(Press-News.org) Children with better academic and behavioral functioning when they start kindergarten often have better educational and societal opportunities as they grow up. For instance, children entering kindergarten with higher reading and math achievement are more likely to go to college, own homes, be married, and live in higher-income neighborhoods as adults. Now a new study points to very early roots of differences in school readiness, with growth in vocabulary playing a particularly important role. The study found that children with larger oral vocabularies by age 2 arrived at kindergarten better prepared academically and behaviorally than their peers. This information can help target early intervention efforts.
The study was conducted by researchers at the Pennsylvania State University, the University of California, Irvine, and Columbia University, who analyzed nationally representative data for 8,650 children in the Early Childhood Longitudinal Study-Birth Cohort. The study appears in the journal Child Development.
Two-year-olds' vocabularies were measured via a parent survey, and their academic achievement in kindergarten was gauged via individually administered measures of reading and math. Kindergarten teachers independently rated the children's behavioral self-regulation and frequency of acting out or anxious behavior. Researchers took into account a wide range of background characteristics (such as sociodemographics) and experiences (such as parenting quality) to more fully isolate the role of vocabulary growth. They evaluated whether 2-year-olds with larger oral vocabularies achieved more academically and functioned at more optimal levels behaviorally when they later entered kindergarten.
Gaps in oral vocabulary were evident between specific groups of children as young as age 2, with children from higher-income families, females, and those experiencing higher-quality parenting having larger oral vocabularies than their peers. Children born with very low birthweight or from households where the mother had health problems had smaller oral vocabularies.
When the researchers examined the children three years later, they found that children who had a larger oral vocabulary at age 2 were better prepared academically and behaviorally for kindergarten, with greater reading and math achievement, better behavioral self-regulation, and fewer acting out or anxiety-related problem behaviors. This oral vocabulary advantage could not be explained by many other factors, including the children's own general cognitive and behavioral functioning and the families' socioeconomic resources.
"Our findings provide compelling evidence for oral vocabulary's theorized importance as a multifaceted contributor to children's early development," notes Paul Morgan, associate professor of education at the Pennsylvania State University, who led the study. "Our findings are also consistent with prior work suggesting that parents who are stressed, overburdened, less engaged, and who experience less social support may talk, read, or otherwise interact with their children less frequently, resulting in their children acquiring smaller oral vocabularies."
Adds George Farkas, professor of education at the University of California, Irvine, who coauthored the study: "These oral vocabulary gaps emerge as early as 2 years. Early interventions that effectively increase the size of children's oral vocabulary may help at-risk 2-year-olds subsequently enter kindergarten classrooms better prepared academically and behaviorally. Interventions may need to be targeted to 2-year-olds being raised in disadvantaged home environments."
Examples of such interventions include home visitation programs, through which nurses regularly visit disadvantaged first-time mothers during and after their pregnancies to help with parenting matters and link them with social services and other support systems. These could play an important role in the school readiness of disadvantaged children, the authors suggest.
INFORMATION:
The study was funded by the National Center for Special Education Research, Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education, the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, and the National Institutes of Health.
Summarized from Child Development, 24-Month-Old Children with Larger Oral Vocabularies Display Greater Academic and Behavioral Functioning at Kindergarten Entry by Morgan, PL (The Pennsylvania State University), Farkas, G (University of California, Irvine), Hillemeier, MM (The Pennsylvania State University), Hammer, CS (Columbia University), and Maczuga, S (The Pennsylvania State University). Copyright 2015 The Society for Research in Child Development, Inc. All rights reserved.
Adolescents who have romantic relationships tend to have more problems with psychosocial adjustment. In contrast, young adults who have romantic relationships tend to have fewer problems with psychosocial adjustment. Although the links between having a romantic relationship and psychosocial adjustment change with age, a new longitudinal study has found that it's not just having a relationship that matters, but the quality of the relationship: Higher-quality romantic relationships are associated with fewer psychosocial difficulties across adolescence and young adulthood.
The ...
