(Press-News.org) CAMBRIDGE, Mass., Nov. 3, 2010 -- The language we speak may influence not only our thoughts, but our implicit preferences as well. That's the finding of a study by psychologists at Harvard University, who found that bilingual individuals' opinions of different ethnic groups were affected by the language in which they took a test examining their biases and predilections.
The paper appears in the Journal of Experimental Social Psychology.
"Charlemagne is reputed to have said that to speak another language is to possess another soul," says co-author Oludamini Ogunnaike, a graduate student at Harvard. "This study suggests that language is much more than a medium for expressing thoughts and feelings. Our work hints that language creates and shapes our thoughts and feelings as well."
Implicit attitudes, positive or negative associations people may be unaware they possess, have been shown to predict behavior towards members of social groups. Recent research has shown that these attitudes are quite malleable, susceptible to factors such as the weather, popular culture -- or, now, by the language people speak.
"Can we shift something as fundamental as what we like and dislike by changing the language in which our preferences are elicited?" asks co-author Mahzarin R. Banaji, the Richard Clarke Cabot Professor of Social Ethics at Harvard. "If the answer is yes, that gives more support to the idea that language is an important shaper of attitudes."
Ogunnaike, Banaji, and Yarrow Dunham, now at the University of California, Merced, used the well-known Implicit Association Test (IAT), where participants rapidly categorize words that flash on a computer screen or are played through headphones. The test gives participants only a fraction of a second to categorize words, not enough to think about their answers.
"The IAT bypasses a large part of conscious cognition and taps into something we're not aware of and can't easily control," Banaji says.
The researchers administered the IAT in two different settings: once in Morocco, with bilinguals in Arabic and French, and again in the U.S. with Latinos who speak both English and Spanish.
In Morocco, participants who took the IAT in Arabic showed greater preference for other Moroccans. When they took the test in French, that difference disappeared. Similarly, in the U.S., participants who took the test in Spanish showed a greater preference for other Hispanics. But again, in English, that preference disappeared.
"It was quite shocking to see that a person could take the same test, within a brief period of time, and show such different results," Ogunnaike says. "It's like asking your friend if he likes ice cream in English, and then turning around and asking him again in French and getting a different answer."
In the Moroccan test, participants saw "Moroccan" names (such as Hassan or Fatimah) or "French" names (such as Jean or Marie) flash on a monitor, along with words that are "good" (such as happy or nice) or "bad" (such as hate or mean). Participants might press one key when they see a Moroccan name or a good word, and press another when they see a French name or a bad word. Then the key assignments are switched so that "Moroccan" and "bad" share the same key and "French" and "good" share the other.
Linguist Benjamin Lee Whorf first posited in the 1930s that language is so powerful that it can determine thought. Mainstream psychology has taken the more skeptical view that while language may affect thought processes, it doesn't influence thought itself. This new study suggests that Whorf's idea, when not caricatured, may generate interesting hypotheses that researchers can continue to test.
"These results challenge our views of attitudes as stable," Banaji says. "There still remain big questions about just how fixed or flexible they are, and language may provide a window through which we will learn about their nature."
INFORMATION:
Ogunnaike, Dunham, and Banaji's work was supported by Harvard's Weatherhead Center for International Affairs and the Mellon Mays Foundation.
Language appears to shape our implicit preferences
Study of bilinguals hints language may help create, not just convey, thoughts and feelings
2010-11-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers expand cyberspace to fight chronic condition in breast cancer survivors
2010-11-04
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Lymphedema is a chronic condition that causes swelling of the limbs and affects physical, mental and social health. It commonly occurs in breast cancer survivors and is the second-most dreaded effect of treatment, after cancer recurrence. Every day, researchers throughout the world learn more about the condition and how it can be treated. Now, University of Missouri researchers are developing a place in cyberspace where relevant and timely information can be easily stored, searched, and reviewed from anywhere with the goal of improving health care through ...
Earth's climate change 20,000 years ago reversed the circulation of the Atlantic Ocean
2010-11-04
The Atlantic Ocean circulation (termed meridional overturning circulation, MOC) is an important component of the climate system. Warm currents, such as the Gulf Stream, transport energy from the tropics to the subpolar North Atlantic and influence regional weather and climate patterns. Once they arrive in the North the currents cool, their waters sink and with them they transfer carbon from the atmosphere to the abyss. These processes are important for climate but the way the Atlantic MOC responds to climate change is not well known yet.
An international team of investigators ...
