(Press-News.org) Along with eggs, soup and rubber toys, the list of the chicken's most lasting legacies may eventually include advanced materials such as self-organizing colloids, or optics that can transmit light with the efficiency of a crystal and the flexibility of a liquid.
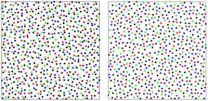
The unusual arrangement of cells in a chicken's eye constitutes the first known biological occurrence of a potentially new state of matter known as "disordered hyperuniformity," according to researchers from Princeton University and Washington University in St. Louis. Research in the past decade has shown that disordered hyperuniform materials have unique properties when it comes to transmitting and controlling light waves, the researchers report in the journal Physical Review E.
States of disordered hyperuniformity behave like crystal and liquid states of matter, exhibiting order over large distances and disorder over small distances. Like crystals, these states greatly suppress variations in the density of particles — as in the individual granules of a substance — across large spatial distances so that the arrangement is highly uniform. At the same time, disordered hyperuniform systems are similar to liquids in that they have the same physical properties in all directions. Combined, these characteristics mean that hyperuniform optical circuits, light detectors and other materials could be controlled to be sensitive or impervious to certain light wavelengths, the researchers report.
"Disordered hyperuniform materials possess a hidden order," explained co-corresponding author Salvatore Torquato, a Princeton professor of chemistry. It was Torquato who, with Frank Stillinger, a senior scientist in Princeton's chemistry department, first identified hyperuniformity in a 2003 paper in Physical Review E.
"We've since discovered that such physical systems are endowed with exotic physical properties and therefore have novel capabilities," Torquato said. "The more we learn about these special disordered systems, the more we find that they really should be considered a new distinguishable state of matter."
The researchers studied the light-sensitive cells known as cones that are in the eyes of chickens and most other birds active in daytime. These birds have four types of cones for color — violet, blue, green and red — and one type for detecting light levels, and each cone type is a different size. The cones are packed into a single layer of eye tissue called the epithelium, but not in nature's usual way, the researchers report.
In many creatures' eyes, visual cells are evenly distributed in an obvious pattern such as the familiar hexagonal compact eyes of insects. In many creatures, the different types of cones are laid out so that they are not near cones of the same type. At first glance, however, the chicken eye appears to have a scattershot of cones distributed in no particular order.
The lab of co-corresponding author Joseph Corbo, an associate professor of pathology and immunology, and genetics at Washington University in St. Louis, studies how the chicken's unusual visual layout evolved. Thinking that perhaps it had something to do with how the cones are packed into such a small space, Corbo approached Torquato, whose group studies the geometry and dynamics of densely packed objects such as particles.
Torquato then worked with the paper's first author Yang Jiao, who received his Ph.D. in mechanical and aerospace engineering from Princeton in 2010 and is now an assistant professor of materials science and engineering at Arizona State University. Torquato and Jiao developed a computer-simulation model that went beyond standard packing algorithms to mimic the final arrangement of chicken cones and allowed them to see the underlying method to the madness.
It turned out that each type of cone has an area around it called an "exclusion region" that other cones cannot enter. Cones of the same type shut out each other more than they do unlike cones, and this variant exclusion causes distinctive cone patterns. Each type of cone's pattern overlays the pattern of another cone so that the formations are intertwined in an organized but disordered way — a kind of uniform disarray. So, while it appeared that the cones were irregularly placed, their distribution was actually uniform over large distances. That's disordered hyperuniformity, Torquato said.
"Because the cones are of different sizes it's not easy for the system to go into a crystal or ordered state," Torquato said. "The system is frustrated from finding what might be the optimal solution, which would be the typical ordered arrangement. While the pattern must be disordered, it must also be as uniform as possible. Thus, disordered hyperuniformity is an excellent solution."
The researchers' findings add a new dimension called multi-hyperuniformity. This means that the elements that make up the arrangement are themselves hyperuniform. While individual cones of the same type appear to be unconnected, they are actually subtly linked by exclusion regions, which they use to self-organize into patterns. Multi-hyperuniformity is crucial for the avian system to evenly sample incoming light, Torquato said. He and his co-authors speculate that this behavior could provide a basis for developing materials that can self-assemble into a disordered hyperuniform state.
