(Press-News.org) When a University of Oklahoma researcher and an international team of experts analyzed the dental calculus or plaque from teeth preserved for 1,000 years, the results revealed human health and dietary information never seen before. The team discovered disease-causing bacteria in a German Medieval population, which is the same or very similar to inflammatory disease-causing bacteria in humans today—unlikely scientific results given modern hygiene and dental health practices.
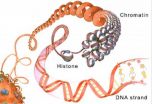
Christina Warinner, research associate in the Molecular Anthropologies Laboratories, OU College of Arts and Sciences, assembled an international team of experts using the most cutting-edge technology available to build a detailed picture of people from the Medieval period by extracting DNA from samples of the dental calculus. The samples were small, but dental calculus has a thousand times more DNA than bone. Warinner and her team also looked at and analyzed the protein in the samples for an even more detailed look.
"Through protein sequencing, we can reconstruct infection and immune processes. It is like excavating a battlefield archaeological site, just at a molecular scale," says Enrico Cappellini, a senior researcher from the University of Copenhagen in Denmark.
"What makes dental calculus so unique," according to Warinner, "is that it acts both as a long-term reservoir of the oral microbiome and as a trap for dietary and environmental debris. This allows us to investigate health and disease, as well as reconstruct aspects of an individual's life history and activities. Never before have we been able to retrieve so much information from one small sample."
Warinner's research grew from the need for more health and dietary information, but now she wants to know why the inflammatory disease-causing bacteria found in a Medieval population also causes periodontal disease in 13 percent of humans today. Why are humans even susceptible to periodontal disease, when most animals do not get periodontal disease? Is it human behavior or something else that contributes to chronic inflammatory disease in humans? Warinner says the archaeological record provides clues.
Matthew Collins, a researcher from the University of York in the United Kingdom, says, "The preservation of biomolecules in dental calculus is remarkable — a microbial Pompeii." He added, "As we learn more about the evolution of the oral microbiome, I can imagine a future in which most archaeologists regard calculus as more interesting than the teeth themselves."
Warinner's research was initially considered high-risk because no one knew what, if anything, would be preserved in dental calculus. The results were significant and have contributed valuable information on the long-term relationship between humans and their resident microbes. "The study of ancient microbiomes helps us understand the evolutionary history of human health and disease," says Frank Rühli, director of the Centre for Evolutionary Medicine at the University of Zürich. "It informs modern medicine."
INFORMATION:
A journal article on this research was published in the February 23, 2014, issue of Nature Genetics and is available at http://www.nature.com/ng. For more information about Warinner's recent or forthcoming research, please email her at Christina.warinner@ou.edu.
OU researcher and team discover disease-causing bacteria in dental plaque preserved for 1,000 years
Bacteria found similar to bacteria in oral cavities of humans today
2014-02-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Gauging what it takes to heal a disaster-ravaged forest
2014-02-24
Recovering from natural disasters usually means rebuilding infrastructure and reassembling human lives. Yet ecologically sensitive areas need to heal, too, and scientists are pioneering new methods to assess nature's recovery and guide human intervention.
The epicenter of China's devastating Wenchuan earthquake in 2008 was in the Wolong Nature Reserve, a globally important valuable biodiversity hotspot and home to the beloved and endangered giant pandas. Not only did the quake devastate villages and roads, but the earth split open and swallowed sections of the forests ...
Penn researchers 'design for failure' with model material
2014-02-24
When deciding what materials to use in building something, determining how those materials respond to stress and strain is often the first task. A material's macroscopic, or bulk, properties in this area — whether it can spring back into shape, for example — is generally the product of what is happening on a microscopic scale. When stress causes a material's constituent molecules to rearrange in a way such that they can't go back to their original positions, it is known as "plastic deformation."
Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania have devised a method to study ...
Parents' attitudes about helping their grown children affect their mental health
2014-02-24
Older parents frequently give help to their middle-aged offspring, and their perceptions about giving this help may affect their mental health, according to a team of researchers.
