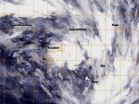
(Press-News.org) A swirling Eastern Pacific Ocean storm system headed for California was spotted by NOAA's GOES-West satellite on February 28. According to the National Weather Service, this storm system has the potential to bring heavy rainfall to the drought-stricken state.
The storm was captured using visible data from NOAA's GOES-West or GOES-15 satellite on Feb. 28 at 1430 UTC/6:30 a.m. PST was made into an image by NASA/NOAA's GOES Project at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. The storm's center appeared as a tight swirl, with bands of clouds and showers already sweeping over the state extending from northern California to Baja California, Mexico.
At 11:30 a.m. PST on February 28, Bill Patzert, climatologist at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif. said, "Right now from northern to southern California we are being battered by very heavy rain, strong winds and our coastal communities are being battered by high surf. Through the weekend we are bracing for mud and rock slides in areas that recently burned [from wildfires]. Flooding is looming up and down the state."
The National Weather Service (NWS) serving Los Angeles posted a Flood Watch for the region on Friday, February 28. The Flood Watch notes the "potential for flash flooding and debris flows for some 2013 and 2014 burn areas in Los Angeles County from this morning through Saturday evening (March 1)."
The NWS Flood Watch also noted "a very strong and dynamic storm will bring a significant amount of rain to much of southwestern California through Saturday evening. A flash flood watch has been issued for several recent burn areas in Los Angeles County due to the abundant rainfall expected. Rain rates at times are expected to range from a half inch to one inch per hour which could cause significant mud and debris flows. There will be a chance of thunderstorms with locally higher rainfall rates."
"Californians haven't seen rain and wind this powerful in 3 years," Patzert said. "By early next week, as this system moves east, this powerful system will wreak havoc causing snow and ice storms through the Midwest into the Northeast."
GOES satellites provide the kind of continuous monitoring necessary for intensive data analysis. Geostationary describes an orbit in which a satellite is always in the same position with respect to the rotating Earth. This allows GOES to hover continuously over one position on Earth's surface, appearing stationary. As a result, GOES provide a constant vigil for the atmospheric "triggers" for severe weather conditions such as tornadoes, flash floods, hail storms and hurricanes.
On a positive note, Patzert noted, "This is a nice down payment on drought recovery in the parched Western U.S."
INFORMATION:
For updated information about the storm system, visit NOAA's National Weather Service website: http://www.weather.gov
For more information about GOES satellites, visit: http://www.goes.noaa.gov/ or http://goes.gsfc.nasa.gov/
GOES-West satellite eyes soggy storm approaching California
2014-02-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA satellite sees great freeze over Great Lakes
2014-02-28
At night, as cold settles in, lake ice creaks and groans. It's been excessively cold, and I camped exposed on the snow-swept surface. Other than the lack of vegetation and the sounds at night, you'd never know you were on a lake. It feels like an empty plain. In some places, you see pressure ridges where ice has pushed into itself, sticking up like clear blue stegosaurus plates. -- Craig Childs
Author Craig Childs is not describing an Arctic lake. He's describing the bitterly cold and frozen scene on Lake Superior, during his February 2014 trek on the ice near the coast ...
Ultra-fast laser spectroscopy lights way to understanding new materials
2014-02-28
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Ames Laboratory are revealing the mysteries of new materials using ultra-fast laser spectroscopy, similar to high-speed photography where many quick images reveal subtle movements and changes inside the materials. Seeing these dynamics is one emerging strategy to better understanding how new materials work, so that we can use them to enable new energy technologies.
Physicist Jigang Wang and his colleagues recently used ultra-fast laser spectroscopy to examine and explain the mysterious electronic properties of iron-based superconductors. ...
Detection of water vapor in the atmosphere of a hot jupiter
2014-02-28
Although liquid water covers a majority of Earth's surface, scientists are still searching for planets outside of our solar system that contain water. Researchers at Caltech and several other institutions have used a new technique to analyze the gaseous atmospheres of such extrasolar planets and have made the first detection of water in the atmosphere of the Jupiter-mass planet orbiting the nearby star tau Boötis. With further development and more sensitive instruments, this technique could help researchers learn about how many planets with water—like Earth—exist within ...
