International scientists warn of growing threat of wheat rust epidemics worldwide
2011-04-21
ALEPPO, SYRIA (20 April 2011): Researchers meeting at a scientific conference in Aleppo this week reported that aggressive new strains of wheat rust diseases – called stem rust and stripe rust – have decimated up to 40% of farmers' wheat fields in recent harvests. Areas affected are North Africa, the Middle East, Central Asia and the Caucuses, including Syria, Egypt, Yemen, Turkey, Iran, Uzbekistan, Morocco, Ethiopia, and Kenya.
“These epidemics increase the price of food and pose a real threat to rural livelihoods and regional food security,” said Mahmoud Solh, Director ...
Contemporary climate change alters the pace and drivers of extinction
2011-04-21
Local extinction rates of American pikas have increased nearly five-fold in the last 10 years, and the rate at which the climate-sensitive species is moving up mountain slopes has increased 11-fold, since the 20th century, according to a study soon to be published in Global Change Biology. The research strongly suggests that the American pika's distribution throughout the Great Basin is changing at an increasingly rapid rate. The pika (Ochotona princeps), a small, hamster-looking animal sensitive to climate, occurs commonly in rocky talus slopes and lava flows throughout ...
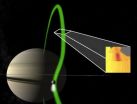
Beams of electrons link Saturn with its moon Enceladus
2011-04-21
Data from NASA's Cassini spacecraft have revealed that Enceladus, one of Saturn's diminutive moons, is linked to Saturn by powerful electrical currents - beams of electrons that flow back and forth between the planet and moon. The finding is part of a paper published in Nature today.
CAPS, one of the instruments on board Cassini which made the electron beam discovery, includes a electron sensor called CAPS-ELS – led by UCL (University College London).
Since Cassini's arrival at Saturn in 2004 it has passed 500km-wide Enceladus 14 times, gradually discovering more of ...
Avoiding Home Loan Modification Scams
2011-04-21
The nationwide economic recession has cost tens of thousands their jobs, forced millions into foreclosure and resulted in countless bankruptcy filings. Despite their best efforts, many people are falling behind on mortgage payments due to financial circumstances beyond their control. In an effort to avoid foreclosure, more and more people are seeking loan modifications as a way to lower payments temporarily (or permanently), making them more affordable and making keeping the home a real possibility.
Unfortunately, at a time when foreclosures are at a record high, unscrupulous ...
Molecule Nutlin-3a activates a signal inducing cell death and senescence in primary brain tumors
2011-04-21
Researchers of Apoptosis and Cancer Group of the Bellvitge Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBELL) have found that a small molecule, Nutlin-3a, an antagonist of MDM2 protein, stimulates the signalling pathway of another protein, p53. By this way, it induces cell death and senescence (loss of proliferative capacity) in brain cancer, a fact that slows its growth. These results open the door for MDM2 agonists as new treatments for glioblastomas. The study has been published at the journal PLoS ONE.
Glioblastoma multiforme is the most common brain tumour in adults and the ...
How molecules get to the right place at the right time
2011-04-21
In a multicellular organism, different cells fulfill a range of diversified functions. Often such specialization depends on the delivery of molecular goods to distinct places within a cell. It ensures that particular functions only occur at defined cellular sites. This establishment of intracellular asymmetry in the otherwise fluid environment of the cell cytoplasm requires active transport processes. Messenger RNAs (mRNA) represent an especially important type of freight. They are copies of genetic information stored in the nucleus. In the cytoplasm the information encoded ...
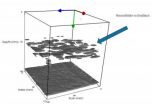
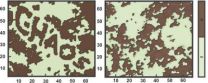
Lightning-fast materials testing using ultrasound
2011-04-21
Expectant mothers are familiar with the procedure: the physician examines them with an ultrasound apparatus that displays lifelike images of the fetus on the monitor. The application of this technology has been customary in medicine for years; in materials testing though, it has been used only in relatively rudimentary form to date. Researchers at the Fraunhofer Institute for Non-Destructive Testing IZFP in Saarbrücken have adapted the conventional sonar procedure – a simple ultrasound method – and have succeeded in generating three-dimensional images with the aid of innovative ...
Nassau County Crime Lab Shut Down
2011-04-21
Prosecutors trust that the information they receive from crime labs is correct and accurate. The results from tests run at the lab are used to help build cases against those accused of crimes. When this information is inaccurate it can lead to questions for both past and future cases, and in some instances, lead to innocent people being convicted of crimes they did not commit. The Nassau County crime lab recently became the only police lab in the nation to completely close its doors due to its inability to follow procedures.
The lab's troubles started in December 2010. ...
How can we measure infants' pain after an operation?
