B-cell discovery suggests why women suffer more autoimmune disease
2011-08-06
Researchers at National Jewish Health have discovered a type of cell that may contribute to autoimmune disease and suggests why diseases such as lupus, multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis strike women more frequently than men. The cells, a subset of immune-system B cells, make autoantibodies, which bind to and attack the body's own tissue. The researchers reported in the August 4, 2011, issue of the journal Blood, that they found higher levels of these cells in elderly female mice, young and old mice prone to autoimmune disease, and humans with autoimmune diseases. ...
Poorly controlled asthma costly
2011-08-06
Poorly controlled asthma more than doubles healthcare costs associated with the disease and threatens educational achievement through a dramatic increase in school absence, according to researchers at National Jewish Health. The research team reported in the August 2011 issue of The Archives of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology that children with "very poorly controlled" asthma missed an average of 18 days of school each year, compared to 2 or less for other asthma patients.
"This study looks for the first time at how effective and ineffective management of severe asthma impacts ...
AviCoS replaces vehicle owner's manuals
2011-08-06
The avatar is displayed on the monitor of the Audi Mulitmedia Interface that comes standard in all new Audi models. The virtual figure understands complete sentences. Using artificial intelligence, AviCoS interprets questions by the vehicle occupants and answers in spoken language. The driver can view descriptive images or videos on-screen and the avatar points to the relevant areas during the explanation.
A further option – in addition to speech – for communicating with AviCoS is a Touch&Tell mode. If a driver is unfamiliar with a specific control element, a simple touch ...
SpeakingPal Announces Recent Launch to the iPhone
2011-08-06
SpeakingPal, a young startup company that is pioneering the development of English teaching mobile programs, announced that it has just launched its award-winning language learning application for the iPhone, which is now available in the iTunes stores. SpeakingPal has developed a unique and highly interactive solution that focuses on developing English speaking skills for non-native learners. The unique mobile learning application allows users to simply speak into their phone in amusing dialogs with a video character and get instant feedback on how well their sentences ...
Designing diamond circuits for extreme environments
2011-08-06
There is a new way to design computer chips and electronic circuitry for extreme environments: make them out of diamond.
A team of electrical engineers at Vanderbilt University has developed all the basic components needed to create microelectronic devices out of thin films of nanodiamond. They have created diamond versions of transistors and, most recently, logical gates, which are a key element in computers.
"Diamond-based devices have the potential to operate at higher speeds and require less power than silicon-based devices," Research Professor of Electrical Engineering ...
New study shows how to eliminate motion sickness on tilting trains
2011-08-06
An international team of researchers led by scientists at Mount Sinai School of Medicine have found that motion sickness on tilting trains can be essentially eliminated by adjusting the timing of when the cars tilt as they enter and leave the curves. They found that when the cars tilt just at the beginning of the curves instead of while they are making the turns, there was no motion sickness. The findings were published online Monday, July 25 in the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB) Journal.
When a tilting train enters a curve, sensors ...
A patient's own skin cells may one day treat multiple diseases
2011-08-06
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) — The possibility of developing stem cells from a patient's own skin and using them to treat conditions as diverse as Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease and cancer has generated tremendous excitement in the stem cell research community in recent years. Such therapies would avoid the controversial need for using stem cells derived from human embryos, and in theory, also bypass immunological problems inherent in using cells from one person to treat another.
However, in the nearly five years since the first article describing the development of ...
US physician practices spend 4 times Canadian practices
2011-08-06
NEW YORK (Aug. 4, 2011) -- Physicians in the United States spend nearly four times as much dealing with health insurers and payers compared with doctors in Canada. Most of the difference stems from the fact that Canadian physicians deal with a single payer, in contrast to the multiple payers in the United States.
These findings are published in the August issue of the journal Health Affairs -- the result of a research collaboration among Weill Cornell Medical College, Cornell University–Ithaca, the University of Toronto, and the Medical Group Management Association.
Administrative ...
Wireless network in hospital monitors vital signs
2011-08-06
A clinical warning system that uses wireless sensors to track the vital signs of at-risk patients is undergoing a feasibility study at Barnes-Jewish Hospital in St. Louis.
When the full system is operational sensors will take blood oxygenation and heart-rate readings from at-risk patients once or twice a minute. The data will be transmitted to a base station, where they will be combined with other data in the patient's electronic medical record, such as lab test results.
