West Hollywood Cosmetic Dentist, Dr. Ghasri, is Now Offering a Summer Special for Chairside Teeth Whitening Treatments
2012-07-30
For individuals that would like a bright and vibrant smile, it may often seem that achieving lustrous teeth is a lost cause. It can be exceedingly difficult to remove staining and discoloration, even for those that adhere to a strict regime of dental hygiene habits within their home. This is why many local patients are now turning to West Hollywood cosmetic dentist, Poneh Ghasri DDS, in order to receive effective chairside whitening for as low as $89 this summer.
Many patients are surprised to find that many of the foods and beverages that they ingest will gradually ...
Northridge Dental Group is Now Offering Discounted Prices on All CT Scans
2012-07-30
Many individuals grow up throughout the years believing that a bright and healthy smile will be the result of brushing and flossing multiple times a day. These habits are essential when it comes to great oral health and vibrant teeth, but they will not always be enough to completely remove one's chances of developing some common health conditions that exist today. This is why Northridge Dental Group is now offering discounts on C.T. scans, one of the most effective tools that is used detect and treat serious oral health complications in their earliest stages. Visit YourNorthridgeDentist.com ...
WoodMaxx Power Equipment is Now Providing Customers with Hassle Free Financing on All Products
2012-07-30
For those that are ready to begin some of the larger projects on their property, they will need affordable tools that will stand up to heavy-duty use and continue working year after year. While this type of maintenance may seem like an expensive and ongoing process, those that have access to some of the leading products will be able to turn these laborious jobs into quick and painless tasks. The one trusted equipment manufacturer, WoodMaxx Power Equipment, is now offering hassle-free financing on all of their products, including wood chipper shredders, to get customers ...
Injured In Pennsylvania? Beware What You're Posting On Facebook, Twitter; A Word Of Warning From The Injury Attorneys At MyPhillyLawyer
2012-07-30
Social media is part of everyday life. At Silvers, Langsam & Weitzman, P.C., we maintain a blog, make status updates on Facebook and Tweet regularly. We understand that social media is a common way to communicate with others - whether you're having a good day, a bad day, are sick or injured.
We also understand that when something happens - a car accident, a workplace injury or even a slip and fall - your first instinct might be to post about it on a social media website. But, as experienced personal injury attorneys who fight for the rights of injured people throughout ...
NYC Personal Injury Lawyer Comments on the Limitations of Wrongful Death Laws in New York
2012-07-30
Attorney Jeffrey Lichtman of Trolman, Glaser & Lichtman in New York City says that the recent tragic death of a 12-year-old boy brings to light how inadequate New York state's wrongful death statutes are when it comes to seeking justice.
According to the New York Times, the boy cut his arm in the school gymnasium while diving for a basketball. Less than three days later, he was dead. What emergency room physicians thought was an upset stomach and dehydration turned out to be sepsis. Hospital records noted that the boy died from severe septic shock brought on by ...
Kalamazoo Clients Get Results from Aggressive Defense
2012-07-30
Kalamazoo-based Kalamazoo criminal defense law firm Aggressive Criminal Defense Law Firm- a division of Willis Law prevails for another of their clients.
At first, their client faced a charge for failure to stop at an accident with property damage. With the help of an aggressive defense, the client's charge was dismissed and avoided being placed on their criminal record.
Michigan law states that anyone involved in an accident must take the necessary steps to locate and notify the owner or person in charge of the property of that fact. Leaving the scene of the accident ...
Video Release: How to Win With Medicare Supplemental Insurance
2012-07-30
Centaur Medicare Solutions LLC., an independent insurance agency that helps Baby Boomers find low cost Medigap insurance, released a video entitled "How to Win With Medicare Supplemental Insurance". The short three minute long video will help those who are retiring and shopping for Medicare insurance for the first time from making a few simple mistakes. From using the right kind of Medigap insurance agent to how best to shop for Medicare supplemental insurance quotes on the Internet, this video will give it to you straight.
Centaur Medicare Solutions LLC. (CMS) ...
Ground Force Environmental Announces Emergency Spill Response Division
2012-07-30
In the event of an emergency, Ground Force staff will be on-site within 4 hours of receiving the call.
We will assess, contain and clean up the spill before it can become an environmental catastrophe, and will also inform The Spills Action Centre (SAC), as required by Part X of the Environmental Protection Act.
After the initial response, it is imperative to have a consultant on-site to work alongside Ground Force's Environmental Remediation Crew to delineate the extent of the spill and to take samples to determine if the spill has impacted the soil or groundwater ...
EE Technologies' Expansion to Three Shifts
2012-07-30
EE Technologies is excited to announce expansion to three (3) shifts at its Reno, Nevada manufacturing plant. This change comes in preparation for the August installation of its new Assembleon iFlex, an intelligent and flexible pick & place solution. Having three shifts will increase capacity and flexibility increasing EE Technologies responsiveness to customers.
