that many of our patients utilize their phones to get on the Internet frequently and I'm happy that they will now be able to easily access our website on these devices. I hope that any of our patients that use smartphones or tablets will spend some time exploring our ...
Sterling Heights Dentist Uses Social Media to Reach Out to Patients
2012-08-08
Dr. Michael Young, Sterling Heights dentist, and his staff have been maintaining and updating a Facebook and Twitter account, as well as frequently updating their practice's blog. Dr. Young hopes that the increased online presence will continue to lead to more communication between him and his patients.
"I'm very happy that our practice has been able to jump into the world of social media with our Facebook and Twitter accounts. We have had a lot of fun with them and it's been great to interact with our patients online. I hope all of our patients take some time ...
Dentist in Ellicott City, MD Shares Patient Reviews Through Interactive Website
2012-08-08
Knowing about previous patients' experiences at a dental office are important to ensure patients will receive the care they need. Dr. Ray Becker, dentist in Ellicott, MD, is happy to share dozens of reviews from his patients, showcasing their experience while in his office. As a five-star dentist, each review further provides why so many patients would refer their friends and family to Dr. Becker, Ellicott City, MD dentist, for their dental care.
"I thoroughly enjoy hearing what my patients have to say about their time spent in my office because it allows me to ...
Bolingbrook Dentist Invites Patients to Review Bolingbrook Dental Care Online
2012-08-08
To help improve Bolingbrook Dental Care, Dr. Rani Seeth, Bolingbrook dentist, invites her patients to leave reviews of their experience while receiving treatment in her office. Patients are encouraged to leave reviews through the practice's Google page to offer Dr. Seeth insight into their thoughts concerning their dental care. With these reviews, Dr. Seeth and her team of dental professionals can provide exceptional service.
"I always enjoy hearing what my patients have to say about their treatment and time spent in my office. By offering patients a chance to ...
Dentist in Milpitas, CA Uses The Latest in Technology to Provide Quality and Comfort
2012-08-08
From the online website for Montague Dental Excellence to the office's many advancements, Drs. Nick Khoury and Steven Kolnes, dentists in Milpitas, CA, offer their patients the best ways to receive quality dental health care. Through their website, Drs. Khoury and Kolnes, Milpitas sedation dentists, are pleased to introduce online appointment requests for the easiest way to seek dental care from Montague Dental Excellence.
From routine cleanings to Invisalign in Milpitas, patients can visit the website for Montague Dental Excellence at http://www.montaguedentalexcellence.com ...
Baltimore Cosmetic Dentist Offers Interactive Website For Increased Dental Knowledge
2012-08-08
Patients can receive valuable information on an array of dental topics and information about Dr. K. Michael Murphy & Associates through the practice's valuable website. Dr. K. Michael Murphy, Baltimore cosmetic dentist, created an interactive website to offer patients a way to gain insight and knowledge into various dental topics and further information about the practice and its Baltimore dentists.
"Creating a website for my practice was essential. Today, majority of my patients are constantly on the Internet-whether on their phone, or their work or home computer. ...
Advanced Foot and Ankle Care of Memphis, LLC Launches Mobile Website
2012-08-08
In order to offer patients instant access to important information on Advanced Foot & Ankle Care of Memphis, LLC, and various podiatric topics including Memphis, TN CoolTouch laser for toenail fungus treatment, Dr. Nathan Lucas is happy to announce the launch of the practice's mobile website. Dr. Lucas chose to create a mobile website for Advanced Foot & Ankle Care of Memphis, LLC in order to provide patients who are constantly on the go an easier way to access the information they need.
Eliminating the slow loading traditional websites, mobile websites offer ...
Charlotte, NC Podiatrist Completes Board Recertification For Foot Surgery
2012-08-08
Dr. Scott Basinger, Charlotte, NC podiatrist, maintains the highest levels of accreditation and pursues ongoing education to remain abreast of the latest trends in podiatry. Recently, Dr. Basinger took and passed his board recertification for foot surgery. By receiving his board recertification in foot surgery, Dr. Basinger ensures that he has completed appropriate training, successfully performed a diverse range of podiatric surgical procedures, and passed an extensive written and oral examination.
The importance of board certification is reflected in trends by hospitals, ...
TeamSupport.com Boosts Business for Talon Data Systems
2012-08-08
TeamSupport.com (http://www.TeamSupport.com), the popular provider of web-based customer support and help desk software solutions, today acknowledged a successful deployment of the company's Enterprise Edition by Talon Data Systems, Inc., a leading value-added integrator of high speed networking and storage systems.
