(Press-News.org) Our cells don't live in a vacuum. They are surrounded by a complex, nurturing matrix that is essential for many biological functions, including growth and healing.
In all multicellular organisms, including people, cells make their own extracellular matrix. But in the lab, scientists attempting to grow tissue must provide a scaffold for cells to latch onto as they grow and proliferate. This engineered tissue has potential to repair or replace virtually any part of our bodies.
Typically, researchers construct scaffolds from synthetic materials or natural animal or human substances. All have their strengths and weaknesses, but no scaffolds grown in a Petri dish have been able to mimic the highly organized structure of the matrix made by living things, at least until now.
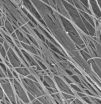
Feng Zhao of Michigan Technological University has persuaded fibroblasts, cells that makes the extracellular matrix, to make just such a well-organized scaffold. Its fibers are a mere 80 nanometers across, similar to fibers in a natural matrix. And, since her scaffold is made by cells, it is composed of the same intricate mix of all-natural proteins and sugars found in the body. Plus, its nanofibers are as highly aligned as freshly combed hair.
The trick was to orient the cells on a nano-grate that guided their growth—and the creation of the scaffold.
"The cells did the work," Zhao said. "The material they made is quite uniform, and of course it is completely biological."
Stem cells placed on her scaffold thrived, and it had the added advantage of provoking a very low immune response.
"We think this has great potential," she said. "I think we could use this to engineer softer tissues, like skin, blood vessels and muscle."
INFORMATION:
The work is described in the paper "Highly Aligned Nanofibrous Scaffold Derived from Decellularized Human Fibroblasts," coauthored by Zhao, postdoctoral researcher Qi Xing and undergraduate Caleb Vogt of Michigan Technological University and Kam W. Leong of Duke University and published Jan. 29 in Advanced Functional Materials. Zhao designed the project. Xing and Vogt did the work, and Leong developed the template for cell growth.
The work was funded by the National Institutes of Health (1R15HL115521-01A1), the Flight Attendant Medical Research Institute (062518-YCSA) and Michigan Technological University.
New biological scaffold offers promising foundation for engineered tissues
Cells set up housekeeping on highly aligned nanofibers
2014-02-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Is previous hypoglycemia a risk factor for future hypoglycemic episodes?
2014-02-24
New Rochelle, NY, February 24, 2014—The automatic "threshold suspend" (TS) feature of an insulin pump helps prevent life-threatening hypoglycemic events when the device's sensor detects blood glucose concentrations below the preset threshold. However, in individuals with type 1 diabetes who have had previous episodes of hypoglycemia the TS feature may be less effective at preventing subsequent events, according to important new results from the ASPIRE study published in Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics (DTT), a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. ...
Vitamin water: Measuring essential nutrients in the ocean
2014-02-24
The phrase, 'Eat your vitamins,' applies to marine animals just like humans. Many vitamins, including B-12, are elusive in the ocean environment.
University of Washington researchers used new tools to measure and track B-12 vitamins in the ocean. Once believed to be manufactured only by marine bacteria, the new results show that a whole different class of organism, archaea, can supply this essential vitamin. The results were presented Feb. 24 at the Ocean Sciences meeting in Honolulu.
"The dominant paradigm has been bacteria are out there, making B-12, but it turns ...
OU researcher and team discover disease-causing bacteria in dental plaque preserved for 1,000 years
2014-02-24
When a University of Oklahoma researcher and an international team of experts analyzed the dental calculus or plaque from teeth preserved for 1,000 years, the results revealed human health and dietary information never seen before. The team discovered disease-causing bacteria in a German Medieval population, which is the same or very similar to inflammatory disease-causing bacteria in humans today—unlikely scientific results given modern hygiene and dental health practices.
Christina Warinner, research associate in the Molecular Anthropologies Laboratories, OU College ...
Gauging what it takes to heal a disaster-ravaged forest
2014-02-24
Recovering from natural disasters usually means rebuilding infrastructure and reassembling human lives. Yet ecologically sensitive areas need to heal, too, and scientists are pioneering new methods to assess nature's recovery and guide human intervention.
The epicenter of China's devastating Wenchuan earthquake in 2008 was in the Wolong Nature Reserve, a globally important valuable biodiversity hotspot and home to the beloved and endangered giant pandas. Not only did the quake devastate villages and roads, but the earth split open and swallowed sections of the forests ...
Penn researchers 'design for failure' with model material
2014-02-24
When deciding what materials to use in building something, determining how those materials respond to stress and strain is often the first task. A material's macroscopic, or bulk, properties in this area — whether it can spring back into shape, for example — is generally the product of what is happening on a microscopic scale. When stress causes a material's constituent molecules to rearrange in a way such that they can't go back to their original positions, it is known as "plastic deformation."
Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania have devised a method to study ...
Parents' attitudes about helping their grown children affect their mental health
2014-02-24
Older parents frequently give help to their middle-aged offspring, and their perceptions about giving this help may affect their mental health, according to a team of researchers.
"We usually view the elderly as needy, but our research shows that parents ages 60 and over are giving help to their children, and this support is often associated with lower rates of depression among the older adults," said Lauren Bangerter, Ph.D. student in human development and family studies, Penn State.
The team -- which included researchers at Penn State, the University of Texas ...
Specialized cognitive therapy improves blood sugar control in depressed diabetes patients
2014-02-24
Although maintaining good blood sugar control is crucial for avoiding complications of diabetes, it has been estimated that only about half of patients are successful in meeting target blood glucose levels. The prevalence of depression among diabetes patients – up to twice as high as in the general population – can interfere with patients' ability to manage their diabetes. Now a group of Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) investigators report that a program of cognitive behavioral therapy that addresses both mood and diabetes self-care led to improved blood sugar control ...
Almost 200 new species of parasitoid wasps named after local parataxonomists in Costa Rica
2014-02-24
An inventory of wild-caught caterpillars, its food plants and parasitoids, has been going on for more than 34 years in Area de Conservación Guanacaste (ACG), a protected area of approximately 1200 km2 in northwestern Costa Rica. As a result, more than 10,000 species of moths and butterflies are estimated to live in ACG. Their caterpillars are in turn attacked by many parasitoid wasps, also numbering thousands of species. However, most of those wasps have never been described and remain unknown.
For the past few years researchers from Canada, Costa Rica and the United ...
New technology detect cellular memory
2014-02-24
Cells in our body are constantly dividing to maintain our body functions. At each division, our DNA code and a whole machinery of supporting components has to be faithfully duplicated to maintain the cell's memory of its own identity. Researchers at BRIC, University of Copenhagen, have developed a new technology that has revealed the dynamic events of this duplication process and the secrets of cellular memory. The results are published in Nature Cell Biology.
In 2009, two women at BRIC, University of Copenhagen joined forces to develop a new technology that could elucidate ...
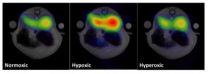
Researchers make the invisible visible
2014-02-24
The 2003 development of the so-called hyperpolarization technique by a Danish research was a groundbreaking moment that made it possible to see all the body's cells with the help of a new contrast agent for MRI scans. Researchers from Aarhus have now taken another big step towards understanding the body's cells and with it also the development of diseases:
"With the hyperpolarization method, sensitivity to specific contrast agents is up to 10,000 times higher than with a traditional MRI scanning. What we have now documented is that with the hyperpolarization MRI scanning ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
[Press-News.org] New biological scaffold offers promising foundation for engineered tissuesCells set up housekeeping on highly aligned nanofibers