New model for treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder created
2011-09-16
A new model of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) that mirrors both symptoms of the disease and the timing of its treatment in humans has been created by University of Chicago researchers, according to a new study.
Using the model, researchers isolated a single neurotransmitter receptor in a specific brain region responsible for their model's OCD-like symptoms, offering new insight into the cause of the disorder. Further research with the model may point the way to new treatments for both OCD and autism, said Nancy Shanahan, PhD, lead author of the paper in Biological ...
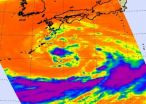
Tropical Storm Roke closing in on Kadena Air Base: Infrared NASA satellite imagery
2011-09-16
Tropical Storm Roke is showing some signs of intensification on NASA infrared satellite imagery, as areas of strong convection and very cold cloud tops were spotted. Kadena Air Base in Okinawa is now in Roke's sights and should be making preparations.
NASA's Aqua satellite flew over Roke yesterday and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument showed powerful convection building around the storm's center and over the northern edge. Meanwhile, dry air is wrapping into the low-level center from the southwest, and limiting cloud development.
Infrared imagery provides ...
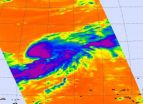
Infrared NASA satellite imagery confirmed newborn Tropical Storm Sonca
2011-09-16
Infrared satellite imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite yesterday showed powerful convection building in the low pressure area known as System 94W and provided forecasters with an inside look that the low was strengthening. System 94W did intensify and became Tropical Storm Sonca today.
Infrared imagery is gathered by the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies on NASA's Aqua satellite. It provides valuable information to forecast organizations such as the Joint Typhoon Warning Center and National Hurricane Center about cloud temperatures and heights and ...
CakeDecoratingTeacher.com Launches New Blog Site
2011-09-16
Cake Decorating Teacher's blog is dedicated to serving online viewers with a listing of easy to make recipes. Weekly blog posts include delicious dessert recipes at www.cakedecoratingteacher.com along with how to instructions for their readers convenience.
Life has never been this easy when it comes to finding free access to great baking recipes since the Internet and its listing of blog sites such as Cake Decorating Teacher. Posts can easily be viewed under the posts section of their website. To stay updated on the latest posts readers can subscribe to the blog's RSS ...
Iowa State astronomer: 'Beware of the wildlife, even in apparently quiet galaxies'
2011-09-16
AMES, Iowa – Even though a dwarf galaxy clear across the Milky Way looks to be a mouse, it may have once been a bear that slashed through the Milky Way and created the galaxy's spiral arms, writes an Iowa State University astronomer in the journal Nature.
Curtis Struck, an Iowa State professor of physics and astronomy, uses a News & Views commentary in the Sept. 15 issue of Nature to add context and color to a study published in the same issue by a research team led by Chris W. Purcell of the University of Pittsburgh.
The Purcell group reports that the Sagittarius Dwarf ...
Team Massachusetts Competes in U.S. Department of Energy's 2011 Solar Decathlon with 4D Home Design
2011-09-16
After nearly two years of committed planning and design, the 2011 Solar Decathlon Team Massachusetts heads to Washington, D.C. where its completed "4D Home" will participate alongside 19 other collegiate entries in this year's competition. A unique dwelling that boasts both affordable and sustainable design elements, the "4D Home" is fully solar-powered, cost-effective and energy-efficient.
"Team Massachusetts showcases public higher education at its best. The creation of this self-sustaining home designed and developed by students at Massachusetts ...
4TH R Foundation: Science Has a Closed Mind on Wisdom - Wisdom is Super Mature Emotional Intelligence (Now Defined Within the Paradigm of Science); Wisdom Education is Emotional Intelligence Education
2011-09-16
From the very beginning our philosophers and scientists realized that the key to great societies was wisdom. They saw that wisdom was real and that if only they could figure out what it is and how to teach it; they would be able to create wise societies. Ever since the times of Aristotle till today, man has been trying to figure out wisdom by putting wisdom under the microscope. As wisdom is an innate property of the pure self it is a secondary entity; just like fragrance is a property of the flower. It is exactly like a symptom of a disease. So by putting wisdom under ...
Study update: Cancer information on Wikipedia is accurate, but not very readable
2011-09-16
PHILADELPHIA--It is a commonly held that information on Wikipedia should not be trusted, since it is written and edited by non-experts without professional oversight. But researchers from the Kimmel Cancer Center at Jefferson have found differently, according to a study published online Sept. 15 in the Journal of Oncology Practice.
Reassuringly, they found that cancer information found on a wiki was actually similar in accuracy and depth to the information on a peer-reviewed, patient-oriented cancer web site. There is one caveat, however: they found that the information ...