The rapid growth company has seen annual revenue double in recent years, said Mike Bott, head of engineering. "We implemented TeamSupport just ahead of a huge managed services contract for a major new client; they had a hard requirement for a customer ...
Mach III Introduces New Ultra-Low Torque Clutches and Brakes at Labelexpo Americas
2012-08-08
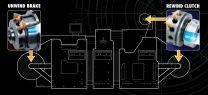
Mach III Clutch, Inc. will showcase nineteen new ultra-low torque additions to the SENSIFLEX rewind clutch and unwind brake line at Labelexpo Americas, September 11-13, 2012. Used to maintain tension on a web by holding back the unwind shaft and/or driving the rewind shaft, SENSIFLEX brakes and clutches deliver smooth slip performance over the range of torque output required. The new SENSIFLEX Ultra-Low torque models are ideal for challenging label printing and narrow web processing conditions where web tensions are low and the range of torque output required from the brake ...
Allen Samuels Dodge Chrysler Jeep Ram Hyundai Will be Closed on Sunday And Open on Saturday Starting August 11, 2012
2012-08-08
After over 15 years of being open on Sunday, Allen Samuels Dodge Chrysler Jeep Ram Hyundai located in Fort Worth will be open on Saturday starting August 11th.
"We are excited to start serving our customers and community on Saturday beginning August 11th. We believe that by being open on Saturday it will make it more convenient for customers to shop. Our Saturday hours will be longer than they were on Sunday. Our sales hours will be from 9:00am to 8:00pm. Service will also be open from 7:30am to 4:00pm so that customers can more conveniently get maintenance and ...
Preventative Dentistry
2012-08-08
Your dental health and systemic health rely on preventative dentistry. The primary focus of general dentistry is the prevention of common oral health issues, but you can't solely rely on your dentist to keep your teeth and gums clean. You must take responsibility at home as well.
Preventative Dentistry at Home
Preventing tooth decay and gum disease starts with a daily oral hygiene routine. Your routine should include:
- Brushing your teeth after every meal
- Flossing at least once a day, but preferably morning and night
Brush your teeth with a fluoride toothpaste ...
Choosing a Divorce Attorney
2012-08-08
Amicability during divorce proceedings is preferable, but not always possible. When it isn't possible to be amicable, your choice of divorce attorneys can have a significant impact on the fairness of the proceedings. When you try to represent yourself or choose inadequate or inexperienced representation, you may be surprised to find out how much you stand to lose.
An aggressive and dedicated divorce attorney will be essential to an equitable outcome. Laws vary from state to state, making it important that you choose a lawyer who has sufficient experience in family law ...
Benefits of Professional Teeth Whitening
2012-08-08
There are a variety of ways to whiten your teeth. Although there are many over-the-counter products readily available, professional teeth whitening has several advantages, chiefly high-quality results reached within a short period of time. Over-the-counter products cost less, but lack the supervision and quality control of a cosmetic dentist.
In-Office Teeth Whitening Performed by a Cosmetic Dentist
The benefits of in-office teeth whitening overseen by your cosmetic dentist or a dental assistant include:
- Considerable color change within one hour
- Professional ...
Nighttime Driving and Car Accidents
2012-08-08
Nighttime driving presents motorists with a new set of circumstances that can quickly become dangerous if you are not careful. Your ability to perceive distance and make good driving judgments is significantly impaired at night, since the human eye requires light to see. Because of this, nighttime driving is a top contributor to car accidents.
The Importance of Visual Clarity When Driving
Around 95% of all decisions made by a driver are based on visual perception. Your eyes are still capable of seeing in limited or dim light, but the combination of road lights and ...
Tough New Law Will Impact All Virginia Drivers Convicted of Drunk Driving
2012-08-08
Tough New Law Will Impact All Virginia Drivers Convicted of Drunk Driving
Beginning on July 1, 2012, one of the nation's toughest drunk driving laws took effect in Virginia. The new law requires all drivers convicted of driving under the influence of alcohol who receive restricted driver's licenses to install ignition interlock devices, also called IIDs, in their vehicles. Prior to this law taking effect, only first-offense drunk drivers with a blood-alcohol content of 0.15 percent or higher and repeat offenders were required to install ignition interlock devices in ...