Smoke in the water: Understanding the effects of smoke compounds on seed germination
2014-02-28
Although seemingly destructive, wildfires help to maintain biodiversity and are an important element of many ecosystems throughout the world. Not only do fires discourage non-native and invasive species from becoming established, but the quick release of nutrients, heat, and compounds found in ash and smoke play an important role in the life cycle of the native flora. For plants that are adapted to ecosystems where fire is a regular occurrence—such as savannas, grasslands, and coniferous forests—exposure to fire may initiate seed germination or enhance plant growth.
Recent ...
The nature of color: New formula to calculate hue improves accuracy of color analysis
2014-02-28
A stroll through the produce aisle in your local grocery store exhibits a plethora of vivid colors. From opposing hues, like red apples next to green celery, to subtler variations, such as light to dark purple grapes, every color seems to hold its own unique attraction. Is there a way to precisely measure these hundreds of colors? This is a crucial question for scientists studying the biological importance of color in nature, but measuring color is much more challenging than measuring other characteristics, like size or weight. In recent work, University of Colorado researcher ...
Tropical Cyclone 16P forms near Fiji
2014-02-28
Tropical Cyclone 16P formed near Fiji after lingering in the region for several days as a tropical low pressure area. NOAA's GOES-West satellite captured an infrared image of the storm on February 28.
NOAA's GOES-West satellite image showed the center of Tropical Cyclone 16P to the northeast of Fiji and over Vanua Levu. Broken bands of thunderstorms wrapping from the north to the east and southeast reached Wallis and Fortuna, Samoa, Niue and Tonga.
At 0900 UTC/4 a.m. EST, Tropical Cyclone 16P was centered about 170 nautical miles/`95.6 miles/314.8 km northeast of Suva, ...
To teach scientific reproducibility, start young
2014-02-28
DURHAM, N.C. -- The ability to duplicate an experiment and its results is a central tenet of the scientific method, but recent research has shown an alarming number of peer-reviewed papers are irreproducible.
A team of math and statistics professors has proposed a way to address one root of that problem by teaching reproducibility to aspiring scientists, using software that makes the concept feel logical rather than cumbersome.
Researchers from Smith College, Duke University and Amherst College looked at how introductory statistics students responded to a curriculum ...
Asthma drug aids simultaneous desensitization to several food allergies, study finds
2014-02-28
STANFORD, Calif. — An asthma drug accelerates the process of desensitizing patients with food allergies to several foods at the same time, a new study by researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine and Lucile Packard Children's Hospital Stanford shows.
The findings come on the heels of a recent study by the same team showing that people with multiple food allergies can be desensitized to several foods at once. The two studies, both phase-1 safety trials, provide the first scientific evidence that a promising new method for treating people for multiple food ...
Beneficial anti-inflammatory effects observed when plant extracts fed to sick pigs
2014-02-28
URBANA, Ill. – Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) is the most expensive and invasive disease for pig producers on a global scale. Though it is not occurring on every farm, it is the biggest disease problem in the pig industry, said a University of Illinois animal sciences researcher.
E. coli has also been a problem historically and continues to be on an industry-wide basis, said James Pettigrew. "Either disease can sweep through a farm so their alleviation would substantially reduce production costs. Even though many management practices have been used ...
Waterloo physicists solve 20-year-old debate surrounding glassy surfaces
2014-02-28
University of Waterloo physicists have succeeded in measuring how the surfaces of glassy materials flow like a liquid, even when they should be solid.
A series of simple and elegant experiments were the solution to a problem that has been plaguing condensed matter physicists for the past 20 years.
Understanding the mobility of glassy surfaces has implications for the design and manufacture of thin-film coatings and also sets practical limits on how small we can make nanoscale devices and circuitry.
The work is the culmination of a project carried out by a research ...