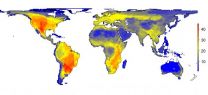
(Press-News.org) The fact that the greatest diversity of large mammals is found in Africa reflects past human activities - and not climatic or other environmental constraints. This is determined in a new study, which presents what the world map of mammals would look like if modern man (Homo sapiens) had never existed.
In a world without humans, most of northern Europe would probably now be home to not only wolves, Eurasian elk (moose) and bears, but also animals such as elephants and rhinoceroses.
This is demonstrated in a new study conducted by researchers from Aarhus University, Denmark. In a previous analysis, they have shown that the mass extinction of large mammals during the Last Ice Age and in subsequent millennia (the late-Quaternary megafauna extinction) is largely explainable from the expansion of modern man (Homo sapiens) across the world. In this follow-up study, they investigate what the natural worldwide diversity patterns of mammals would be like in the absence of past and present human impacts, based on estimates of the natural distribution of each species according to its ecology, biogeography and the current natural environmental template. They provide the first estimate of how the mammal diversity world map would have appeared without the impact of modern man.
"Northern Europe is far from the only place in which humans have reduced the diversity of mammals - it's a worldwide phenomenon. And, in most places, there's a very large deficit in mammal diversity relative to what it would naturally have been", says Professor Jens-Christian Svenning, Department of Bioscience, Aarhus University, who is one of the researchers behind the study.
Africa is the last refuge
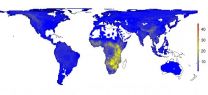
The current world map of mammal diversity shows that Africa is virtually the only place with a high diversity of large mammals. However, the world map constructed by the researchers of the natural diversity of large mammals shows far greater distribution of high large-mammal diversity across most of the world, with particularly high levels in North and South America, areas that are currently relatively poor in large mammals.
"Most safaris today take place in Africa, but under natural circumstances, as many or even more large animals would no doubt have existed in other places, e.g., notably parts of the New World such as Texas and neighboring areas and the region around northern Argentina-Southern Brazil. The reason that many safaris target Africa is not because the continent is naturally abnormally rich in species of mammals. Instead it reflects that it's one of the only places where human activities have not yet wiped out most of the large animals," says Postdoctoral Fellow Soren Faurby, Department of Bioscience, Aarhus University, who is the lead author on the study.
The existence of Africa's many species of mammals is thus not due to an optimal climate and environment, but rather because it is the only place where they have not yet been eradicated by humans. The underlying reason includes evolutionary adaptation of large mammals to humans as well as greater pest pressure on human populations in long-inhabited Africa in the past.
Better understanding helps nature preservation
The study's openly accessible data set of natural range maps for all late-Quatenary mammals provides researchers with the first opportunity to analyse the natural patterns in the species diversity and composition of mammals worldwide. Hereby, it can be used to provide a better understanding of the natural factors that determine the biodiversity in a specific area.
Today, there is a particularly large number of mammal species in mountainous areas. This is often interpreted as a consequence of environmental variation, where different species have evolved in deep valleys and high mountains. According to the new study, however, this trend is much weaker when the natural patterns are considered.
"The current high level of biodiversity in mountainous areas is partly due to the fact that the mountains have acted as a refuge for species in relation to hunting and habitat destruction, rather than being a purely natural pattern. An example in Europe is the brown bear, which now virtually only live in mountainous regions because it has been exterminated from the more accessible and most often more densely populated lowland areas," explains Soren Faurby.
Hereby, this new study can provide an important base-line for nature restoration and conservation.
The study has been published in the scientific journal Diversity and Distributions.
INFORMATION:
For more information, please contact
Postdoctoral Fellow Soren Faurby
Department of Bioscience
Aarhus University, Denmark
(now employed at the Museum of Natural History, Madrid)
soren.faurby@bios.au.dk
+34 665 66 99 26
Professor Jens-Christian Svenning
Department of Bioscience
Aarhus University, Denmark
svenning@bios.au.dk
+45 2899 2304
In a new study published today in the Journal of Health Psychology, researchers from the University of Surrey have found dieters who eat 'on the go' may increase their food intake later in the day which could lead to weight gain and obesity. The findings from the study also showed that eating while walking around triggered more overeating compared to eating during other forms of distraction such as watching TV or having a conversation with a friend.