2011-04-21
It turns out to be difficult to find out exactly how much a child who cannot yet speak suffers after a surgical operation. Researchers at the University Hospital of La Paz, in Madrid, have validated the 'Llanto' scale, the first, and only, tool in Spanish which measures infant pain rapidly and simply.
"The lack of appropriate tools prevents health professionals from knowing if a pre-verbal child who cannot tell us how much a surgical wound hurts, is being treated correctly", explains Francisco Reinoso, lead author of the study and head of the section of Paediatric Anaesthesia ...
Shades of gray: LSU researcher studies South Louisiana's historical ties to the oil industry
2011-04-21
BATON ROUGE – On the one year anniversary of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill that took the lives of 11 men and devastated the livelihoods of many residents of coastal Louisiana, it's difficult to put the complicated relationship between people and oil into perspective. While the environmental impacts have thus far not been as pervasive as originally feared, most scientists are in agreement that it is still simply too early to tell. However, dependence upon oil has not lessened over the past year, laying the groundwork for some very significant debates between environmentalists ...
Bus Accidents In Northeast The Most Recent In A Decade Long List
2011-04-21
The Northeast has seen three tour bus accidents in less than a month. On March 21, a New Jersey-based PRT tour bus rolled over in New Hampshire, seriously injuring five people.
The bus was travelling to Boston from Quebec, carrying 25 Koreans. The driver apparently lost control on a snowy highway.
On March 15, a bus headed from Chinatown to Philadelphia crashed on the New Jersey Turnpike in East Brunswick, killing two, the driver and a passenger.
The worst accident of the three happened on March 12, with 15 passengers killed when a Worldwide Tours Bus headed to ...
Rotten meat doesn't stand a chance
2011-04-21
Is the vacuum-packed chicken leg really still fresh and edible? Looks alone do not tell the whole story. And the "best-before" date is no guarantee, either. Scandals involving the sale of rotten meat have added to the uncertainty, and the customer him- or herself may be shortening the shelf life through improper storage. This is an area in which a sensor film developed by the Fraunhofer Research Institution for Modular Solid State Technologies EMFT in Munich can immediately give a green – or rather: yellow light, or warn of spoiled goods. EMFT developed the film in a project ...
California Family Courts: Take a Number ... A Very Large Number
2011-04-21
California Family Courts deal with a huge volume of traffic every year. Just the Los Angeles Superior Court -- Family Law handles 100,000 filings per year.
The high number of filings combined with the fact that over 70 percent of litigants in family law are unrepresented -- meaning they don't have an attorney -- many courts have adopted local rules and procedures in an attempt to more efficiently process the high volume of family law cases.
While some of these rules and procedures help speed up the process, the price that efficiency comes at was the virtual elimination ...
A galactic rose highlights Hubble's 21st anniversary
2011-04-21
This image, taken by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, shows a group of interacting galaxies called Arp 273. The larger of the spiral galaxies, known as UGC 1810, has a disc that is tidally distorted into a rose-like shape by the gravitational pull of the companion galaxy below it, known as UGC 1813. The swathe of blue jewels across the top is the combined light from clusters of intensely bright and hot young blue stars. These massive stars glow fiercely in ultraviolet light.
The smaller, nearly edge-on companion shows distinct signs of intense star formation at its ...
New Loan Modification Proposal Would Help Distressed Homeowners
2011-04-21
While the foreclosure crisis has had a devastating effect on the real estate market, loan modifications have been equally as troubling for struggling homeowners. The Home Affordable Modification Program (HAMP) was supposed to help millions of Americans struggling to pay their mortgages by modifying home loans to reflect the current value of their properties.
Unfortunately, HAMP has not been as effective as first contemplated. As of March 2011, less than 500,000 mortgages have been modified through this program, when it was estimated that 3-4 million mortgages would be ...
How TRIM5 fights HIV
2011-04-21
Thanks to a certain protein, rhesus monkeys are resistant to HIV. Known as TRIM5, the protein prevents the HI virus from multiplying once it has entered the cell. Researchers from the universities of Geneva and Zurich have now discovered the protein's mechanism, as they report in Nature. This also opens up new prospects for fighting HIV in humans.
Unlike people, certain monkey species, such as rhesus or night monkeys, are resistant to HIV thanks to TRIM5, a cellular protein: In the case of an HIV infection, the protein intercepts the virus as soon as it enters the ...
MicroRNA mediates gene-diet interaction related to obesity
2011-04-21
BOSTON (April 20, 2011, 5pm ET) − Eating more n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, commonly known as omega-3 fatty acids, may help carriers of a genetic variant on the perilipin 4 (PLIN4) gene locus lose weight more efficiently. Based on this observation, researchers at the Jean Mayer Human Nutrition Research Center on Aging (USDA HNRCA) at Tufts University identified a microRNA (miRNA) which may elucidate the underlying biological mechanism.