EE Technologies President Sonny Newman shares, "Serving our customers is our number one priority. We take pride in our employee's commitment to continually demonstrate flexibility and loyalty. This ...
Plackers Introduces Flossing Solution for Tight Teeth, Sensitive Gums
2012-07-30
Plackers(R), makers of the first disposable flosser, introduces its newest specialty product to its innovative line of flossers. Patent-pending GentleSlide(R) is now ready to ship to retailers nationwide.
Featuring a high-performance, shred-resistant polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) floss technology, GentleSlide makes flossing between tight teeth easy and comfortable, and is gentle on sensitive gums. Cool mint flavoring gives a fresh, clean mouth feel.
"For 40 years, Plackers has been a leader in innovative, high quality consumer oral care products," said ...
The Race is On at CiCi's Pizza
2012-07-30
CiCi's Pizza kicks off its "Race for the CiCi's Cup" promotion today to get people to "Race into CiCi's Today," featuring a limited edition Coca-Cola Racing Family beverage cup and dine-in and To Go specials.
Through Oct. 14, guests can race into participating CiCi's locations for "$5 Faves" each Monday-Thursday. During Happy Hour from 2-4 p.m., an adult buffet is just $5, including a regular drink. Guests also can take home a large, one-topping To Go pizza for just $5 anytime Monday-Thursday.
The 32-ounce limited edition Coca-Cola Racing ...
Turn Your Old Mobile Phone Into Money with BingoBongo.ca
2012-07-30
BingoBongo.ca has just launched in Canada. This revolutionary new website allows customers to log on and get an instant cash value for their mobile devices. If the customer feels the price is fair they are one-click away from selling their phone to BingoBongo.ca, using the easiest method in the country. A free postage paid envelope will be supplied and the customer simply needs to drop their phone in the mail to receive payment.
Not only will the customer get quick cash for their old phones and tablets, but so too will they avoid sending the technology to Canadian landfills. ...
LifeShield Security Releases Video Featuring Soon-to-Launch New LifeView Product
2012-07-30
LifeShield Security today announced a new video introducing its new LifeView product designed with a state-of-the-art interface that grants users full access to every feature and benefit of LifeShield through any smartphone, computer or tablet device.
"We developed the new LifeView in concert with customer feedback and usage data to ensure we are delivering exactly what the customers want and in the way they want to use it," said Evan Kramer, SVP Interactive Marketing, LifeShield. "We are as much a technology company as we are a home security company, ...
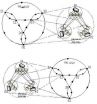
A new high performance and fault-tolerant datacenter network for modular datacenters was proposed
2012-07-29
A modular datacenter network (MDCN) is the key component in building mega-datacenters. Huang Feng, Li Dongsheng, and their group from the National Key Laboratory of Parallel and Distributed Processing, School of Computers, National University of Defense Technology present a novel hybrid intra-container network for a modular datacenter (MDC), called SCautz, together with a suite of routing protocols. SCautz is able to provide high network throughput for various traffic patterns, and achieves graceful performance degradation when failures occur and increase. Their work, entitled ...
Shock Consult Sponsors 'Salon of the Year, Classic' at Kitomba Business Awards
2012-07-29
From the Desk of Malcolm Gibbons, Managing Director, Shock Consult Ltd.
I'm thrilled to announce that Shock Consult is the sponsor of the prestigious award, 'Salon of the Year, Classic' at the Kitomba/NZARH/HITO Business Awards where winners will be announced at the Wellington Town Hall on Sunday 11th November 2012.
The Kitomba NZARH Business Awards are an annual event that recognizes top performing salons in New Zealand and is sponsored by industry leaders. The Business Awards are part of the Industry Awards weekend in collaborating with HITO (Hairdressing Industry ...
Austin Welcomes Little Fattys to the Downtown Food Truck Scene
2012-07-29
The brainchild of the mother-in-law/son-in-law team of Chela Stoklosa and Chris Williamson, Little Fattys blends traditional family recipes with bold, international fillings to create gorditas that are anything but conventional. Top-sellers include the Pork Me Pull Me - slow roasted pork and balsamic onion marmalade - and the Chicken Envy - shredded chicken in a green chile sauce.
"It's been a tremendously rewarding experience starting this business with my mother-in-law," Chris Williamson said. "We've been able to combine our individual cooking talents ...
Pro SEO Advice is Now Offering SEO Outsource Service: The Service is Free With no Hidden Charges.
2012-07-29
Businesses all over the world ask the question "Why do I need a Twitter or Facebook page? Who cares about that stuff anyway? I just want to rank higher, isn't optimizing our web pages enough?"
"If you want to be even better and rank higher than your competitors it's a good idea to make sure you're covering every base and doing what they might not know about yet. If they are already doing it, then do it better. The world's largest brands are using social media - Yes, they have Twitter and Facebook accounts - And there is reason.
Pro Seo Advice, an Internet ...