The team examined 60 females who were either dieters or non-dieters and gave them all a cereal bar to eat under three different ...
A "substantial" proportion of NHS hospital staff--around one in eight, in some places--treat the victims of people trafficking, with maternity services most likely to do so, finds research published in the online journal BMJ Open.
Although understanding of the sorts of health problems trafficked patients are likely to have, is generally high, few NHS staff feel adequately prepared to respond appropriately, the findings suggest.
International law requires that the UK provides victims of human trafficking with whatever medical treatment they require, which includes psychological ...
Nine potentially modifiable risk factors may contribute to up to two thirds of Alzheimer's disease cases worldwide, suggests an analysis of the available evidence, published online in the Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery & Psychiatry.
The analysis indicates the complexity of Alzheimer's disease development and just how varied the risk factors for it are.
But the researchers suggest that preventive strategies, targeting diet, drugs, body chemistry, mental health, pre-existing disease, and lifestyle may help to stave off dementia. This could be particularly important, ...
In a Policy View published in The Lancet Neurology journal, a group of leading experts on the epidemiology of dementia state that the number of people with dementia - both new cases and total numbers with the disease - in some Western European countries is stabilising despite population ageing, in direct contrast to the "dementia epidemic" reported in some recent studies.
The Policy View discusses data from five large epidemiological studies done in Sweden, the Netherlands, the UK, and Spain that compare dementia occurrence in old people across two periods of time using ...
Highlights
Among kidney transplant recipients, patients with mostly IgG3 donor-specific HLA antibodies had a higher likelihood of organ rejection soon after transplantation.
If rejection occurred in those with mostly IgG4 antibodies, it was usually much later after transplantation.
Washington, DC (August 20, 2015) -- The dominant antibody type present in the blood of transplant recipients may indicate their likelihood of experiencing organ rejection, according to a study appearing in an upcoming issue of the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology (JASN). ...
DALLAS, Aug. 20, 2015 -- Caregiver spouses of stroke survivors are at an increased risk of mental and physical health issues that may continue for years, according to research in the American Heart Association journal Stroke.
Swedish researchers evaluated 248 stroke survivors, below age 70 (average mid-sixties), and their spouses at stroke onset and compared the results with 245 non-stroke controls for seven years after the stroke event.
At the seven-year follow-up, 16.5 percent of survivors had suffered a recurrent stroke. Spouses of survivors reported lower scores ...
Boston, MA -- A widely used class of industrial chemicals linked with cancer and interference with immune function--perfluorinated alkylate substances, or PFASs--appears to build up in infants by 20%-30% for each month they're breastfed, according to a new study co-authored by experts from Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. It is the first study to show the extent to which PFASs are transferred to babies through breast milk, and to quantify their levels over time.
"We knew that small amounts of PFAS can occur in breast milk, but our serial blood analyses now show ...
In-depth interviews conducted by researchers at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine of 20 young women attending an urban sexually transmitted disease clinic have documented a variety of unexpected, unintended sexual encounters linked to their alcohol use before sex occurs.
Links between alcohol use and risky or deleterious sexual encounters are not necessarily new, say investigators, but this small study identifies very specifically the disconnect between what young women have in mind when they drink and have sex and what really happens.
"The idea behind ...
According to a survey conducted by Rhode Island Hospital researchers, there is significant variability regarding how clinicians manage catheters placed in the arteries of patients in intensive care units. Some practices may increase risk of infection associated with these catheters. Fewer than half of those surveyed complied with current Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) infection prevention guidelines for arterial catheter insertions. The study was published today in Critical Care Medicine.
"Barrier precautions are employed inconsistently by critical care ...
Washington, DC - August 20, 2015 - Swedish exchange students who studied in India and in central Africa returned from their sojourns with an increased diversity of antibiotic resistance genes in their gut microbiomes. The research is published 10 August in Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
In the study, the investigators found a 2.6-fold increase in genes encoding resistance to sulfonamide, a 7.7-fold increase in trimethoprim resistance genes, and a 2.6-fold increase in resistance to beta-lactams, all of this without ...