(Press-News.org) VIDEO:
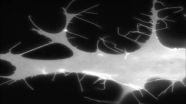
Aberrant filopodia are induced by co-expression of fluorescently labeled Cdc42 and non-fluorescent IRSp53. Fluorescence shows the cell shape, because Cdc42 localizes to the plasma membrane.
Click here for more information.
PHILADELPHIA - "Cell movement is the basic recipe of life, and all cells have the capacity to move," says Roberto Dominguez, PhD, professor of Physiology at the Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania. Motility – albeit on a cellular spatial scale -- is necessary for wound healing, clotting, fetal development, nerve connections, and the immune response, among other functions. On the other hand, cell movement can be deleterious when cancer cells break away from tumors and migrate to set up shop in other tissues during cancer metastasis.
The Dominguez team, with postdoctoral fellow David Kast, PhD, and colleagues, report online ahead of print in Nature Structural & Molecular Biology how a key cell-movement protein called IRSp53 is regulated in a resting and active state, and what this means for cancer-cell metastasis.
"We characterized how IRSp53 connects to the cell-motility machinery," says Kast. "It does this by starting the formation of cell filopodia - extensions that form when a cell needs to move."
"Cells move like an inchworm," explains Dominguez. "Filopodia are at the leading edge of moving cells." The trailing end of the cell follows the move forward through contraction of actin and myosin in the cytoskeleton, much like muscle contraction. A cell pushes out the leading edge of its membrane, and sticks it down on whatever it is moving across, namely other cells, and then moves the cell body along, unsticking the back end. This sets the cell up for its next move.
IRSp53 contains a region called a BAR domain that binds to and shapes cell membranes. Other parts of the protein connect it to the cytoskeleton (internal bits that give a cell structure and shape). Together, through the binding of cell membranes and other proteins IRSp53 regulates cell movement. The team found that in the resting state, human IRSp53 adopts a closed shape that prevents it from interacting with the membrane and the cytoskeleton. However, the binding of a signaling protein, called Cdc42, opens IRSp53, setting in motion the recruitment of a complex cellular machinery needed for motility.
One of the cytoskeleton components IRSp53 connects to is the tumor-promoting protein Eps8. IRSp53 is synergistically activated by the combined action of Cdc42 and binding of Eps8, which is upregulated in metastatic cancers.
Co-authors Tatyana Svitkina and Changsong Yang from the Penn Department of Biology, brought their expertise with living cells to the study. By introducing normal and mutant proteins into cells they could see how these proteins induced filopodia to form. The team found that mutations in critical regions of IRSp53 can either lead to enhanced or reduced filopodia formation and, as a consequence, cell motility. "This finding shows how all these different proteins converge on IRSp53 to execute precise cellular functions, and that when one factor is disrupted, other proteins are affected down the activity pathway," says Dominguez.
The team's next steps will be to screen libraries of small molecule inhibitors that interfere with the IRSp53-Eps8 interaction, to figure out how to stop unwanted cell movement before it gets too far.
INFORMATION:
Coauthors include Yadaiah Madasu and Malgorzata Boczkowska, also from Physiology, and Andrea Disanza and Giorgio Scita from the Institute of Molecular Oncology and the University of Milan School of Medicine in Italy.
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health (R01 MH087950, T32 AR053461, GM095977) and the American Cancer Society (PF-13-033-01-DMC).
Penn Medicine is one of the world's leading academic medical centers, dedicated to the related missions of medical education, biomedical research, and excellence in patient care. Penn Medicine consists of the Raymond and Ruth Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania (founded in 1765 as the nation's first medical school) and the University of Pennsylvania Health System, which together form a $4.3 billion enterprise.
The Perelman School of Medicine has been ranked among the top five medical schools in the United States for the past 17 years, according to U.S. News & World Report's survey of research-oriented medical schools. The School is consistently among the nation's top recipients of funding from the National Institutes of Health, with $392 million awarded in the 2013 fiscal year.
