With Resources, Children with Cerebral Palsy Can Succeed
2011-07-14
Maybe you've had concerns for your child's well-being since the day of his or her birth because your labor was mismanaged, delivery was delayed, too much Pitocin was used or your baby was in fetal distress.
Maybe you suspected there was a problem when you noticed your infant didn't reach for you with two hands or seemed excessively stiff or floppy. He or she just didn't move like other babies.
Even if you thought there might be problems, an actual diagnosis of cerebral palsy is still devastating. It's a diagnosis that thousands of parents hear every year, as almost ...
Study explores best motivating factors for pursuing a shared goal such as giving
2011-07-14
People who see the "glass as half empty" may be more willing to contribute to a common goal if they already identify with it, according to researchers from The University of Texas at Austin, University of Chicago and Sungkyunkwan University.
According to the studies, individuals who already care a lot (highly identify) with a cause are more likely to financially support the cause if a solicitation is framed by how much is still needed (for example, "we still need $50,000 to reach our goal"). However, if individuals care very little prior to a solicitation (low identify), ...
Research provides insight into new drug resistance in hospital microbes
2011-07-14
Boston (July 13, 2011) – Hospitals struggle to prevent the infections that complicate treatment for cancer, joint replacement, heart surgery and other conditions. Hospital-acquired infections are often resistant to multiple antibiotics, leading to approximately 100,000 deaths and more than $30 billion in additional health care costs yearly. New drugs are being developed to combat these infections, but resistance invariably emerges to these last-line drugs.
Daptomycin, a new antibiotic approved by the FDA in 2003, is used to treat infections caused by multi-drug resistant ...
Student Loans May Be Reclassified As Dischargeable in Bankruptcy
2011-07-14
With the nation's economy struggling, and unemployment still at historic levels, it is no surprise that many former students are struggling with repaying their loans. Last year, the United States Student Association estimated that borrowers held $730 billion in student loan debt, with 60 percent ($440 billion) in deferment or default. With student loan debt outpacing revolving credit card debt, bankruptcy is becoming a consideration for more struggling with crippling student loan debt, even though current law does not allow discharge of such debt, except under limited circumstances.
There ...
ONR-funded researchers examine new approaches for aircraft operations aboard carriers
2011-07-14
ARLINGTON, Va.--An Office of Naval Research (ONR)-sponsored effort to examine how aircraft carrier flight deck crews will manage manned and unmanned air vehicles (UAVs) completed a successful live demonstration, ONR announced July 13.
The Deck operations Course of Action Planner (DCAP) demonstration was performed at the Humans and Automation Laboratory at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT).
DCAP is a software tool designed to aid in planning on aircraft carrier flight decks--a congested and often times chaotic environment that not only includes a variety ...
Family-Focused Divorces: How to Prepare Children for an Imminent Divorce
2011-07-14
Divorcing couples must not only ready themselves for the struggles that lie ahead, but they also need to prepare their children for how to deal with an imminent dissolution. In order to do this, the focus needs to be on cooperation and co-parenting for the good of the children.
Children of divorcing parents are probably dealing with a variety of emotions as they figure out how things are changing. When approaching the subject of divorce with kids, especially younger ones, keep the language and topics simple. Focus on addressing how the divorce will change concrete things ...
Notre Dame research reveals brain network connections
2011-07-14
Research conducted by Maria Ercsey-Ravasz and Zoltan Toroczkai of the University of Notre Dame's Interdisciplinary Center for Network Science and Applications (iCeNSA), along with the Department of Physics and a group of neuroanatomists in France, has revealed previously unknown information about the primate brain.
The researchers published an article in the journal Cerebral Cortex showing that the brain is characterized by a highly consistent, weighted network among the functional areas of the cortex, which are responsible for such functions as vision, hearing, touch, ...
Twin ARTEMIS probes to study moon in 3-D
2011-07-14
On Sunday, July 17, the moon will acquire its second new companion in less than a month. That's when the second of two probes built by the University of California, Berkeley, and part of NASA's five-satellite THEMIS mission will drop into a permanent lunar orbit after a meandering, two-year journey from its original orbit around Earth.
The first of the two probes settled into a stable orbit around the moon's equator on June 27. If all goes well, the second probe will assume a similar lunar orbit, though in the opposite direction, sometime Sunday afternoon. The two spacecraft ...
Virginia Graeme Baker and the Hidden Dangers of Swimming Pools
2011-07-14
Many kids across the United States will spend their summer days swimming and having fun in neighborhood pools. However, it is important to remember that pools pose many dangers to young swimmers.
