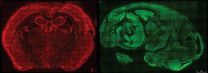
(Press-News.org) Australian astronomers have discovered what makes some spiral galaxies fat and bulging while others are flat discs — and it's all about how fast they spin.
The research, led by the International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research (ICRAR) in Perth, found that fast-rotating spiral galaxies are flat and thin while equally sized galaxies that rotate slowly are fatter.
The study was published today in the prestigious Astrophysical Journal and was part of "The Evolving Universe" research theme of the ARC Centre of Excellence for All-sky Astrophysics (CAASTRO).
ICRAR Research Associate Professor Danail Obreschkow, from The University of Western Australia, said it is a much-debated mystery why galaxies look so different to each other.
"Some galaxies are very flat discs of stars and others are more bulging or even spherical," he said.
"Much of the last century of research has been dedicated to understanding this diversity of galaxies in the Universe and with this paper we've made a step towards understanding how this came about by showing that the rotation of spiral galaxies is a key driver for their shape."
The study looked at 16 galaxies — all between 10 million and 50 million light years from Earth — using data from a survey called THINGS.
"The THINGS survey shows you the cold gas in the galaxies, not only where it is but how it moves," Dr Obreschkow said.
"That's a crucial point if you want to measure the spin, you can't just take a photograph, you have to take a special picture that shows you the motion."
Dr Obreschkow said the shape of a spiral galaxy is determined by both its spin and its mass and if you leave a galaxy on its own for billions of years both quantities will stay the same.
He said the way galaxies are formed looks a bit similar to a carousel made of an elastic disc.
"If the carousel is at rest, the elastic disc is quite small," Dr Obreschkow said.
"But when the whole thing is spinning the elastic disc becomes larger because it's feeling the effects of centrifugal force."
Our own Milky Way is a relatively flat disc with only a small bulge, the shape of which can be seen in the night sky.
"The white band of the Milky Way across the sky is a relatively thin band of constant thickness. However when you look right at the centre near the Sagittarius constellation you can actually see a thickening of the Milky Way, which is the bulge," Dr Obreschkow said.
He and co-author, Swinburne University Professor Karl Glazebrook, were able to measure the effect of spin on galaxies more than ten times better than anyone previously.
The study used data collected at the Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array in the United States, one of the most famous radio telescopes in the world and a significant pathfinder for the Square Kilometre Array.
INFORMATION:
Further Information:
ICRAR is a joint venture between Curtin University and The University of Western Australia that receives funding from the State Government of Western Australia.
CAASTRO is a collaboration between Curtin University, The University of Western Australia, the University of Sydney, the Australian National University, the University of Melbourne, Swinburne University of Technology and the University of Queensland.
It is funded under the Australian Research Council Centre of Excellence program and receives additional funding from the seven participating universities and the NSW State Government Science Leveraging Fund.
Original publication:
"Fundamental Mass-Spin-Morphology Relation of Spiral Galaxies" The Astrophysical Journal, 28/2/2014. Full text available on request.
Fat or flat: Getting galaxies into shape
2014-02-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Purification, culture and multi-lineage differentiation of zebrafish neural crest cells
2014-02-27
Researchers at the Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH)/Harvard Medical School, Drs. Beste Kinikoglu and Yawei Kong, led by Dr. Eric C. Liao, cultured and characterized for the first time multipotent neural crest cells isolated from zebrafish embryos. This important study is reported in the February 2014 issue of Experimental Biology and Medicine. Neural crest is a unique cell population induced at the lateral border of the neural plate during embryogenesis and vertebrate development depends on these multipotent migratory cells. Defects in neural crest development result ...
Targeting metabolism to develop new prostate cancer treatments
2014-02-27
HOUSTON, Feb. 27, 2014 – A University of Houston (UH) scientist and his team are working to develop the next generation of prostate cancer therapies, which are targeted at metabolism.
With approximately one out of six American men being diagnosed and nearly a quarter of a million new cases expected this year, prostate cancer is the most common malignancy among men in the U.S. Since prostate cancer relies on androgens for growth and survival, androgen ablation therapies are the standard of care for late-stage disease. While patients initially respond favorably to this ...