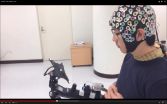
Scientists working at Korea University, Korea, and TU Berlin, Germany have developed a brain-computer control interface for a lower limb exoskeleton by decoding specific signals from within the user's brain.
Using an electroencephalogram (EEG) cap, the system allows users to move forwards, turn left and right, sit and stand simply by staring at one of five flickering light emitting diodes (LEDs).
The results are published today (Tuesday 18th August) in the Journal of Neural Engineering.
Each of the five LEDs flickers at a different frequency, and when the user focusses ...
A new test for offers the possibility of near real time monitoring of bone diseases, such as osteoporosis and multiple myeloma. The functionality of the test, which measures changes in calcium isotope ratios, has been validated on blood samples from NASA space shuttle astronauts.
Our bones are largely built of calcium, and the turnover of calcium can indicate the development of bone diseases such as osteoporosis and the cancer multiple myeloma. Geochemists have developed extremely accurate ways of measuring calcium isotope ratios, for example for the study of sea shell ...
For an embargoed PDF, please contact Cara Graeff or 215-351-2513 or Angela Collom or 215-351-2514.
1. Anonymous essay exposes scandalous doctor behavior
Free abstract: http://www.annals.org/article.aspx?doi=10.7326/M14-2168
Editorial: http://www.annals.org/article.aspx?doi=10.7326/M15-1144
URLs go live when embargo lifts
An anonymous and provocative essay published in Annals of Internal Medicine exposes the dark underbelly of medicine where doctors displayed stomach-churning disrespect for vulnerable patients. The author describes teaching a medical humanities ...
PHILADELPHIA - Websites for national and state health insurance marketplaces show evidence of improved efforts to assist patients in choosing health insurance plans, such as providing decision support tools, experts from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania have found. However, in a letter published in the August 18 issue the Annals of Internal Medicine, the Penn team recommends taking more steps to better support consumers in making informed health plan decisions.
The marketplaces, also called health exchanges, were established by the Patient ...
Research has shown that a regular dose of aspirin reduces the long-term risk of cancer in those who are overweight in an international study of people with a family history of the disease.
The study, conducted by researchers at Newcastle University and the University of Leeds, UK, is published today in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
They found that being overweight more than doubles the risk of bowel cancer in people with Lynch Syndrome, an inherited genetic disorder which affects genes responsible for detecting and repairing damage in the DNA. Around half of these ...
Testing for genetic risk factors could improve treatment for myeloma - a cancer of the blood and bone marrow - by helping doctors identify patients at risk of developing more aggressive disease.
New research, published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology today (Monday), found as few as nine genetic features would need to be tested to identify high-risk patients who might benefit from intensive treatment.
The study, led by researchers at The Institute of Cancer Research, London, is the first to link genetic mutations in myeloma cells to the chances of surviving the disease.
The ...
Drinking caffeinated coffee daily significantly reduced cancer recurrence and death in stage III colon cancer.
Greatest benefits were in those drinking four or more cups a day.
Researchers are not recommending people drink more coffee pending further studies.
BOSTON - Regular consumption of caffeinated coffee may help prevent the return of colon cancer after treatment and improve the chances of a cure, according to a new, large study from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute that reported this striking association for the first time.
The patients, all of them treated ...
CLEVELAND - A first-of-its-kind study published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology finds that music therapy lessened anxiety for women undergoing surgical breast biopsies for cancer diagnosis and treatment. The two-year study out of University Hospitals Seidman Cancer Center involved 207 patients.
"To the best of our knowledge, this is the first randomized controlled trial to test music therapy for anxiety management with women undergoing outpatient breast cancer surgery, and the largest study of its kind to use live music therapy in the surgical arena," said lead ...
NEW YORK, NY - August 17, 2015 - Schizophrenia is associated with structural and functional alterations of the visual system, including specific structural changes in the eye. Tracking such changes may provide new measures of risk for, and progression of the disease, according to a literature review published online in the journal Schizophrenia Research: Cognition, authored by researchers at New York Eye and Ear Infirmary of Mount Sinai and Rutgers University.
Individuals with schizophrenia have trouble with social interactions and in recognizing what is real. Past research ...