"You also can think of each one of these five different visual cones as hyperuniform," Torquato said. "If I gave you the avian system with these cones and removed the red, it's still hyperuniform. Now, let's remove the blue — what remains is still hyperuniform. That's never been seen in any system, physical or biological. If you had asked me to recreate this arrangement before I saw this data I might have initially said that it would be very difficult to do."
The discovery of hyperuniformity in a biological system could mean that the state is more common than previously thought, said Remi Dreyfus, a researcher at the Pennsylvania-based Complex Assemblies of Soft Matter lab (COMPASS) co-run by the University of Pennsylvania, the French National Centre for Scientific Research and the French chemical company Solvay. Previously, disordered hyperuniformity had only been observed in specialized physical systems such as liquid helium, simple plasmas and densely packed granules.
"It really looks like this idea of hyperuniformity, which started from a theoretical basis, is extremely general and that we can find them in many places," said Dreyfus, who is familiar with the research but had no role in it. "I think more and more people will look back at their data and figure out whether there is hyperuniformity or not. They will find this kind of hyperuniformity is more common in many physical and biological systems."
The findings also provide researchers with a detailed natural model that could be useful in efforts to construct hyperuniform systems and technologies, Dreyfus said. "Nature has found a way to make multi-hyperuniformity," he said. "Now you can take the cue from what nature has found to create a multi-hyperuniform pattern if you intend to."
Evolutionarily speaking, the researchers' results show that nature found a unique workaround to the problem of cramming all those cones into the compact avian eye, Corbo said. The ordered pattern of cells in most other animals' eyes are thought to be the "optimal" arrangement, and anything less would result in impaired vision. Yet, birds with the arrangement studied here — including chickens — have impeccable vision, Corbo said.
"These findings are significant because they suggest that the arrangement of photoreceptors in the bird, although not perfectly regular, are, in fact, as regular as they can be given the packing constraints in the epithelium," Corbo said.
"This result indicates that evolution has driven the system to the 'optimal' arrangement possible, given these constraints," he said. "We still know nothing about the cellular and molecular mechanisms that underlie this beautiful and highly organized arrangement in birds. So, future research directions will include efforts to decipher how these patterns develop in the embryo."
INFORMATION:
The paper, "Avian photoreceptor patterns represent a disordered hyperuniform solution to a multiscale packing problem," was published Feb. 24 in Physical Review E. The work was supported by grants from the National Science Foundation (grant no. DMS-1211087), National Cancer Institute (grant no. U54CA143803); the National Institutes of Health (grant nos. EY018826, HG006346 and HG006790); the Human Frontier Science Program; the German Research Foundation (DFG); and the Simons Foundation (grant no. 231015).
In the eye of a chicken, a new state of matter comes into view
2014-02-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Watching how the brain works
2014-02-24
Coral Gables, Fla (Feb. 19, 2014) -- There are more than a trillion cells called neurons that form a labyrinth of connections in our brains. Each of these neurons contains millions of proteins that perform different functions. Exactly how individual proteins interact to form the complex networks of the brain still remains as a mystery that is just beginning to unravel.
For the first time, a group of scientists has been able to observe intact interactions between proteins, directly in the brain of a live animal. The new live imaging approach was developed by a team of ...
Costs vary widely for care of children with congenital heart defects across US hospitals
2014-02-24
Ann Arbor, Mich. – Costs of care differ significantly across hospitals for children born with heart defects, according to new research led by a University of Michigan researcher. Congenital heart defects are known to be the most common birth defects, impacting nearly 1 in every 100 births.
The cost of care for children with congenital heart disease undergoing surgical repair varied as much as nine times across a large group of U.S. children's hospitals, says lead author Sara K. Pasquali, M.D., M.H.S., associate professor of pediatrics at the University of Michigan Medical ...