Pool Safely Campaign
The summer of 2011 marks the second year for the Consumer Product Safety Commission's (CPSC) "Pool Safely: Simple Steps Save Lives" campaign. The campaign is a public education and awareness campaign aimed at reducing the number of drownings and non-fatal submersion and entrapment accidents involving children. The campaign provides simple safety ...
Cancer data not readily available for future research
2011-07-14
Durham, NC — A new study finds that -- even in a field with clear standards and online databases -- the rate of public data archiving in cancer research is increasing only slowly. Furthermore, research studies in cancer and human subjects are less likely than other research studies to make their datasets available for reuse.
The results come from a study of patterns of research data availability conducted by Dr Heather Piwowar of the National Evolutionary Synthesis Center.
Data collected in scientific research is often useful for future studies by other investigators, ...
Spreading the Word about Pool Safety
2011-07-14
With the weather warming up, it is important to taking special care in and around water. In an ongoing initiative, the United States Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) is taking steps to protect children who use pools to reduce the number of swimming pool-related accidents and injuries.
Law Requires Safety Features, Empowers Education Campaign
The Virginia Graeme Baker Pool & Spa Safety Act was signed into law in December of 2007. Named for Virginia Graeme Baker, a 7-year-old who drowned after becoming entrapped by a hot tub drain, the act mandates that ...
Heart failure: Doing what your doctor says works
2011-07-14
Doctors have been dispensing advice to heart failure patients and for the first time researchers have found that it works. While self-care is believed to improve heart failure outcomes, a highlight of the recent American Heart Association scientific statement on promoting heart failure self-care was the need to establish the mechanisms by which self-care may influence neurohormonal, inflammatory, and hemodynamic function.
Christopher S. Lee, PhD, RN of the Oregon Health & Science University School of Nursing led a team of researchers who examined the biological mechanisms ...
Improving K-12 science education in the US
2011-07-14
A FRAMEWORK FOR K-12 SCIENCE EDUCATION, new from the National Research Council, identifies the key scientific concepts and practices that all students in these grades should learn. The framework offers a new vision for K-12 education in science and engineering and embodies a significant shift in how these subjects are viewed and taught. It will serve as the basis for new science education standards, to replace those last issued over a decade ago, and will inform the work of curriculum and assessment developers, teacher educators, and researchers.
###
Advance copies ...
Shelter From the Storm - Using Chapter 13 Bankruptcy to Save Your Home
2011-07-14
Saving House from Foreclosure
The collapse of the housing bubble in mid-2006 triggered a mortgage crisis that has severely impacted our nation's economy. Excessive subprime lending during the boom created a vulnerable banking industry. Holders of adjustable-rate mortgages found themselves forced into foreclosure when home values fell and they were unable to refinance their homes. Zero money down and "liar loans" (loans issued by lenders who failed to verify borrower income), weakened banks as homeowners defaulted. Borrowers who had overextended themselves by ...
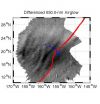
Tsunami airglow signature could lead to early detection system
2011-07-14
Researchers at the University of Illinois have become the first to record an airglow signature in the upper atmosphere produced by a tsunami using a camera system based in Maui, Hawaii.
The signature, caused by the March 11 earthquake that devastated Japan, was observed in an airglow layer 250 kilometers above the earth's surface. It preceded the tsunami by one hour, suggesting that the technology could be used as an early-warning system in the future. The findings were recently published in the peer-reviewed Geophysical Research Letters.
The observation confirms a ...
Divorce ... for the Sake of the Children
2011-07-14
One of the most common reasons that people stay in difficult marriages, even if they would like to get a divorce, is "for the sake of the children." People assume that it is better for their children to have both parents in the home, even in an unhappy marriage, than to have to grow up as children of divorced parents. However, there is debate among mental health professionals about which is more detrimental to children in the long run: having divorced parents or having parents who stay together but who are unhappy.
Traditional Notions About Divorce and Children
Conventional ...
Study identifies patients at increased risk after bilateral knee replacement surgery
2011-07-14
A new study by researchers at Hospital for Special Surgery has identified patients who are at a higher risk of morbidity and mortality when undergoing knee replacement surgery in both legs at the same time. The study found that patients who have a history of significant medical problems, especially congestive heart failure or pulmonary hypertension, are at increased risk for major complications.
"What we sought to do for the first time with this study, was to provide evidence-based risk stratification for who should be considered at high risk for morbidity and mortality ...