New tool to unlock genetics of grape-growing
2014-02-27
University of Adelaide researchers have developed a new web-based tool to help unlock the complex genetics and biological processes behind grapevine development.
Published in the journal BMC Genomics, the researchers describe their online database that can be used to examine how almost 30,000 genes work together in groups and networks to produce the vine and its grapes.
"The complexity of plants is easily overlooked when we're enjoying a glass of wine," says project leader Associate Professor Christopher Ford at the University's School of Agriculture, Food and Wine. ...
American Bar Association awards lower ratings to women and minorities
2014-02-27
For more than half a century, the American Bar Association has vetted the nation's judicial nominees, certifying candidates as "well qualified," "qualified," or "not qualified" and in the process rankling conservatives and liberals alike when nominees earn less than stellar marks.
Now a new study suggests that the sometimes-controversial ratings could be tilted against minorities and women. An analysis of 1,770 district court nominations from 1960 to 2012 finds that the ABA systematically awards lower ratings to minorities and women than to white or male candidates. However, ...
Study identifies possible new target for future brain cancer drugs
2014-02-27
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A molecule in cells that shuts down the expression of genes might be a promising target for new drugs designed to treat the most frequent and lethal form of brain cancer, according to a new study by researchers at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute (OSUCCC – James).
The findings, published in the journal Cancer Research, show that high levels of the enzyme PRMT5 are associated with aggressive growth of the brain cancer glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). The malignancy ...
Social workers' roles in patient care expand under affordable care act
2014-02-27
CHESTNUT HILL, Mass. (Feb. 27, 2014) — Social workers will see their roles in patient care expand as hospitals and other providers draw on a range of professionals to meet the demands of the Affordable Care Act, experts told the Boston College Graduate School of Social Work Forum "Health Care Reform: From Policy to Practice."
Former Harvard Pilgrim Health Care CEO Charles D. Baker Jr., the keynote speaker, said social workers bring an expansive view of care options and can play crucial roles, particularly under a "team-based care" approach.
"When I think of social workers, ...
Bison ready for new pastures?
2014-02-27
A new study from the USDA Animal and Plant Health Inspection Services (APHIS) and the Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) demonstrates that it is possible to qualify bison coming from an infected herd as free of brucellosis using quarantine procedures. These bison can then be used to seed conservation herds in other landscapes without the threat of spreading the disease.
In response to Interagency Bison Management Plan (IBMP) guidelines on federal and state bison management actions, the USDA, APHIS Brucellosis Eradication: Uniform Methods and Rules protocol for the quarantine ...
10,000 years on the Bering land bridge
2014-02-27
SALT LAKE CITY, Feb. 27, 2014 – Genetic and environmental evidence indicates that after the ancestors of Native Americans left Asia, they spent 10,000 years in shrubby lowlands on a broad land bridge that once linked Siberia and Alaska. Archaeological evidence is lacking because it drowned beneath the Bering Sea when sea levels rose.
University of Utah anthropologist Dennis O'Rourke and two colleagues make that argument in the Friday, Feb. 28, issue of the journal Science. They seek to reconcile existing genetic and paleoenvironmental evidence for human habitation on ...
A bird's eye view of cellular RNAs
2014-02-27
BOSTON -- In biology, as in real estate, location matters. Working copies of active genes -- called messenger RNAs or mRNAs -- are positioned strategically throughout living tissues, and their location often helps regulate how cells and tissues grow and develop. But to analyze many mRNAs simultaneously, scientists have had to grind cells to a pulp, which left them no good way to pinpoint where those mRNAs sat within the cell.
Now a team at the Wyss Institute of Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University and Harvard Medical School, in collaboration with ...
Scientists uncover trigger for most common form of intellectual disability and autism
2014-02-27
NEW YORK (February 27, 2014) -- A new study led by Weill Cornell Medical College scientists shows that the most common genetic form of mental retardation and autism occurs because of a mechanism that shuts off the gene associated with the disease. The findings, published today in Science, also show that a drug that blocks this silencing mechanism can prevent fragile X syndrome – suggesting similar therapy is possible for 20 other diseases that range from mental retardation to multisystem failure.
Fragile X syndrome occurs mostly in boys, causing intellectual disability ...