Yale journal explores new environmental applications of ICT
2010-11-04
(Press-News.org) New Haven, Conn. -- New applications of information and communication technology (ICT) that could save society significant amounts of energy and money and reduce greenhouse gas emissions that are warming the planet are explored in a special issue of Yale's Journal of Industrial Ecology.
These applications exploit recent advances in ICT, such as social networking and Web 2.0, smart energy monitoring and geographic information systems, and are explored in depth in the special issue "Environmental Applications of ICT," published with support from the Leading Edge Forum of CSC, a global information technology services firm. The research examines the following:
computer models that estimate quantities and types of residential energy use with striking geographic detail—to the zip code level;
electronic systems that provide continuous appliance-level energy monitoring for households;
smart irrigation technologies that lower the associated costs of water use and carbon emissions
energy-saving electronic control systems for small- and medium-sized manufacturers;
applications of Web 2.0 for streamlining the organization of knowledge in industrial ecology; and
Internet-based modeling of carbon-reduction technologies for use in large cities.
Additional studies in the special issue assess the environmental impacts of the ICT and entertainment and media sectors, investigate digital music technology's potential for reducing carbon emissions, and estimate the net environmental impact—considering the positive and negative—of the ICT industry.
"It is easy to see that information and communication technology is transforming our society," says Sir Peter Crane, Dean of the Yale School of Forestry & Environmental Studies. "This research brings insight and clarity to less-obvious dimensions of their environmental impacts."
INFORMATION:The Journal of Industrial Ecology (www.wileyonlinelibrary.com/journal/jie) is a peer-reviewed, international bimonthly journal that examines the relationship between industry and the environment from the perspective of the emerging field of industrial ecology. It is owned by Yale University, headquartered at the Yale School of Forestry & Environmental Studies and published by Wiley-Blackwell.
Articles in the special issue are free on the Web at http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jiec.2010.14.issue-5/issuetoc. Journalists, students and representatives from developing countries or nongovernmental organizations can request a print copy of the special issue by writing to indecol@yale.edu.
Eric Masanet, acting deputy leader of the International Energy Studies Group at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, and H. Scott Matthews, professor of civil and environmental engineering and public policy at Carnegie Mellon University, served as guest editors for this special issue.
Funding for the special issue was provided by the Leading Edge Forum of CSC (www.csc.com), a global information technology services firm. The Leading Edge Forum (LEF www.lef.csc.com) is a research and advisory program, focusing on the intersection of business, IT and management.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2010-11-04
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite traveled over Tomas twice on Tuesday, Nov. 2. The second time was at 2005 UTC (4:05 p.m. EDT) when it was still classified as a tropical storm. During TRMM's second overpass, Tomas' center of circulation wasn't evident. Today, Nov. 3 that center is reforming.
During the morning hours on Nov. 3, an Air Force hurricane hunter aircraft found no tropical storm force winds so Tomas was downgraded by the National Hurricane Center to a tropical depression.
At 2 p.m. EDT on Nov. 3, Tomas was undergoing some changes, and ...
2010-11-04
VIDEO:
Two spiral galaxies undergo a protracted crash lasting two billion years, eventually merging into a single elliptical galaxy.
Click here for more information.
As scientists and engineers work to make NASA's James Webb Space Telescope a reality, they find themselves wondering what new sights the largest space-based observatory ever constructed will reveal. With Webb, astronomers aim to catch planets in the making and identify the universe's first stars and galaxies, yet ...
2010-11-04
NEW YORK (Nov. 3, 2010) -- Scientists at Weill Cornell Medical College have taken an important step toward a better understanding of prostate cancer by uncovering evidence that it is not one disease, as previously believed, but rather several factors which can be measured and, in the future, destroyed by targeted therapy.
The research team led by of Dr. Mark A. Rubin, the Homer T. Hirst Professor of Oncology in Pathology and vice chair for experimental pathology at Weill Cornell Medical College, identified secondary mutations that cause some types of prostate cancer ...
2010-11-04
More than 30 million people in the United States travel to resource-limited areas of the world each year. This global mobility may contribute to the spread of infectious diseases – such as influenza, measles, and meningitis – and may also put individual travelers at risk for malaria, typhoid, dengue fever and hepatitis. Despite these potential risks, a recent study conducted by the Division of Infectious Diseases at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and published in the Journal of Travel Medicine found that 46 percent of travelers to resource-limited countries did ...
2010-11-04
NEW YORK (Nov. 3, 2010) -- Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is a type of aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma that accounts for approximately 40 percent of lymphomas among adults. If left untreated, it is fatal. The existing treatments have a cure rate that is slightly over 50 percent but destroy healthy cells along with the cancer cells.
Researchers at Weill Cornell Medical College have found a combination therapy that is more effective than traditional treatments and is able to kill the cancer cells without harm to surrounding tissues. In a paper published in the ...
2010-11-04
CINCINNATI—Researchers at the University of Cincinnati (UC) and the Cincinnati Veterans Affairs (VA) Medical Center have found that about one-third of chronic kidney disease patients who are prescribed therapies for high blood pressure do not often adhere to treatments.
This report was published in the Nov. 2 online edition of the American Journal of Nephrology.
The study, led by researchers at UC and the Cincinnati VA, showed that treatment of hypertension in patients with chronic kidney disease continues to be a challenge in their care and that by simply improving ...
2010-11-04
Researchers at Mount Sinai School of Medicine have found that 98 percent of the U.S. population lives in communities within 60 minutes of a hospice provider, suggesting that disparities in use of hospice are not likely due to a lack of access to a hospice provider. The results are published in the current issue of the Journal of Palliative Medicine.
"Despite a significant increase in the availability of hospice services during the past decade, the majority of Americans die without hospice care," said Melissa D.A. Carlson, PhD, Assistant Professor of Geriatrics and Palliative ...
2010-11-04
VIDEO:
Video opens with footage of a common cornstarch and water experiment. Ian Oberst, a visiting student from Portland Community College who participated in the University of Oregon's UCORE program for...
Click here for more information.
Mix two parts cornstarch and one part water. Swirl your fingers in it slowly and the mixture is a smoothly flowing liquid. Punch it quickly with your fist and you meet a rubbery solid -- so solid you can jump up and down on a vat of it.
It ...
2010-11-04
Melt water flowing through ice sheets via crevasses, fractures and large drains called moulins can carry warmth into ice sheet interiors, greatly accelerating the thermal response of an ice sheet to climate change, according to a new study involving the University of Colorado at Boulder.
The new study showed ice sheets like the Greenland Ice Sheet can respond to such warming on the order of decades rather than the centuries projected by conventional thermal models. Ice flows more readily as it warms, so a warming climate can increase ice flows on ice sheets much faster ...
2010-11-04
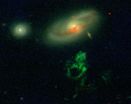
New Haven, Conn.—While sorting through hundreds of galaxy images as part of the Galaxy Zoo citizen science project two years ago, Dutch schoolteacher and volunteer astronomer Hanny van Arkel stumbled upon a strange-looking object that baffled professional astronomers. Two years later, a team led by Yale University researchers has discovered that the unique object represents a snapshot in time that reveals surprising clues about the life cycle of black holes.
In a new study, the team has confirmed that the unusual object, known as Hanny's Voorwerp (Hanny's "object" in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Yale journal explores new environmental applications of ICT