Opioid abuse initiates specific protein interactions in neurons in brain's reward system
2014-02-24
(New York) – Identifying the specific pathways that promote opioid addiction, pain relief, and tolerance are crucial for developing more effective and less dangerous analgesics, as well as developing new treatments for addiction. Now, new research from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai reveals that opiate use alters the activity of a specific protein needed for the normal functioning of the brain's reward center. Investigators were able to block the protein, as well as increase its expression in the mouse nucleus accumbens, a key component of the brain's reward ...
Abdominal fat accumulation prevented by unsaturated fat
2014-02-24
New research from Uppsala University shows that saturated fat builds more fat and less muscle than polyunsaturated fat. This is the first study on humans to show that the fat composition of food not only influences cholesterol levels in the blood and the risk of cardiovascular disease but also determines where the fat will be stored in the body. The findings have recently been published in the American journal Diabetes.
The study involved 39 young adult men and women of normal weight, who ate 750 extra calories per day for seven weeks. The goal was for them to gain three ...
Medical researchers use light to quickly and easily measure blood's clotting properties
2014-02-24
VIDEO:
This video shows the rapid "twinkling " or intensity fluctuations of the speckle pattern in a drop of unclotted whole blood. The rapid "twinkling " is due to the fast thermally-driven motion...
Click here for more information.
WASHINGTON, Feb. 24—Defective blood coagulation is one of the leading causes of preventable death in patients who have suffered trauma or undergone surgery. The body's natural defense against severe blood loss is the clotting ...
NIST microanalysis technique makes the most of small nanoparticle samples
2014-02-24
Researchers from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) have demonstrated that they can make sensitive chemical analyses of minute samples of nanoparticles by, essentially, roasting them on top of a quartz crystal. The NIST-developed technique, "microscale thermogravimetric analysis," holds promise for studying nanomaterials in biology and the environment, where sample sizes often are quite small and larger-scale analysis won't work.*
Chemical analysis of nanoparticles is a challenging task, and not just because ...
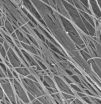
New biological scaffold offers promising foundation for engineered tissues
2014-02-24
Our cells don't live in a vacuum. They are surrounded by a complex, nurturing matrix that is essential for many biological functions, including growth and healing.
In all multicellular organisms, including people, cells make their own extracellular matrix. But in the lab, scientists attempting to grow tissue must provide a scaffold for cells to latch onto as they grow and proliferate. This engineered tissue has potential to repair or replace virtually any part of our bodies.
Typically, researchers construct scaffolds from synthetic materials or natural animal or human ...
Is previous hypoglycemia a risk factor for future hypoglycemic episodes?
2014-02-24
New Rochelle, NY, February 24, 2014—The automatic "threshold suspend" (TS) feature of an insulin pump helps prevent life-threatening hypoglycemic events when the device's sensor detects blood glucose concentrations below the preset threshold. However, in individuals with type 1 diabetes who have had previous episodes of hypoglycemia the TS feature may be less effective at preventing subsequent events, according to important new results from the ASPIRE study published in Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics (DTT), a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. ...
Vitamin water: Measuring essential nutrients in the ocean
2014-02-24
The phrase, 'Eat your vitamins,' applies to marine animals just like humans. Many vitamins, including B-12, are elusive in the ocean environment.
University of Washington researchers used new tools to measure and track B-12 vitamins in the ocean. Once believed to be manufactured only by marine bacteria, the new results show that a whole different class of organism, archaea, can supply this essential vitamin. The results were presented Feb. 24 at the Ocean Sciences meeting in Honolulu.
"The dominant paradigm has been bacteria are out there, making B-12, but it turns ...
OU researcher and team discover disease-causing bacteria in dental plaque preserved for 1,000 years
2014-02-24
When a University of Oklahoma researcher and an international team of experts analyzed the dental calculus or plaque from teeth preserved for 1,000 years, the results revealed human health and dietary information never seen before. The team discovered disease-causing bacteria in a German Medieval population, which is the same or very similar to inflammatory disease-causing bacteria in humans today—unlikely scientific results given modern hygiene and dental health practices.
Christina Warinner, research associate in the Molecular Anthropologies Laboratories, OU College ...