Study finds an increase of children accidentally poisoned with pharmaceuticals
2011-09-16
Cincinnati, OH, September 16, 2011 -- Pharmaceutical poisoning remains a common childhood injury, despite years of concerted prevention efforts, such as improved safe guards on packaging. Over half a million children are exposed to pharmaceuticals each year. A new study soon to be published in The Journal of Pediatrics attempts to understand this growing problem to aid in the progress of reducing the number of childhood injuries due to pharmaceutical poisoning.
Dr. Randall Bond and colleagues from Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center and the University of Cincinnati ...
Yuval Tal, Payoneer Founder to Speak at Take Charge Summit
2011-09-16
Yuval Tal, founder of the global electronic payment provider Payoneer, will speak at the Take Charge 2011 Digital Commerce Summit from September 13 to 14. The conference, which will take place in Airport City, Israel, will feature the most cutting-edge ecommerce creations and trends for vendors and affiliates.
Attendees can expect to have a global experience, with potential for boosting online sales, taking advantage of new marketing, and improving conversion rates. Vendors and affiliates also will have the opportunity to network, sell and discover products, participate ...
Number of children poisoned by medication rising dramatically, study says
2011-09-16
The number of young children admitted to hospitals or seen in emergency departments because they unintentionally took a potentially toxic dose of medication has risen dramatically in recent years, according to a new Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center study.
The rise in exposure to prescription products has been so striking that the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has established the PROTECT Initiative, intended to prevent unintended medication overdoses in children.
Randall Bond, MD, an emergency medicine physician at Cincinnati Children's, will ...
Investment Banker and Fine Arts Photographer Scott Mead Showcases His Works at the Royal Academy of Arts Summer Exhibition
2011-09-16
With over 20 years of dedicated work within the investment banking sector, Scott Mead has begun to showcase his artistic talents in a number of exhibitions, with his most recent works being exhibited at the Royal Academy of Arts Summer Exhibition.
Scott Mead's two photographs on display at the Summer Exhibition are an untitled piece and a piece entitled Evening Light. Evening Light was created in 1975 during Scott Mead's college years at Harvard College, when he studied under recognized American photographers William Eggleston, Emmet Gowin and Minor White. The photograph, ...
Total Family Dental Group Announces the Appointment of Maria Gomez to Its Full-Service Dental Practice
2011-09-16
Total Family Dental Group is delighted to announce the appointment of a new staff member, Maria Gomez, to its Torrance dental office. Maria has joined the group as treatment coordinator after spending 23 years with Village Family Dental in Torrance.
Maria has over 30 years' experience in the dental field and uses her considerable knowledge to guide patients through every step of the treatment process; coordinating treatment plans, insurance benefits and financial options. Maria was very happy with her previous employers, making friends among staff and patients alike ...
deVere Sponsors the Annual Geneva Charity Ball for Third Consecutive Year
2011-09-16
The Geneva Charity Ball is about "having a good time doing good". It takes place once a year with the prime aim of raising funds for a selected number of charities, while also leveraging the skills and passions of individuals in order to make things happen.
Senior Managing Partner for deVere Group Switzerland and Italy, Mr Paul Dodds, commented, "We are proud to have the opportunity to support a passionate committee this year who are working for a memorable cause. We are looking forward to a fun evening and hope to raise even more funds than last year!" ...
Mobile Internet Nearing 50% Worldwide But International Roaming Costs Remain High...With One Exception: abroadband.com
2011-09-16
The rise of Internet use on mobile devices has made it hard to forget data roaming charges. abroadband.com has alleviated this problem by offering a unique mobile roaming solution. Users of their service can now access broadband on their mobile devices at only EUR0.59 per megabyte of data.
A quick comparison of operators across the world illustrates the rarity of this type of flat rate service (source: BBC Website/Technology). abroadband was launched by Telekoms Austria earlier this year in February. The idea grew out of the unrest with high roaming charges that has ...
Yet Another Successful deVere Group WE Annual Advisers' Conference
2011-09-16
The event was spread out between the 1st and the 3rd of September and was aimed at providing Western Europe-based Financial Advisers with the latest financial planning knowledge, in order to help them continue providing the best possible financial advice to the deVere client.
The now-prestigious event included motivational talks; workshops from deVere's main partners including Close, JP Morgan Asset Management, Morgan Stanley, Generali International, Skandia International, Friends Provident, Prudential International and Sovereign; and also team-building exercises.
Mike ...
"100 Language Challenge for Interdependence" Launching as a Healing Antidote to 9/11...
2011-09-13
Webby Awards Founder and award-winning filmmaker Tiffany Shlain's new, globally crowd-sourced film, "A Declaration of Interdependence," featuring music by Moby and translations enabled by dotSUB, will be transformed into a multi-cultural celebration of interdependence in action, as volunteers from around the world translate the 4-minute film into 100 different languages.
The "100 Language Challenge for Interdependence," brought to you by dotSUB, Moxie Institute and the film Connected, will launch after the premier of "A Declaration of Interdependence" ...