Mixed Verdict on Foreclosure Suit for Colorado Springs Council President
2012-07-29
Mixed Verdict on Foreclosure Suit for Colorado Springs Council President
Colorado Springs City Council President Scott Hente and his business partner Robert Ormston recently obtained a mixed verdict in a real estate lawsuit with an ANB Bank affiliate over 44 acres of property in northeast Colorado Springs.
The two former Air Force officers purchased the land with an $8.8 million loan in 2005, which they personally guaranteed. The officers transacted the deal "on a handshake," their lawyer said in his opening statement, and "didn't worry about the fine ...
New Federal Law Bans Synthetic Drugs
2012-07-29
New Federal Law Bans Synthetic Drugs
It is hard to forget the story of the man who ate another man's face while allegedly under the influence of bath salts. It turns out that the attacker had no synthetic compounds in his system, but was only under the influence of marijuana. The federal government has not forgotten, and in early July, President Obama signed a bill that bans many synthetic drugs, including bath salts. As a result, an individual who possesses or sells synthetic drugs in Pennsylvania may face state and federal drug charges.
Is the Law Going to Make ...
Jo Ann Koontz Named to the Faculty of the 2012 Symposium for Financial Planning Professionals
2012-07-29
Jo Ann Koontz of the Koontz & Associates law firm in Sarasota, Florida, has been selected to serve on the faculty for the 2012 Florida Symposium for Financial Planning Professionals.
Scheduled for August 2-3 in Tampa, this annual symposium by the Financial Planning Association of Tampa Bay presents cutting-edge sessions on a wide variety of financial planning topics. Specific areas covered include retirement planning, elder care, health insurance, business planning and succession, and investments.
With a dual certification as an attorney and Certified Public ...
Dakota Dental Accommodates Summertime Dental Emergencies
2012-07-29
The Dakota Dental family dentists in Apple Valley, MN, are reminding Minnesotans to be careful with their teeth this summer because dental emergencies can quickly ruin an otherwise fun experience. One of the best ways to protect teeth is to schedule regular checkups and cleanings with family dentists such as your friends at Dakota Dental. It is also important to wear properly fitting protective gear, including a mouth guard, when participating in sports, in-line skating, or skateboarding. And never use teeth as a tool to open, pry, or cut things.
If dental emergencies ...
Got Vape Introduces "Hot" New PuFFit Portable Vaporizer.
2012-07-29
Got Vape has introduced a hot new vaporizer to the market called the PUFFit portable vaporizer. The PUFFit is a portable vaporizer manufactured by Discreet Vape (http://discreetvape.com/) of Hong Kong and distributed by Got Vape (www.gotvape.com) of CA. It went on sale on July 1, 2012. There was a significant amount of interest in the unit before it came out as several thousand units were sold during the pre-order period.
The PUFFiT portable vaporizer features a discreet and lightweight design, and measures only 3.5 Inches in Height and 1 1/8 Inches in width, weighting ...
Belle Chevre's Tasia Malakasis Launches www.tasiastable.com
2012-07-29
Tasia Malakasis, president at Belle Chevre and renowned lifestyle expert, has launched a new website at http://www.tasiastable.com. The launch of the new website coincides with the upcoming release of Tasia's first cookbook, Tasia's Table: Cooking with the Artisan Cheesemaker at Belle Chevre. It is to be released in September 2012 by New South publishers. Signed copies will be available for purchase exclusively on http://www.tasiastable.com.
The website, with its clean, bright look, will serve as a gathering place for Tasia's recipes, entertaining tips, and information ...
Eight Young Stars Earn Fall 2012 Scholarships To John McEnroe Tennis Academy
2012-07-29
Eight boys and girls ranging in age from 7-16 were introduced this week as winners of full or partial scholarships to the John McEnroe Tennis Academy (JMTA). Each were among approximately 170 participants ages 6-17 in an open tryout on July 21, and the eight were honored on-court on Wednesday night during the World TeamTennis matchup between the New York Sportimes and Washington Kastles at Sportime Randall's Island.
The eight winners were: Cameron Daniels, Oakland Gardens, 15, N.Y.; Diane McCready, 11, Brooklyn, N.Y.; Leonte Wilder, 11, Plainfield, N.J.; Sean Wei, 12, ...
Women's Business Development Center 'Teaming for Contracts' Workshop August 9 in Clayton, Missouri
2012-07-29
Women Business Enterprises (WBEs) and established business owners seeking to do business with corporations and government agencies should attend, "Teaming for Contracts," a regional workshop presented by the Women's Business Development Center (WBDC).
The event will be held on Thursday, August 9, from 9 a.m. to 12 p.m., at Rubin Brown, One North Brentwood Boulevard, in Clayton, MO. Host sponsor is Rubin Brown.
Teaming for Contracts is designed for women-owned businesses in all industries who seek to grow their business and expand their capacity through partnerships ...
[1] ... [6217]
[6218]
[6219]
[6220]
[6221]
[6222]
[6223]
[6224]
6225
[6226]
[6227]
[6228]
[6229]
[6230]
[6231]
[6232]
[6233]
... [8803]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.