Led by Jose M. Ordovas, PhD, director of the Nutrition and Genomics Laboratory at the USDA HNRCA, researchers genotyped seven ...
Breastfeeding tied to stronger maternal response to baby's cry
2011-04-21
A new study from the Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry finds that mothers who feed their babies breast milk exclusively, as opposed to formula, are more likely to bond emotionally with their child during the first few months after delivery. The breastfeeding mothers surveyed for the study showed greater responses to their infant's cry in brain regions related to caregiving behavior and empathy than mothers who relied upon formula as the baby's main food source. This is the first paper to examine the underlying neurobiological mechanisms as a function of breastfeeding, ...
What Every Registered Domestic Partner in Washington State Needs to Know
2011-04-21
In February 2011, U.S. President Barack Obama made the ground-breaking announcement that his administration would no longer defend the Defense of Marriage Act (DOMA), which bans federal recognition of same-sex marriages. While the change in federal DOMA enforcement is a great stride forward in equal rights for the LGBT community, there are still alarming conflicts between federal law and Washington state law. If you are considering registering for a domestic partnership, are in a registered domestic partnership or if you advise people who are in a registered domestic partnerships, ...
Strong protection for weak passwords
2011-04-21
The passwords of the future could become more secure and, at the same time, simpler to use. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for the Physics of Complex Systems in Dresden have been inspired by the physics of critical phenomena in their attempts to significantly improve password protection. The researchers split a password into two sections. With the first, easy to memorize section they encrypt a Captcha – an image that computer programs per se have difficulty in deciphering. The researchers also make it more difficult for computers, whose task it is to automatically ...
Consider Bankruptcy to Discharge Credit Card Debt
2011-04-21
When Congress' recent revisions to federal laws governing credit card usage went into effect, some consumers saw interest rates double or even triple. The law now allows for credit providers to be more flexible with interest rate raises, provided they give the cardholders notice of the action and share information about the total amount of the debt and approximately how long it will take to pay it off.
The changes in the law were initially introduced as a way to protect consumers, but, in practice they are much more biased toward lenders. Following the enacting of those ...
Study group looks at the future of corporate boards
2011-04-21
New York, NY, April 20, 2011 - A 20-member blue-ribbon panel, the Study Group on Corporate Boards, co-sponsored by Columbia Business School and the John L. Weinberg Center for Corporate Governance at the University of Delaware, today released "Bridging Board Gaps," a report designed to improve board performance and effectiveness by offering a series of recommendations in critical areas of governance. The report calls for a renewed commitment to the purpose of corporate boards, and suggests guidelines to improve board practices and standards along seven core dimensions: ...
Childhood music lessons may provide lifelong boost in brain functioning
2011-04-21
WASHINGTON — Those childhood music lessons could pay off decades later - even for those who no longer play an instrument – by keeping the mind sharper as people age, according to a preliminary study published by the American Psychological Association.
The study recruited 70 healthy adults age 60 to 83 who were divided into groups based on their levels of musical experience. The musicians performed better on several cognitive tests than individuals who had never studied an instrument or learned how to read music. The research findings were published online in the APA ...
New battery produces electricity where freshwater meets saltwater
2011-04-21
Scientists are reporting development of a new battery that extracts and stores energy produced from the difference in saltiness at the point where freshwater in rivers flows into oceans. A report on the battery, which could supply about 13 percent of the world's energy needs, appears in ACS' journal Nano Letters.
Yi Cui and colleagues cite the intensive global scientific effort to develop renewable energy sources to supplement supplies of oil and other traditional fuels like coal, which contribute to global warming. Solar, wind, and geothermal are renewable, sustainable ...
Using the energy in oil shale without releasing carbon dioxide in a greenhouse world
2011-04-21
New technology that combines production of electricity with capture of carbon dioxide could make billions of barrels of oil shale — now regarded as off-limits because of the huge amounts of carbon dioxide released in its production — available as an energy source in a greenhouse world of the future. That's the conclusion of a report on "electricity production with in situ carbon capture" (EPICC) in ACS' journal Energy & Fuels.
Adam Brandt and Hiren Mulchandani explain that almost 3 trillion barrels of oil are trapped in the world's deposits of oil-shale, a dark-colored ...
[1] ... [7511]
[7512]
[7513]
[7514]
[7515]
[7516]
[7517]
[7518]
7519
[7520]
[7521]
[7522]
[7523]
[7524]
[7525]
[7526]
[7527]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.