The incoming vital signs and data in the medical record will be continually scrutinized by a machine-learning ...
U of Minnesota researchers discover a natural food preservative that kills food-borne bacteria
2011-08-06
University of Minnesota researchers have discovered and received a patent for a naturally occurring lantibiotic — a peptide produced by a harmless bacteria — that could be added to food to kill harmful bacteria like salmonella, E. coli and listeria.
The U of M lantibiotic is the first natural preservative found to kill gram-negative bacteria, typically the harmful kind. "It's aimed at protecting foods from a broad range of bugs that cause disease," said Dan O'Sullivan, a professor of food science and nutrition in the university's College of Food, Agricultural and Natural ...
Females can place limits on evolution of attractive features in males, research shows
2011-08-06
AUDIO:
Male túngara frogs producing their distinctive "whine " and "chuck " calls to attract females.
Click here for more information.
AUSTIN, Texas—Female cognitive ability can limit how melodious or handsome males become over evolutionary time, biologists from The University of Texas at Austin, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center and the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute have observed.
Males across the animal world have evolved ...
University of Virginia researchers uncover new catalysis site
2011-08-06
Mention catalyst and most people will think of the catalytic converter, an emissions control device in the exhaust system of automobiles that reduces pollution.
But catalysts are used for a broad variety of purposes, including the conversion of petroleum and renewable resources into fuel, as well as the production of plastics, fertilizers, paints, solvents, pharmaceuticals and more. About 20 percent of the gross domestic product in the United States depends upon catalysts to facilitate the chemical reactions needed to create products for everyday life.
Catalysts are ...
Potential new eye tumor treatment discovered
2011-08-06
Baltimore, MD — New research from a team including several Carnegie scientists demonstrates that a specific small segment of RNA could play a key role in the growth of a type of malignant childhood eye tumor called retinoblastoma. The tumor is associated with mutations of a protein called Rb, or retinoblastoma protein. Dysfunctional Rb is also involved with other types of cancers, including lung, brain, breast and bone. Their work, which will be the cover story of the August 15th issue of Genes & Development, could result in a new therapeutic target for treating this rare ...
Targeting innate immunity in malaria
2011-08-06
WORCESTER, Mass. – Scientists at the University of Massachusetts Medical School have uncovered a novel DNA-sensing pathway important to the triggering of an innate immune response for malaria. Activation of this pathway appears to stimulate production of an overabundance of type-1 interferon by the immune system that may contribute to inflammation and fever in malaria patients and could play a part in susceptibility for the most common and lethal form of malaria known as plasmodium falciparum. Published online by Immunity this week, the study offers the first evidence that ...
Questions to Ask Your Plastic Surgeon Before Breast Augmentation
2011-08-06
The decision to have breast augmentation surgery is an important one that involves multiple factors. Breast augmentation has the ability to improve your self-esteem, increase self-confidence and feelings of appeal, and even improve your clothing options. It also has physical and aesthetic risks which should be fully considered prior to undergoing the procedure.
Breast augmentation is the most popular form of plastic surgery in the United States, with more than 250,000 performed every year. This does not mean that the procedure is right for you and, like any elective ...
New Montana State research sheds light on South Pole dinosaurs
2011-08-06
BOZEMAN, Mont. – Dog-sized dinosaurs that lived near the South Pole, sometimes in the dark for months at a time, had bone tissue very similar to dinosaurs that lived everywhere on the planet, according to a doctoral candidate at Montana State University.
That surprising fact falsifies a 13-year-old study and may help explain why dinosaurs were able to dominate the planet for 160 million years, said Holly Woodward, MSU graduate student in the Department of Earth Sciences and co-author of a paper published Aug. 3 in the journal "PLoS ONE."
"If we were trying to find evidence ...
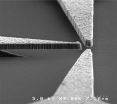
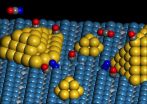
Rice discovery points way to graphene circuits
2011-08-06
HOUSTON -- (Aug. 4, 2011) -- Rice University materials scientists have made a fundamental discovery that could make it easier for engineers to build electronic circuits out of the much-touted nanomaterial graphene.
Graphene's stock shot sky-high last year when the nanomaterial attracted the Nobel Prize in physics. Graphene is a layer of carbon atoms that is just one atom thick. When stacked atop one another, graphene sheets form graphite, the material found in pencils the world over. Thanks to the tools of nanotechnology, scientists today can make, manipulate and study ...
