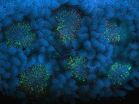
(Press-News.org) Scientists have discovered how earthworms can digest plant material, such as fallen leaves, that would defeat most other herbivores.
Earthworms are responsible for returning the carbon locked inside dead plant material back into the ground. They drag fallen leaves and other plant material down from the surface and eat them, enriching the soil, and they do this in spite of toxic chemicals produced by plants to deter herbivores.
The scientists, led by Dr Jake Bundy and Dr Manuel Liebeke from Imperial College London, have identified molecules in the earthworm gut that counteract the plant's natural defences and enable digestion. Their work is published today (4 August 2015) in Nature Communications and includes support from the Centre for Ecology and Hydrology, the University of Oxford, and Cardiff University.
The molecules, which have been named drilodefensins, are so abundant that Dr Liebeke estimates that for every person on earth there is at least 1kg of drilodefensins present within the earthworms that populate the world's soils. Their abundance is not, however, an excess - drilodefensins are so precious that earthworms recycle the molecules in order to harness their effects again.
A world without drilodefensins would be a very different world, according to the researchers. Dr Bundy, from the Department of Surgery and Cancer at Imperial, said: "Without drilodefensins, fallen leaves would remain on the surface of the ground for a very long time, building up to a thick layer. Our countryside would be unrecognisable, and the whole system of carbon cycling would be disrupted."
Plants make polyphenols, which act as antioxidants and give the plants their colour; they also inhibit the digestion of many herbivores. Earthworms, however, are able to digest fallen leaves and other plant material, thanks to the ability of drilodefensins to counteract polyphenols. Dr Bundy and his team found that the more polyphenols present in the earthworm diet, the more drilodefensins they produce in their guts.
The finding that the molecules are abundant in the gut of earthworms was made possible by using modern visualization techniques based on mass spectrometry (MALDI imaging). Dr Liebeke , formerly of the Department of Surgery and Cancer at Imperial, and now working at the Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology, in Germany, said: "Using these molecular microscopes is changing how we understand complex biochemistry of living beings; we are now able to locate every molecule in, for example, an earthworm to a specific location. Knowing the location of a molecule can help us to figure out what it actually does."
The first record of a molecule that would now be considered a drilodefensin was in 1988 when a patent was filed for a molecule that was thought to dilate blood vessels. In traditional Chinese medicine, this molecule was ingested in the form of dried earthworm products. But Dr Bundy cautioned that the drying process would almost certainly render drilodefensins inactive.
Dr Dave Spurgeon of the Centre for Ecology and Hydrology is a co-author on the paper. He said: "We've established that earthworms, referred to as 'nature's ploughs' by Charles Darwin, have a metabolic coping mechanism to deal with a range of leaf litter diets. In this role, drilodefensin support the role of earthworm as key "ecosystem engineers" within the carbon cycle."
INFORMATION:
The research was funded by the UK's Natural Environment Research Council.
WASHINGTON, D.C., August 4, 2015 -- Terahertz radiation, the no-man's land of the electromagnetic spectrum, has long stymied researchers. Optical technologies can finagle light in the shorter-wavelength visible and infrared range, while electromagnetic techniques can manipulate longer-wavelength radiation like microwaves and radio waves. Terahertz radiation, on the other hand, lies in the gap between microwaves and infrared, whether neither traditional way to manipulate waves works effectively. As a result, creating coherent artificial sources of terahertz radiation in ...
WASHINGTON, D.C., August 4, 2015 -- Studies of the impact a droplet makes on solid surfaces hark back more than a century. And until now, it was generally believed that a droplet's impact on a solid surface could always be separated into two phases: spreading and retracting.
But it's much more complex than that, as a team of researchers from City University of Hong Kong, Ariel University in Israel, and Dalian University of Technology in China report in the journal Applied Physics Letters, from AIP Publishing.
"During the spreading phase, the droplet undergoes an inertia-dominant ...
UBC scientists have opened the doors to new research into malnutrition by creating an animal model that replicates the imbalance of gut bacteria associated with the difficult-to-treat disease.
Malnutrition affects millions of people worldwide and is responsible for one-fifth of deaths in children under the age of five. Children can also experience impaired cognitive development and stunted growth.
The problem arises when people don't have enough food to eat and their diet lacks proper nutrients. The disease also has a lot to do with environmental factors and it has ...
In vitro studies of the cellular effects of modeled osteopathic manipulative therapy (OMT) provide proof of concept for the manual techniques practiced by doctors of osteopathic medicine (DOs), according to researchers from the University of Arizona College of Medicine - Phoenix.
The study, published in The Journal of the American Osteopathic Association, focused on modeling two common OMT techniques, myofascial release and counterstrain. Researchers subjected fibroblast matrices to various strains and employed a scratch wound strain model to test the ability of OMT ...
A new strain of yeast called Yarrowia lipolytica Y-3492 was found to be very active in waste water treatment. The discovery was made by by microbiologists from Kazan Federal University during their research at Western Siberian peat bogs.
The strain is said to be effective against nitro compounds which are used in explosives, herbicides, insecticides, polymers, dyes, and some medications. Oil refineries and military equipment plants produce especially high amounts of such waste. The research was conducted with the use of widely known trinitrotoluene (TNT).
It is well-known ...
COLLEGE STATION -- It's happy hour at a lab in College Station. The cocktail of choice, developed by scientists with Texas A&M AgriLife Research, is one that stops or prevents the deadly Pierce's disease on wine grapes.
The discovery could turn a new leaf on the multimillion-dollar U.S. wine industry. Hear, hear.
The study, published in the academic journal PLOS ONE, describes the use of four bacteriophages that were identified for their ability to attack the bacteria that causes the devastating disease in grapes and several other plants.
A bacteriophage, or phage, ...
A paper from the University of Exeter has highlighted the dangers of relying on climate-based projections of future crop pest distributions and suggests that rapid evolution can confound model results.
Crop pests and pathogens are destructive organisms which pose a huge threat to food security and land management across the world. Much research has been carried out into why the pests are spreading, where they are likely to establish next, what damage they will do and what can be done to reduce their impact.
In a new synthesis, published today in the Annual Review of ...
Diagnosis of deadly brain conditions could be helped by new research that shows how infectious proteins that cause the disease spread.
The study reveals how the proteins - called prions - spread from the gut to the brain after a person or animal has eaten contaminated meat.
Scientists say their findings could aid the earlier diagnosis of prion diseases - which include variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) in people and bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) in cows.
In people, the disease remains very rare - 229 people have died from vCJD since it was first identified ...
The Society of Thoracic Surgeons, the Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists, and the American Society of ExtraCorporeal Technology have released a set of clinical practice guidelines to address management of a patient's temperature during open heart surgery. The guidelines appear in the August issue of The Annals of Thoracic Surgery and were published simultaneously in two other journals.
Numerous strategies are currently used to optimally manage the practice of cooling the blood, temperature maintenance (control of body temperature during surgery), and rewarming ...
This news release is available in French. While it is already possible to obtain in vitro pluripotent cells (ie, cells capable of generating all tissues of an embryo) from any cell type, researchers from Maria-Elena Torres-Padilla's team have pushed the limits of science even further. They managed to obtain totipotent cells with the same characteristics as those of the earliest embryonic stages and with even more interesting properties. Obtained in collaboration with Juanma Vaquerizas from the Max Planck Institute for Molecular Biomedicine (Münster, Germany), these ...