Premarital Agreements in Arizona
2011-07-14
The old adage is that money can't buy you love; but in today's society, money and finances are inextricably linked together. Once you say "I do", a number of things change with regard to your finances. Basically, one spouse's financial habits will affect the other's credit history, as married couples incur shared responsibility on home equity loans, joint credit cards, and other financial obligations. With America's high divorce rate, prenuptial agreements are no longer limited to celebrities and multi-millionaires. While only three percent of first marriages ...
Is meditation the push-up for the brain?
2011-07-14
Two years ago, researchers at UCLA found that specific regions in the brains of long-term meditators were larger and had more gray matter than the brains of individuals in a control group. This suggested that meditation may indeed be good for all of us since, alas, our brains shrink naturally with age.
Now, a follow-up study suggests that people who meditate also have stronger connections between brain regions and show less age-related brain atrophy. Having stronger connections influences the ability to rapidly relay electrical signals in the brain. And significantly, ...
Large waist doubles risk of kidney disease mortality
2011-07-14
MAYWOOD, Ill. -- For kidney disease patients, a large belt size can double the risk of dying.
A study lead by a Loyola University Health System researcher found that the larger a kidney patient's waist circumference, the greater the chance the patient would die during the course of the study.
The study by lead researcher Holly Kramer, MD, MPH, and colleagues is published in the American Journal of Kidney Diseases.
Waist circumference was more strongly linked to mortality than another common measure of obesity, body mass index (BMI).
BMI is a height-to-weight ratio. ...
Virginia and New York Bus Accidents Highlight Need for Better Regulations
2011-07-14
The serious bus accidents of 2011 have put U.S. bus safety into question. Are tour buses, school buses and city buses safe? If not, are there steps that can be taken to improve safety? This article will explore recent bus accidents, current and proposed bus regulations, and initiatives in place to improve bus safety.
Bus Accidents in 2011
Two significant bus accidents have made the news in the last few months. In May, a tour bus travelling from Greensboro, North Carolina to New York City crashed in Virginia, killing four people and injuring dozens more. The bus driver ...
Ocean acidification will seriously impact mussel populations
2011-07-14
Since the birth of the industrial revolution, ocean pH has dropped by 0.1 units. That might not sound like much until you realise that a 0.1 unit fall is a 30% increase in acidity. And, with predictions that ocean pH will continue plummeting, ecologists are becoming increasingly concerned about the impact of ocean acidification on marine populations. Brian Gaylord and his colleagues from the University of California at Davis explain that the open-coast mussel, Mytilus californianus, is a foundation species for many coastal ecosystems on the exposed northwestern coasts of ...
Sudden cardiac death in young athletes: Study suggests many ECG screenings are inaccurate
2011-07-14
Cincinnati, OH, July 14, 2011 -- Incidents of young athletes collapsing during sports practice due to an undiagnosed heart condition are alarming, and have led some health care professionals to call for mandatory electrocardiogram (ECG) screenings before sport participation. Others, however, question the validity of such a mandate. A new study soon to be published in The Journal of Pediatrics examines the accuracy and effectiveness of pre-sport participation ECGs.
Dr. Allison Hill and colleagues from Stanford University School of Medicine and Lucile Packard Children's ...
How Will Divorce Affect Your Finances?
2011-07-14
Divorce entails both physical and financial separation from one's spouse. And, as the U.S. slowly emerges from a severe recession, many people contemplating divorce are concerned about the effect of divorce on their finances. However, understanding how property division works in divorce and its impact on one's finances can help allay some anxiety over the process.
Because Texas is a community property state, almost all assets -- whether physical or financial -- either spouse acquires during a marriage is classified as martial property. When a couple gets divorced in ...
Pediatric cardiologists not always accurate in interpreting ECG results for young athletes
2011-07-14
STANFORD, Calif. — Pediatric cardiologists are prone to misinterpreting electrocardiograms when using the results to determine whether young athletes have heart defects that could make exercising perilous, according to a new study from the Stanford University School of Medicine and Lucile Packard Children's Hospital. This is the first research to examine the acumen of pediatric cardiologists from several health-care institutions in using ECGs to detect rare heart conditions associated with sudden cardiac death.
Public outcries about sudden cardiac deaths among athletes ...
[1] ... [7061]
[7062]
[7063]
[7064]
[7065]
[7066]
[7067]
[7068]
7069
[7070]
[7071]
[7072]
[7073]
[7074]
[7075]
[7076]
[7077]
... [8801]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.