Does a Breast Lift Result in Smaller Breasts?
2011-08-06
When your breasts begin to sag or droop due to factors such as weight fluctuations, age or pregnancy, a breast lift can restore a firm, youthful look. Unlike breast reduction surgery, which removes excess breast tissue from pendulous or overly-large breasts, a breast lift is best for women who are not experiencing physical discomfort from the weight of their breasts.
A breast lift is performed with three incisions from which excess skin is removed. Once removed, your remaining skin is firmed over your breast, and your breast is gently lifted and reshaped to provide a ...
Fusion diagnostic developed at PPPL sheds light on plasma behavior at EAST
2011-08-06
An instrument developed by researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) has enabled a team at the EAST fusion experiment in China to observe--in startling detail--how a particular type of electromagnetic wave known as a radiofrequency (RF) wave affects the behavior of hot ionized gas.
In the experiment at EAST (the Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak located at the Institute of Plasma Physics in Hefei, China), scientists employed a high-resolution, X-ray imaging crystal spectrometer (XICS) to observe how an RF wave ...
Prescriptions for antidepressants increasing among individuals with no psychiatric diagnosis
2011-08-06
Americans are no strangers to antidepressants. During the last 20 years the use of antidepressants has grown significantly making them one of the most costly and the third most commonly prescribed class of medications in the U. S. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, from 2005-2008 nearly 8.9 percent of the U.S. population had at least one prescription in this drug class during any given month. A new study led by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health examines national trends in antidepressant prescribing and finds much ...
What parasites eat is the key to better drug design
2011-08-06
A team led by Professor Malcolm McConville from the Bio21 Institute, University of Melbourne developed a new analytical method which can be used for many infectious parasites and bacteria. The technique has revealed which metabolic pathways are essential for the parasite's survival, down to the particular atoms it uses as a food source.
"This a very significant breakthrough in this field because the more we know about these dangerous pathogens and how they live, the better we can fight them with new, effective drugs," said Professor McConville.
"Current anti-parasitic ...
Mindless eating: Losing weight without thinking
2011-08-06
WASHINGTON – Dieters may not need as much willpower as they think, if they make simple changes in their surroundings that can result in eating healthier without a second thought, said a consumer psychologist at the American Psychological Association's 119th Annual Convention.
"Our homes are filled with hidden eating traps," said Brian Wansink, PhD, who presented his findings and strategies for a healthier lifestyle in a plenary address entitled "Modifying the Food Environment: From Mindless Eating to Mindlessly Eating Better."
"Most of us have too much chaos going ...
Right to remain silent not understood by many suspects
2011-08-06
WASHINGTON — Movies and TV shows often depict crime with a police officer handcuffing a suspect and warning him that he has the right to remain silent. While those warnings may appear clear-cut, almost 1 million criminal cases may be compromised each year in the United States because suspects don't understand their constitutional rights, according to research presented at the 119th Annual Convention of the American Psychological Association.
"The public, police and sometimes courts wrongly believe that people in custody understand their rights," said Richard Rogers, ...
Weight loss improves sexual health of overweight men with diabetes
2011-08-06
A new study published in The Journal of Sexual Medicine reveals that in obese men with type 2 diabetes, weight loss improves erectile function, sexual desire and lowers urinary tract symptoms.
Researchers led by Professor Gary Wittert, MBBch, MD, FRACP, FRCP, of the University of Adelaide studied 31 obese men with type 2 diabetes over 8 weeks. The men received either a meal replacement-based low-calorie diet or a low-fat, high-protein, reduced-carbohydrate diet prescribed to decrease intake by 600 calories a day.
In obese men with type 2 diabetes, results found that, ...
LASIK Versus Contact Lenses
2011-08-06
Many treatments are available to correct vision, and it is important that you choose a solution best suited for your specific needs and expectations. LASIK vision correction and contact lenses are both treatments letting you live free from glasses, but choosing between the two should involve your consideration of the risks and your candidacy for each treatment. You should also think about how each will affect your day-to-day life.
Risks Associated with LASIK Surgery and Contact Lenses
You may assume LASIK is the more dangerous treatment when compared to contacts. ...
[1] ... [7054]
[7055]
[7056]
[7057]
[7058]
[7059]
[7060]
[7061]
7062
[7063]
[7064]
[7065]
[7066]
[7067]
[7068]
[7069]
[7070]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.