Asvathaa Launches Facebook Social Game Karma Kingdom Allows Players to "Create Their Better World"
2011-09-13
Asvathaa Pte. Ltd., a Singapore based game development company has recently launched Karma Kingdom, an exciting quest driven online island game that can be played on Facebook. The tagline of the game, "Create Your Better World", best encapsulates the game on many levels. From an innovative non-linear user layout, an intrinsic positive message, to the opportunities afforded users to give to charities; the game is designed to lay new ground and direction for social games.
Asvathaa' s intention is to bring to the market a new generation of original games based ...
BookWhirl.com Partners with BlueInk for Book Review Combo
2011-09-13
Just eight days after BookWhirl.com launched their first book review package, the company will release another book review service today. To cap the third quarter of this year, BookWhirl.com joins BlueInk for a Book Review Combo service. For the past months, BookWhirl.com has become more dynamic in creating new products and services in strategizing book marketing campaigns.
As the years pass, book marketing services are becoming more innovative. For independent authors, getting their books reviewed is an effective way to gain publicity and increase their book's marketing ...
The Rainbow Dance Festival Debuts In Palm Springs
2011-09-13
The Rainbow Dance Festival starting on September 16 at the Riviera Resort & Spa in Palm Springs provides dance workshops, shows and evening parties in a fun and family-friendly environment for the LGBTQ community to dance, connect and celebrate.
"We're excited to introduce the Rainbow Dance Festival to the LGBTQ community. This festival provides a great environment for the LGBTQ community to invite their friends and family to learn new dance styles or enhance their dance skills," states Nitza Basoco, founder of Rainbow Dance Festival. "We've received ...
9/13/11 Wellness, Wholeness & Wisdom Radio Host, Psychologist Parthenia Izzard, CNHP rebroadcasts her interview with Wayne Dyer's Immaculee Ilibagiza, author of, Left to Tell: Discovering God.
2011-09-13
Every Tuesday evening at 8:00 PM Eastern Time, you can listen to Wellness, Wholeness & Wisdom radio with host Psychologist Parthenia Izzard, CNHP. We are now airing three nights a week, Tuesdays, Wednesdays, and Thursdays, at 8:00 PM ET on BlogTalkRadio. The program is archived within minutes of the live broadcast on the internet. On your computer go to http://www.amtherapies.com and click on the Radio link to listen to the show live online or on your phone! Program topics range from authors like Bishop Jordan, James Redfield, Immaculee Ilibagiza, and William Tiller ...
GeoReader, LLC to be at ION GNSS 2011 Conference as Bronze Medalist in USA Challenge.
2011-09-13
GeoReader , an app from GeoReader LLC, was named as a "top five" finalist in the USA Challenge of the European Satellite Navigation Competition. The founder of the company, David Moreau, will present the app at the upcoming ION GNSS conference taking place in Portland, OR from Sept 19-23, 2011.
GeoReader is an app that allows smartphones to read out loud site specific information as a user approaches a GPS location. Originally designed to add interest and provide relevant information to travelers, GeoReader provides the user the ability to listen to community ...
AFootSpa offers a Name that Gift Competition
2011-09-13
Schamp Marketing Concepts is hosting a contest to find the perfect name for three Special Order Products. The website is designed to bring the professional foot spa experience to the home, along with many helpful tips and articles.
The rules are simple. Review the three Special Order Products currently called Essential Pedicure Collection, Premium Home Spa Collection and Ultimate Home Spa Collection. The participants review the items in each of the collections and suggest a new name for each. It is that simple! Contestants can be creative and have fun. The winner will ...
Hidden Beach Signs Jazz Legend Ramsey Lewis
2011-09-13
Los Angeles based boutique label Hidden Beach Recordings announced earlier this month the signing of legendary jazz pianist Ramsey Lewis. The three time Grammy winner who rose to prominence in the early 1970's will release his 80th collection on September 20, 2011 entitled Ramsey, Taking Another Look., On the ten song CD Lewis and his Electric Band breathe new life into many of Lewis' favorite tunes including a new rendition of the Stevie Wonder penned "Living for the City" and a new edit of the original "Sun Goddess" recording featuring Earth, Wind ...
"Global Dismemberment: Through the Shaman's Eye" on September 20 "Why Shamanism Now?" Radio Show
2011-09-13
Streaming live on the Co-Creator Radio Network on Tuesday, September 20, at 11 a.m. Pacific time/2 p.m. Eastern time, on her show "Why Shamanism Now?: A Practical Path to Authenticity," shaman and founder of the Last Mask Center for Shamanic Healing Christina Pratt asks the question so very many are asking these days: What is happening around us? We see severe weather, colossal oil spills, and species dying off. We see illness, obesity, and rising incidents of mental illness and coping disorders. We see corruption and an unfathomable void of ethics in banking, ...
[1] ... [6972]
[6973]
[6974]
[6975]
[6976]
[6977]
[6978]
[6979]
6980
[6981]
[6982]
[6983]
[6984]
[6985]
[6986]
[6987]
[6988]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.