(Press-News.org) Researchers from UCLA's Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center have developed an innovative cancer-fighting technique in which custom-designed nanoparticles carry chemotherapy drugs directly to tumor cells and release their cargo when triggered by a two-photon laser in the infrared red wavelength.
The research findings by UCLA's Jeffrey Zink, a professor of chemistry and biochemistry, and Fuyu Tamanoi, a professor of microbiology, immunology and molecular genetics, and their colleagues were published online Feb. 20 in the journal Small and will appear in a later print edition.
Light-activated drug delivery holds promise for treating cancer because it give doctors control over precisely when and where in the body drugs are released. Delivering and releasing chemotherapy drugs so that they hit only tumor cells and not surrounding healthy tissues can greatly reduce treatment side effects and increase the drugs' cancer-killing effect. But the development of a drug-delivery system that responds to tissue-penetrating light has been a major challenge.
To address this, the teams of Tamanoi and Zink, which included scientists from the Jonsson Cancer Center's cancer nanotechnology and signal transduction and therapeutics programs, collaborated with Jean-Olivier Durand from France's University of Montpellier to develop a new type of nanoparticle that can absorb energy from tissue-penetrating light.
These new nanoparticles are equipped with thousands of pores, or tiny tubes, that can hold chemotherapy drugs. The ends of the pores are capped with nanovalves that keep the drugs in, like a cork in a bottle. The nanovalves contain special molecules that respond to energy from two-photon light exposure, which prompts the valves to open and release the drugs.
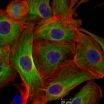
The operation of the nanoparticles was demonstrated in the laboratory using human breast cancer cells.
Because the effective range of the two-photon laser in the infrared red wavelength is 4 centimeters from the skin surface, this delivery system would work best for tumors within that range, which possibly include breast, stomach, colon and ovarian tumors, the researchers said.
In addition to their light sensitivity, the new nanoparticles are fluorescent and can be monitored in the body using molecular imaging techniques. This allows researchers to track the progress of the nanoparticle into the targeted cancer cell before light activation. The ability to track a targeted therapy in this way has been given the name "theranostics" — a portmanteau of therapy and diagnostics — in the scientific literature.
"We have a wonderful collaboration," Zink said. "When the Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center brings together totally diverse fields — in this case, a physical chemist and a cell signaling scientist — we can do things that neither one could do alone."
"Our collaboration with scientists at Charles Gerhardt Institute was important to the success of this two-photon–activated technique, which provides controls over drug delivery to allow local treatment that dramatically reduces side effects," said Tammanoi.
INFORMATION:
This research was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the French American Cultural Exchange–Partner University Fund (FACE-PUF).
UCLA's Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center has more than 240 researchers and clinicians engaged in disease research, prevention, detection, control, treatment and education. One of the nation's largest comprehensive cancer centers, the Jonsson center is dedicated to promoting research and translating basic science into leading-edge clinical studies. In July 2013, the Jonsson Cancer Center was named among the top 12 cancer centers nationwide by U.S. News & World Report, a ranking it has held for 14 consecutive years.
For more news, visit the UCLA Newsroom and follow us on Twitter.
Let there be tissue-penetrating light: Scientists develop new nanoscale method to fight cancer
2014-02-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Robert Avery, D.O., M.S.C.E., studies innovations to improve vision in children with tumors
2014-02-28
Robert Avery, DO, MSCE, of Children's National Health System and colleagues are establishing innovative approaches with technology and medication to improve the vision of young children who have visual pathway glioma, a type of brain tumor.
Most optic pathway gliomas cause vision loss in children between one and eight years of age. As many as 20 percent of children with neurofibromatosis type 1 -- a genetic disorder that occurs in 1 in every 4,000 births – may develop these tumors. It is estimated that nearly half of those children may experience vision problems from ...
Tackling tumors with space station research
2014-02-28
In space, things don't always behave the way we expect them to. In the case of cancer, researchers have found that this is a good thing: some tumors seem to be much less aggressive in the microgravity environment of space compared to their behavior on Earth. This observation, reported in research published in February by the FASEB Journal, could help scientists understand the mechanism involved and develop drugs targeting tumors that don't respond to current treatments. This work is the latest in a large body of evidence on how space exploration benefits those of us on ...