Psyllid identification key to area-wide control of citrus greening spread
2010-11-04
At least six psyllid species have been found in the citrus-growing areas of the Rio Grande Valley of Texas, according to a U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) scientist who is working to control the spread of the psyllid-transmitted citrus greening disease.
A few years ago, citrus growers in south Texas noticed a new insect, the Asian citrus psyllid, on their citrus trees. This was a cause for concern, because this tiny pest is responsible for transmitting citrus greening, also known as Huanglongbing (HLB). The disease was first detected in Florida in 2005 and now ...
Main squeeze not needed for boa mom
2010-11-04
In a finding that upends decades of scientific theory on reptile reproduction, researchers at North Carolina State University have discovered that female boa constrictors can squeeze out babies without mating.
More strikingly, the finding shows that the babies produced from this asexual reproduction have attributes previously believed to be impossible.
Large litters of all-female babies produced by the "super mom" boa constrictor show absolutely no male influence – no genetic fingerprint that a male was involved in the reproductive process. All the female babies ...
UGA study finds moving animals not a panacea for habitat loss
2010-11-04
Athens, Ga. – New University of Georgia research suggests moving threatened animals to protected habitats may not always be an effective conservation technique if the breeding patterns of the species are influenced by a social hierarchy.
Research, published in the early online edition of the journal Biological Conservation, found an initial group of gopher tortoises released on St. Catherine's Island, Ga. were three times more likely to produce offspring than a later-introduced group, although the initial group had a much smaller proportion of reproduction-aged males.
"There ...
Most river flows across the US are altered by land and water management
2010-11-04
The amount of water flowing in streams and rivers has been significantly altered in nearly 90 percent of waters that were assessed in a new nationwide USGS study. Flow alterations are a primary contributor to degraded river ecosystems and loss of native species.
"This USGS assessment provides the most geographically extensive analysis to date of stream flow alteration," said Bill Werkheiser, USGS Associate Director for Water. "Findings show the pervasiveness of stream flow alteration resulting from land and water management, the significant impact of altered stream ...
The developmental dynamics of the maize leaf transcriptome
2010-11-04
Photosynthesis is arguably the most impressive feat of nature, where plants harvest light energy and convert it into the building blocks of life at fantastically high efficiency. Indeed modern civilization became possible only with the cultivation of plants for food, shelter and clothing.
While scientists have been able to discover details of the fascinating process by which plants store solar energy as chemical energy, how developing plants build and regulate their solar reactors is still poorly understood. How many genes are involved, and which are the most important? ...
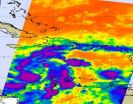
Tropical Storm Anggrek is tightly wrapped in NASA satellite imagery
2010-11-04
Bands of strong thunderstorms are wrapping around the center of Tropical Storm Anggrek in the Southern Indian Ocean, according to satellite imagery. NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared look at those strong thunderstorms today.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Anggrek on Nov. 3 at 07:05 UTC (3:05 a.m. EDT) and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument onboard captured an infrared image of the cold thunderstorms within the system. The image showed that strong, high thunderstorm cloud tops tightly circled the storm's center. There was also strong convection ...
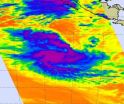
NASA satellite sees Tomas weaken to a tropical depression ... for now
2010-11-04
NASA infrared satellite data from this morning revealed that Tropical Storm Tomas has weakened into a tropical depression.
Tomas is in the central Caribbean Sea headed for Haiti this weekend, and forecasters are calling for a re-intensification before it makes landfall.
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) in Miami, Fla. reported at 5 a.m. EDT on Nov. 3 that hurricane hunter aircraft found an "ill-defined and elongated circulation with no tropical storm-force winds at the flight level or the surface." Thus, the status of Tomas was changed from a tropical storm to a ...
Volcanoes have shifted Asian rainfall
2010-11-04
Scientists have long known that large volcanic explosions can affect the weather by spewing particles that block solar energy and cool the air. Some suspect that extended "volcanic winters" from gigantic blowups helped kill off dinosaurs and Neanderthals. In the summer following Indonesia's 1815 Tambora eruption, frost wrecked crops as far off as New England, and the 1991 blowout of the Philippines' Mount Pinatubo lowered average global temperatures by 0.7 degrees F—enough to mask the effects of manmade greenhouse gases for a year or so.
Now, scientists have shown ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
[Press-News.org] Language appears to shape our implicit preferencesStudy of bilinguals hints language may help create, not just convey, thoughts and feelings