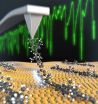
(Press-News.org) Lentiviruses, which belong to the family of retroviruses, are used as vectors to exchange genetic material in cells and can be used to replace a defective gene as defined by gene therapy. Increasing the efficiency of such a treatment poses a major medical challenge: the virus should specifically track the target cells, but the number of virus used should be as low as possible.
A research team led by Dr. Ines Höfig and Dr. Natasa Anastasov from the Institute of Radiation Biology (ISB) at Helmholtz Zentrum München in cooperation with Sirion Biotech GmbH in Munich and the Fraunhofer Institute in Aachen has now developed an adjuvant which enhances the effect of the virus transduction. Thus the transfer into the target cells is optimized without additional toxicity.
Surface molecules fuse viruses with target cells
The scientists equipped the viruses with additional surface molecules that facilitate the attachment of the viruses to their target cells. The surface molecules consist of a glycoprotein which is fused to an antibody fragment. This antibody fragment detects the surface receptors of specific target cells, such as EGFR+ or CD30+, and binds to these.
Higher transduction rate – less virus used
"Through this specific binding to the target cell we can enhance three fold the transduction rate (transfer of the viruses into the target cells)," said research group leader Anastasov. "Thus, the transduction efficiency is improved, and at the same time fewer transfer viruses are needed."
In further studies, analog to the established system, suitable antibody fragments shall be evaluated for specific surface markers of various target cells, e.g. for bone marrow stem cells and immune cells. Gene therapy can thus be used as a treatment for specific genetic disorders (e.g. metachromatic leukodystrophy, Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome).
INFORMATION:
Original Publication:
Höfig, I. et al. (2014), Systematic improvement of lentivirus transduction protocols by antibody fragments fused to VSV-G as envelope glycoprotein. Biomaterials, doi: 10.1016/ j.biomaterials.2014.01.051
Link to journal publication: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0142961214000817
Gene transfer optimization
2014-03-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Screening does not shift breast cancer to earlier stages
2014-03-04
Screening for breast cancer appeared to have a very limited effect on the occurrence of serious and aggressive cancer cases. On the other hand, it appeared to detect many more early cancer cases, cases which would otherwise never have developed - but which are treated due to screening.
This is the conclusion of a study from Aarhus University, Denmark, that has just been published in the European Journal of Public Health based on data from all women over the age of 20 in Norway (approx. 1.8 million in 2010).
Looks at the various stages of cancer
The new element is that ...
Pulling polymers leads to new insights into their mechanical behavior
2014-03-04
In collaboration with colleagues from Berlin and Madrid, researchers at the Department of Physics at the University of Basel have pulled up isolated molecular chains from a gold surface, using the tip of an atomic force microscope (AFM). The observed signal provides insight into the detachment force and binding energy of molecules. The results have been published in the renowned scientific journal PNAS.
Atomic force microscopy is a method normally used for imaging matter with very high resolution. The sharp tip of the microscope is used to scan the surface line by line. ...
Yoga regulates stress hormones and improves quality of life for women with breast cancer undergoing radiation therapy
2014-03-04
HOUSTON — For women with breast cancer undergoing radiation therapy, yoga offers unique benefits beyond fighting fatigue, according to research from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
The preliminary findings were first reported in 2011 by Lorenzo Cohen, Ph.D., professor and director of the Integrative Medicine Program at MD Anderson, and are now published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology. This research is part of an ongoing effort to scientifically validate mind-body interventions in cancer patients and was conducted in collaboration with India's ...
Eliminating bacteria, changing lifestyle could lower risk in people genetically susceptible to colorectal cancer
2014-03-04
New York, NY— Bacteria in the gut are essential for the development of intestinal tumors in mice, according to research led by investigators from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Removing the bacteria may play a critical role in reducing cancer risk, the researchers write, in the March issue of the Journal of Experimental Medicine.
Sergio A. Lira, MD, PhD, Director of the Immunology Institute, and Professor of Immunology and Medicine, and his laboratory at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, used a transgenic mouse model to test the hypothesis that ...
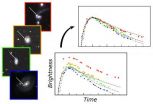
Standard-candle supernovae are still standard, but why?
2014-03-04
Sixteen years ago two teams of supernova hunters, one led by Saul Perlmutter of the U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab), the other by Brian Schmidt of the Australian National University, declared that the expansion of the universe is accelerating – a Nobel Prize-winning discovery tantamount to the discovery of dark energy. Both teams measured how fast the universe was expanding at different times in its history by comparing the brightnesses and redshifts of Type Ia supernovae, the best cosmological "standard candles."
These ...
Virtual bees help to unravel complex causes of colony decline
2014-03-04
Scientists have created an ingenious computer model that simulates a honey bee colony over the course of several years. The BEEHAVE model, published today in the Journal of Applied Ecology, was created to investigate the losses of honeybee colonies that have been reported in recent years and to identify the best course of action for improving honeybee health.
A team of scientists, led by Professor Juliet Osborne from the Environment and Sustainability Institute, University of Exeter (and previously at Rothamsted Research), developed BEEHAVE, which simulates the life of ...
Sardis dig yields enigmatic trove: Ritual egg in a pot
2014-03-04
MADISON, Wis. — By any measure, the ancient city of Sardis — home of the fabled King Croesus, a name synonymous with gold and vast wealth, and the city where coinage was invented — is an archaeological wonder.
The ruins of Sardis, in what is now Turkey, have been a rich source of knowledge about classical antiquity from the 7th century B.C., when the city was the capital of Lydia, through later Greek and Roman occupations.
Now, however, Sardis has given up another treasure in the form of two enigmatic ritual deposits, which are proving more difficult to fathom than ...
World-class orchestras judged by sight not sound
2014-03-04
World-class orchestras can be accurately identified by silent video footage of performances, but not through sound recordings, a UCL study has found.
Both professional musicians and musical novices are better at identifying top-ranked orchestras from non-ranked orchestras when shown silent video footage, suggesting that such judgements are driven at least in part by visual cues about group dynamics and leadership.
When shown two 6-second clips, one from a world-class orchestra ranked among the top ten internationally - which included the London Symphony Orchestra, the ...
Plant extract offers hope for infant motor neurone therapy
2014-03-04
A chemical found in plants could reduce the symptoms of a rare muscle disease that leaves children with little or no control of their movements.
Scientists have found that a plant pigment called quercetin – found in some fruits, vegetables, herbs and grains – could help to prevent the damage to nerves associated with the childhood form of motor neuron disease.
Their findings could pave the way for new treatments for spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) – also known as floppy baby syndrome – which is a leading genetic cause of death in children.
The team has found that the ...
Yeast model reveals Alzheimer's drug candidate and its mechanism of action
2014-03-04
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. (March 3, 2014) – Using a yeast model of Alzheimer's disease (AD), Whitehead Institute researchers have identified a drug that reduces levels of the toxic protein fragment amyloid-β (Aβ) and prevents at least some of the cellular damage caused when Aβ accumulates in the brains of AD patients.
"We can use this yeast model to find small molecules that will address the underlying cellular pathologies of Alzheimer's, an age-related disease whose burden will become even more significant as our population grows older," says Kent Matlack, a former ...