Worm-like mite species discovered on Ohio State's campus
2014-02-28
COLUMBUS, Ohio – It looks like a worm and moves like a worm – sort of. But it is a previously unidentified microscopic species of mite that was discovered by a graduate student on The Ohio State University campus.
Affectionately dubbed the "Buckeye Dragon Mite" by Ohio State's Acarology Laboratory, the mite is officially named Osperalycus tenerphagus, Latin for "mouth purse" and "tender feeding," in a nod to its complex and highly unusual oral structure.
This mite doesn't resemble a mythological winged dragon, but the snake-like Chinese dancing dragons that appear in ...
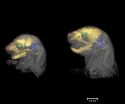
3-D imaging sheds light on Apert syndrome development
2014-02-28
Three dimensional imaging of two different mouse models of Apert Syndrome shows that cranial deformation begins before birth and continues, worsening with time, according to a team of researchers who studied mice to better understand and treat the disorder in humans.
Apert Syndrome is caused by mutations in FGFR2 -- fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 -- a gene, which usually produces a protein that functions in cell division, regulation of cell growth and maturation, formation of blood vessels, wound healing, and embryonic development. With certain mutations, this gene ...
GOES-West satellite eyes soggy storm approaching California
2014-02-28
A swirling Eastern Pacific Ocean storm system headed for California was spotted by NOAA's GOES-West satellite on February 28. According to the National Weather Service, this storm system has the potential to bring heavy rainfall to the drought-stricken state.
The storm was captured using visible data from NOAA's GOES-West or GOES-15 satellite on Feb. 28 at 1430 UTC/6:30 a.m. PST was made into an image by NASA/NOAA's GOES Project at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. The storm's center appeared as a tight swirl, with bands of clouds and showers already ...
NASA satellite sees great freeze over Great Lakes
2014-02-28
At night, as cold settles in, lake ice creaks and groans. It's been excessively cold, and I camped exposed on the snow-swept surface. Other than the lack of vegetation and the sounds at night, you'd never know you were on a lake. It feels like an empty plain. In some places, you see pressure ridges where ice has pushed into itself, sticking up like clear blue stegosaurus plates. -- Craig Childs
Author Craig Childs is not describing an Arctic lake. He's describing the bitterly cold and frozen scene on Lake Superior, during his February 2014 trek on the ice near the coast ...
Ultra-fast laser spectroscopy lights way to understanding new materials
2014-02-28
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Ames Laboratory are revealing the mysteries of new materials using ultra-fast laser spectroscopy, similar to high-speed photography where many quick images reveal subtle movements and changes inside the materials. Seeing these dynamics is one emerging strategy to better understanding how new materials work, so that we can use them to enable new energy technologies.
Physicist Jigang Wang and his colleagues recently used ultra-fast laser spectroscopy to examine and explain the mysterious electronic properties of iron-based superconductors. ...
Detection of water vapor in the atmosphere of a hot jupiter
2014-02-28
Although liquid water covers a majority of Earth's surface, scientists are still searching for planets outside of our solar system that contain water. Researchers at Caltech and several other institutions have used a new technique to analyze the gaseous atmospheres of such extrasolar planets and have made the first detection of water in the atmosphere of the Jupiter-mass planet orbiting the nearby star tau Boötis. With further development and more sensitive instruments, this technique could help researchers learn about how many planets with water—like Earth—exist within ...
Smoke in the water: Understanding the effects of smoke compounds on seed germination
2014-02-28
Although seemingly destructive, wildfires help to maintain biodiversity and are an important element of many ecosystems throughout the world. Not only do fires discourage non-native and invasive species from becoming established, but the quick release of nutrients, heat, and compounds found in ash and smoke play an important role in the life cycle of the native flora. For plants that are adapted to ecosystems where fire is a regular occurrence—such as savannas, grasslands, and coniferous forests—exposure to fire may initiate seed germination or enhance plant growth.
Recent ...
The nature of color: New formula to calculate hue improves accuracy of color analysis
2014-02-28
A stroll through the produce aisle in your local grocery store exhibits a plethora of vivid colors. From opposing hues, like red apples next to green celery, to subtler variations, such as light to dark purple grapes, every color seems to hold its own unique attraction. Is there a way to precisely measure these hundreds of colors? This is a crucial question for scientists studying the biological importance of color in nature, but measuring color is much more challenging than measuring other characteristics, like size or weight. In recent work, University of Colorado researcher ...