Divorce and Property Division in Illinois
2012-08-08
Divorce and Property Division in Illinois
The decision to divorce is a difficult one, and conversations focused on division of property can often be the most contentious. Emotions can easily tangle with finances when attempting to have discussions regarding who can keep the family home and how savings that were carefully set aside are split.
Preparing for these conversations with a basic understanding of state law can ease the confusion associated with who gets what.
State Law: Marital v. Nonmarital Property
Illinois law views property as either marital or nonmarital. ...
Latest IRS Data Book Details Extent of Audit Activity
2012-08-08
Latest IRS Data Book Details Extent of Audit Activity
People who face the challenge of a pending IRS audit turn to tax attorneys not only for advice and representation, but also for immediate peace of mind. Questions about audits, IRS timelines and strategies for repayment are important, but so is the reassurance that a taxpayer has legal rights to due process when federal tax investigators come knocking.
The latest Internal Revenue Service Data Book details a wide variety of IRS activities from fiscal year 2011, ranging from enforcement and collection activities ...
$78 Million For Delayed C-Section Resulting In Lifelong Injury: A Breakdown Of PA Damages
2012-08-08
Victoria Upsey arrived at Pottstown Medical Center 36 weeks into her pregnancy. She was showing signs of placental abruption - a medical term for the placenta detaching prematurely from the lining of the uterus. An ultrasound was ordered to determine the health of the yet-unborn baby Upsey was carrying, but the out-of-date equipment was unable to locate a heartbeat.
Upsey was informed that her baby had died in utero. In disbelief, she argued with her medical care team, telling them that she could still feel her baby kicking inside of her. Over an hour later, after an ...
Boating Under The Influence In North Carolina
2012-08-08
Boating Under The Influence In North Carolina
With more than 37,000 miles of waterways and warm temperatures extending well through the summer months, North Carolina may be a boater's paradise. Relaxing on the pontoon after a hard week's work, drinking a beer while aboard a fishing boat and anchoring out or floating around while having couple of cocktails can lead to trouble with the law for young professionals, military personnel, college students and others who are not aware of North Carolina laws related to drinking and boating.
According to Operation Dry Water, ...
Wading Through the Complex K-1 Visa Process Requires Legal Assistance
2012-08-08
Wading Through the Complex K-1 Visa Process Requires Legal Assistance
For most couples, the engagement period is a happy time. Unfortunately, the visa process for fiances from different countries is complex and can add stress to a couple's marriage preparations. Fortunately, guidance from an experienced immigration attorney can help the process go more smoothly.
K-1 and K-2 Visas Provide Entry for Foreign-Citizen Fiance(e)s and Their Dependents
For a US citizen and his or her foreign-citizen fiance(e) to marry and reside in the United States, the foreign citizen ...
Medical Debt and Bankruptcy
2012-08-08
Medical Debt and Bankruptcy
Medical debt becomes an unfortunate reality when unplanned emergencies happen. No one expects or plans to be diagnosed with a horrible illness or serious injury, but sadly these events become a reality for many Americans each year.
The debt from medical expenses can push a household further into financial distress, but these undesirable circumstances can be managed. In fact, bankruptcy may provide a chance for a fresh start.
Damages to Credit from Medical Debt
At first glance, medical debt appears different from any other type of ...
Law Offices of Scott Warmuth Have Expanded Personal Injury, Workers Compensation Departments
2012-08-08
The Law Offices of Scott Warmuth have more than a quarter century's worth of legal knowledge and expertise in personal injury, immigration and civil litigation and is dedicated to providing quality service to their clients and upholding their civil rights. Due to the increased demands by their clients and their dedication to providing the best legal services, the Law Offices of Scott Warmuth have expanded their personal injury and workers' compensation departments.
The expansion includes increased space at their San Gabriel office location and the addition of more dedicated ...
Emerging Markets: Invest in Africa, Says Currencies Direct
2012-08-08
Foreign exchange specialists Currencies Direct know better than most the countries that are outperforming the global average in terms of economic growth. Not only does it offer a currency exchange service using the latest exchange rates it also offers advice to consumers and businesses about buying abroad and making frequent international payments. It is well placed to advise on which countries in Africa offer the best investment potential and it aims to highlight the benefits of investing in this growing region.
Currencies Direct points to a recent estimate from the ...
[1] ... [6204]
[6205]
[6206]
[6207]
[6208]
[6209]
[6210]
[6211]
6212
[6213]
[6214]
[6215]
[6216]
[6217]
[6218]
[6219]
[6220]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.