Biomimetic dew harvesters
Understanding how a desert beetle harvests water from dew could improve drinking water collection in dew condensers
2014-12-08
(Press-News.org) Insects are full of marvels - and this is certainly the case with a beetle from the Tenebrionind family, found in the extreme conditions of the Namib desert. Now, a team of scientists has demonstrated that such insects can collect dew on their backs - and not just fog as previously thought. This is made possible by the wax nanostructure on the surface of the beetle's elytra. These findings by José Guadarrama-Cetina, then working at ESPCI ParisTech, France - on leave from the University of Navarra, in Spain - and colleagues were recently published in EPJ E. They bring us a step closer to harvesting dew to make drinking water from the humidity in the air. This, the team hopes, can be done by improving the water yield of man-made dew condensers that mimick the nanostructure on the beetle's back.
It was not clear from previous studies whether water harvested by such beetles came from dew droplets, in addition to fog. Whereas fog is made of ready-made microdroplets floating in the air, dew appears following the cooling of a substrate below air temperature. This then turns the humidity of air into tiny droplets of water because more energy - as can be measured through infrared emissions - is sent to the atmosphere than received by it. The cooling capability is ideal, they demonstrated, because the insect's back demonstrates near-perfect infrared emissivity.
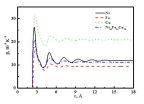
Guadarrama-Cetina and colleagues also performed an image analysis of dew drops forming on the insect's back on the surface of the elytra, which appears as a series of bumps and valleys. Dew primarily forms in the valleys endowed with a hexagonal microstructure, they found, unlike the smooth surface of the bumps. This explains how drops can slide to the insect's mouth when they reach a critical size.
INFORMATION:
Reference: Guadarrama-Cetina, J.M. et al. (2014). Dew condensation on desert beetle skin. European Physical Journal E . DOI 10.1140/epje/i2014-14109-y
For more information visit: http://www.epj.org
The full-text article is available to journalists on request.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-12-08
MOUNT VERNON, WA - Cider - or "hard cider" as it is typically known in the United States - is experiencing a real revival. The fermented apple juice with 0.5% to 7% alcohol-by-volume is the fastest growing alcohol market segment in the US, boasting a 54% increase in production annually from 2007 to 2012. Naturally, increasing consumer demand for cider translates to a need for more apples to make quality cider products.
Carol A. Miles and Jaqueline King from Washington State University's Department of Horticulture published a study in HortTechnology that can provide apple ...
2014-12-08
An article published in the Health Affairs December issue is the first ever comprehensive analysis to investigate the Affordable Care Act's (ACA) Essential Health Benefit (EHB) as it relates to children. The study found that the EHB has resulted in a state-by-state patchwork of coverage for children and adolescents that has significant exclusions, particularly for children with developmental disabilities and other special health care needs.
Previous studies have compared the EHB standard more broadly to the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP), but this analysis ...
2014-12-08
WEST LAFAYETTE, IN/ITHACA, NY - Energy costs account for one of the largest expenses in commercial greenhouse production of annual bedding plants. Naturally, bedding plant producers are searching for more energy-efficient production methods that can reduce fuel usage and increase profits. Christopher Currey, Roberto Lopez, and Neil Mattson published a study in HortTechnology that gives growers in northern latitudes valuable information on finishing practices for annual bedding plants. The researchers compared traditional heated greenhouses with unheated high tunnels for ...
2014-12-08
(SAN FRANCISCO, December 6, 2014) - New treatment combinations and targeted therapies for lymphoma and multiple myeloma are improving outcomes for vulnerable patient populations with hard-to-treat disease, according to studies presented today at the 56th American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting and Exposition.
Despite advances in lymphoma treatments, improving the prognosis for patients with relapsed and treatment-resistant disease remains a challenge. The early success of several precision therapies associated with fewer side effects than conventional approaches ...
2014-12-08
(SAN FRANCISCO, December 7, 2014) - Studies presented at the 56th American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting and Exposition compare new and standard-of-care treatments for blood clots and further illuminate clot risks in vulnerable populations, such as cancer patients.
Although significant advances have been made in the treatment and prevention of blood clots through new and improved therapies for clotting disorders, challenges remain in balancing the benefits and risks of these therapies. Specifically, while these treatments can reduce patients' risk of suffering ...
2014-12-08
It is estimated that about 35 million people worldwide currently suffer from dementia and it is expected that the number will increase to 135 million by the year 2050. The disease is already one of the most common health problems in the elderly, which is why experts predict that the numbers of people affected will increase over time. Researchers at the Department of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy of the University Medical Center of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) have recently gained new insights into how it may in future be possible to treat patients with the currently ...
2014-12-08
The ability to predict macroscopic physical and chemical properties from information derived at the micro-scale or atomic scale for various kinds of materials has yet to be perfected in the field of materials physics and chemistry. Although macro-scopic properties are determined by the micro or atomic structure of materials, it is still difficult to obtain such properties as hardness, intensity, surface tension, density, thermal expansion, thermal diffusion, viscosity and specific heat from a cell with just several atoms because of multi-scale effects.
For solids, particularly ...
2014-12-08
Gallium nitride (GaN) based devices are attractive for harsh environment electronics because of their high chemical and the mechanical stability of GaN itself that has a higher atomic displacement energy than other semiconductor materials.
However, degradation mechanisms of GaN device under radiation environments is not clear mainly because devices consist of many different types of semiconductors, such as p-type and n-type layers in light emitting diode (LED), and each layer has different hardness to radiation.
Now, researchers at the Electronics-Inspired Interdisciplinary ...
2014-12-08
Macrophages are best known for their Pac Man-like ability to gobble up cellular debris and pathogens in order to thwart infection. A new study in The Journal of Cell Biology describes how these immune cells also help resolve inflammation by inducing white blood cells called neutrophils to leave wounded tissue.
Neutrophils are "first responders" that are attracted to wounds by signaling molecules called reactive oxygen species (ROS) that activate a protein kinase. When neutrophils finish their work, inflammation is partly resolved through apoptosis, or cell suicide, and ...
2014-12-08
What does it mean for expectant mothers and hospitals when there are large-scale closures of maternity units? A new study led by researchers at The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia provides an inside view from hospital staff members in Philadelphia, where 13 out of 19 obstetric units closed in a 15-year period.
The researchers found that sharp surges in patient volume in the remaining units strained the healthcare system, eroded workforce morale, and fragmented care for mothers and babies until hospitals adjusted to added demands.
"While the degree of obstetric ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Biomimetic dew harvesters
Understanding how a desert beetle harvests water from dew could improve drinking water collection in dew condensers