Paper-based synthetic gene networks could enable rapid detection of ebola and other viruses
2014-10-23
(Press-News.org) Synthetic gene networks hold great potential for broad biotechnology and medical applications, but so far they have been limited to the lab. A study published by Cell Press October 23rd in the journal Cell reveals a new method for using engineered gene circuits beyond the lab, allowing researchers to safely activate the cell-free, paper-based system by simply adding water. The low-cost, easy-to-use platform could enable the rapid detection of different strains of deadly viruses such as Ebola.
"Our paper-based system could not only make tools currently only available in laboratory readily fieldable, but also improve the development of new tools and the accessibility of these molecular tools to educational programs for the next generation of practitioners," says senior study author James Collins of the Wyss Institute for Biological Inspired Engineering at Harvard University.
The field of synthetic biology aims to re-engineer the molecular components of the cell to harness the power of biology. To accomplish this goal, researchers have designed synthetic gene networks that can control the activity of genes and recognize nucleic acids and small molecules. However, this technology has been restricted to the lab, in part because of biosafety concerns associated with cell-based systems and because the reactions involved have not been practical for field use.
Collins and his team overcame these hurdles by developing a cell-free, paper-based system suitable for use outside the lab. To test the clinical relevance of their method, the researchers developed sensors capable of detecting RNA molecules made from genes that allow bacteria to survive antibiotics, as well as RNA molecules encoding proteins from two different strains of the highly deadly Ebola virus. When freeze-dried onto paper, the sensors quickly detected the presence of these RNA molecules, demonstrating the usefulness of the approach for diagnostic purposes.
"Considering the projected cost, reaction time, ease of use, and no requirement for laboratory infrastructure, we envision paper-based synthetic gene networks significantly expanding the role of synthetic biology in the clinic, global health, industry, research, and education," Collins says.
INFORMATION:
Cell, Pardee et al.: "Paper-based Synthetic Gene Networks."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-10-23
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — A new comprehensive analysis of thyroid cancer from The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network has identified markers of aggressive tumors, which could allow for better targeting of appropriate treatments to individual patients.
The finding suggests the potential to reclassify the disease based on genetic markers and moves thyroid cancer into a position to benefit more from precision medicine.
"This understanding of the genomic landscape of thyroid cancer will refine how it's classified and improve molecular diagnosis. This will help us separate ...
2014-10-23
LA JOLLA, CA – October 23, 2014 - Scientists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have discovered a way to decrease deadly protein deposits in the heart, kidney and other organs associated with a group of human diseases called the systemic amyloid diseases.
"If we can develop a strategy to reduce the load that's coming from these proteins, then we can open up treatment options that could be broadly applied to treat multiple systemic amyloid diseases," said Luke Wiseman, assistant professor at TSRI and a senior author of the new research.
In related studies ...
2014-10-23
California's position as a leader in tobacco control is under threat, according to a new report from the UC San Francisco Center for Tobacco Control Research and Education. Once a highly successful program and international model, the state's anti-tobacco efforts now appear to be waning due to the decreased spending power of the California Tobacco Control Program, a resurgence of the tobacco industry in state politics, and the emergence of new unregulated tobacco products.
"The combination of weak leadership at the state level, willingness of political leaders to accept ...
2014-10-23
Federal Express® and UPS® are no match for the human body when it comes to distribution. There exists in cancer biology an impressive packaging and delivery system that influences whether your body will develop cancer or not.
One area of interest focuses on histones, the chief component of chromatin, a cluster of large molecules. Aberrations in chromatin are thought to lead to DNA damage such as with cancer. Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center announced findings indicating a possible new way of manipulating chromatin and its histones ...
2014-10-23
La Jolla, Calif., October 23, 2014 –A new study by researchers at Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute reveals the process that leads to changes in the brains of individuals with Down syndrome—the same changes that cause dementia in Alzheimer's patients. The findings, published in Cell Reports, have important implications for the development of treatments that can prevent damage in neuronal connectivity and brain function in Down syndrome and other neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative conditions, including Alzheimer's disease.
Down syndrome is characterized ...
2014-10-23
Exosomes, tiny, virus-sized particles released by cancer cells, can bioengineer micro-RNA (miRNA) molecules resulting in tumor growth. They do so with the help of proteins, such as one named Dicer. New research from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center suggests Dicer may also serve as a biomarker for breast cancer and possibly open up new avenues for diagnosis and treatment. Results from the investigation were published in today's issue of Cancer Cell.
"Exosomes derived from cells and blood serum of patients with breast cancer, have been shown to initiate ...
2014-10-23
A comprehensive analysis of the genomes of nearly 500 papillary thyroid carcinomas (PTC) – the most common form of thyroid cancer – has provided new insights into the roles of frequently mutated cancer genes and other genomic alterations that drive disease development. The findings also may help improve diagnosis and treatment. Investigators with The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) Research Network identified new molecular subtypes that will help clinicians determine which tumors are more aggressive and which are more likely to respond to certain treatments. Their ...
2014-10-23
SUMMERLAND, BRITISH COLUMBIA - A new study says that cherry producers need to understand new intricacies of the production-harvest-marketing continuum in order to successfully move sweet cherries from growers to end consumers. For example, the Canadian sweet cherry industry has had to modify logistics strategies--from shorter truck or air shipping to long-distance containerized shipping--to accommodate burgeoning export markets. Keeping cherries fresh and consumer-ready during long ocean crossings challenges producers to find new ways to retain fruit quality for weeks. ...
2014-10-23
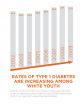
PASADENA, Calif., October 23, 2014 — The rate of non-Hispanic white youth diagnosed with type 1 diabetes increased significantly from 2002 to 2009 in all but the youngest age group of children, according to a new study published today in the journal Diabetes.
The study included data from more than 2 million children and adolescents living in diverse geographic regions of the United States. Within this population, researchers identified 5,842 non-Hispanic white youth, 19 years old and younger, newly diagnosed with type 1 diabetes over the 8-year study period. They ...
2014-10-23
Internet users regularly receive all kinds of personalized content, from Google search results to product recommendations on Amazon. This is thanks to the complex algorithms that produce results based on users' profiles and past activity. It's Big Data at work, and it's often advantageous for users. But such personalization can also be a disadvantage to buyers, according to a team of Northeastern University researchers, when e-commerce websites manipulate search results or customize prices without the user's knowledge—and which in some cases leads to some online shoppers ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Paper-based synthetic gene networks could enable rapid detection of ebola and other viruses