"We usually view the elderly as needy, but our research shows that parents ages 60 and over are giving help to their children, and this support is often associated with lower rates of depression among the older adults," said Lauren Bangerter, Ph.D. student in human development and family studies, Penn State.
The team -- which included researchers at Penn State, the University of Texas ...
Specialized cognitive therapy improves blood sugar control in depressed diabetes patients
2014-02-24
Although maintaining good blood sugar control is crucial for avoiding complications of diabetes, it has been estimated that only about half of patients are successful in meeting target blood glucose levels. The prevalence of depression among diabetes patients – up to twice as high as in the general population – can interfere with patients' ability to manage their diabetes. Now a group of Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) investigators report that a program of cognitive behavioral therapy that addresses both mood and diabetes self-care led to improved blood sugar control ...
Almost 200 new species of parasitoid wasps named after local parataxonomists in Costa Rica
2014-02-24
An inventory of wild-caught caterpillars, its food plants and parasitoids, has been going on for more than 34 years in Area de Conservación Guanacaste (ACG), a protected area of approximately 1200 km2 in northwestern Costa Rica. As a result, more than 10,000 species of moths and butterflies are estimated to live in ACG. Their caterpillars are in turn attacked by many parasitoid wasps, also numbering thousands of species. However, most of those wasps have never been described and remain unknown.
For the past few years researchers from Canada, Costa Rica and the United ...
New technology detect cellular memory
2014-02-24
Cells in our body are constantly dividing to maintain our body functions. At each division, our DNA code and a whole machinery of supporting components has to be faithfully duplicated to maintain the cell's memory of its own identity. Researchers at BRIC, University of Copenhagen, have developed a new technology that has revealed the dynamic events of this duplication process and the secrets of cellular memory. The results are published in Nature Cell Biology.
In 2009, two women at BRIC, University of Copenhagen joined forces to develop a new technology that could elucidate ...
Researchers make the invisible visible
2014-02-24
The 2003 development of the so-called hyperpolarization technique by a Danish research was a groundbreaking moment that made it possible to see all the body's cells with the help of a new contrast agent for MRI scans. Researchers from Aarhus have now taken another big step towards understanding the body's cells and with it also the development of diseases:
"With the hyperpolarization method, sensitivity to specific contrast agents is up to 10,000 times higher than with a traditional MRI scanning. What we have now documented is that with the hyperpolarization MRI scanning ...
Team converts sugarcane to a cold-tolerant, oil-producing crop
2014-02-24
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — A multi-institutional team reports that it can increase sugarcane's geographic range, boost its photosynthetic rate by 30 percent and turn it into an oil-producing crop for biodiesel production.
These are only the first steps in a bigger initiative that will turn sugarcane and sorghum – two of the most productive crop plants known – into even more productive, oil-generating plants.
The team will present its latest findings Tuesday (Feb. 25) at the U.S. Department of Energy's ARPA-E Energy Innovation Summit in Washington, D.C.
"Biodiesel is attractive ...
Pointing is infants' first communicative gesture
2014-02-24
VIDEO:
Catalan researchers have studied the acquisition and development of language in babies on the basis of the temporary coordination of gestures and speech. The results are the first in showing...
Click here for more information.
Catalan researchers have studied the acquisition and development of language in babies on the basis of the temporary coordination of gestures and speech. The results are the first in showing how and when they acquire the pattern of coordination ...
The chemistry of Sriracha: Hot sauce science
2014-02-24
WASHINGTON, Feb. 24, 2014 — Forget ketchup and mustard — Sriracha might be the world's new favorite condiment. Beloved by millions for its unique spicy, garlicky, slightly sweet flavor, the chemistry of "rooster sauce" is the subject of the American Chemical Society's latest Reactions video. The video is available at http://youtu.be/U2DJN0gnuI8.
INFORMATION:
Subscribe to the series at Reactions YouTube, and follow us on Twitter @ACSreactions to be the first to see our latest videos.
The American Chemical Society is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
[Press-News.org] OU researcher and team discover disease-causing bacteria in dental plaque preserved for 1,000 yearsBacteria found similar to bacteria in oral cavities of humans today