The University of Pennsylvania Health System's patient care facilities include: The Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania -- recognized as one of the nation's top "Honor Roll" hospitals by U.S. News & World Report; Penn Presbyterian Medical Center; Chester County Hospital; Penn Wissahickon Hospice; and Pennsylvania Hospital -- the nation's first hospital, founded in 1751. Additional affiliated inpatient care facilities and services throughout the Philadelphia region include Chestnut Hill Hospital and Good Shepherd Penn Partners, a partnership between Good Shepherd Rehabilitation Network and Penn Medicine.
Penn Medicine is committed to improving lives and health through a variety of community-based programs and activities. In fiscal year 2013, Penn Medicine provided $814 million to benefit our community.
Protein key to cell motility has implications for stopping cancer metastasis
2014-03-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Countering the caregiver placebo effect
2014-03-12
How do you know that your pet is benefiting from its pain medication? A new clinical trial design from North Carolina State University researchers could help overcome pet owners' unconscious observation bias and determine whether the drugs they test are effective.
When animals are recruited for clinical trials, particularly for pain medications, researchers must rely on owner observation to determine whether the medication is working. Sounds simple enough, but as it turns out, human and animal behavior can affect the results.
All clinical trials have a "control" ...
'Ultracold' molecules promising for quantum computing, simulation
2014-03-12
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – Researchers have created a new type of "ultracold" molecule, using lasers to cool atoms nearly to absolute zero and then gluing them together, a technology that might be applied to quantum computing, precise sensors and advanced simulations.
"It sounds counterintuitive, but you can use lasers to take away the kinetic energy, resulting in radical cooling," said Yong P. Chen, an associate professor of physics and electrical and computer engineering at Purdue University.
Physicists are using lasers to achieve such extreme cooling, reducing the temperature ...
Turing's theory of morphogenesis validated 60 years after his death
2014-03-12
PITTSBURGH—British mathematician Alan Turing's accomplishments in computer science are well known—he's the man who cracked the German Enigma code, expediting the Allies' victory in World War II. He also had a tremendous impact on biology and chemistry. In his only paper in biology, Turing proposed a theory of morphogenesis, or how identical copies of a single cell differentiate, for example, into an organism with arms and legs, a head and tail.
Now, 60 years after Turing's death, researchers from the University of Pittsburgh and Brandeis University have provided the ...
Large study identifies the exact gut bacteria involved in Crohn's disease
2014-03-12
While the causes of Crohn's disease are not well understood, recent research indicates an important role for an abnormal immune response to the microbes that live in the gut. In the largest study of its kind, researchers have now identified specific bacteria that are abnormally increased or decreased when Crohn's disease develops. The findings, which appear in the March 12 issue of the Cell Press journal Cell Host & Microbe, suggest which microbial metabolites could be targeted to treat patients with this chronic and currently incurable inflammatory bowel disease.
Twenty-eight ...
Newly diagnosed Crohn's disease patients show imbalance in intestinal microbial population
2014-03-12
A multi-institutional study led by investigators from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and the Broad Institute has identified how the intestinal microbial population of newly diagnosed Crohn's disease patients differs from that of individuals free of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). In their paper in the March 12 issue of Cell Host and Microbe, the researchers report that Crohn's patients showed increased levels of harmful bacteria and reduced levels of the beneficial bacteria usually found in a healthy gastrointestinal tract.
Several studies have suggested that ...
Missing link in plant immunity identified
2014-03-12
After a 30-year search, scientists have uncovered how an enzyme critical to plants' rapid immune response against microbes is activated.
"The insights will open up new ways to improve disease resistance and stress tolerance in plants," says Professor Cyril Zipfel of The Sainsbury Laboratory in Norwich.
The enzyme, the NAPDH oxidase RBOHD, triggers a rapid generation of signalling molecules derived from oxygen that are believed to be detrimental to microbial growth. The newly-discovered way this enzyme is activated, by a protein (called BIK1) fills a gap in how plants ...
Microbes help to battle infection
2014-03-12
The human relationship with microbial life is complicated. At almost any supermarket, you can pick up both antibacterial soap and probiotic yogurt during the same shopping trip. Although there are types of bacteria that can make us sick, Caltech professor of biology and biological engineering Sarkis Mazmanian and his team are most interested in the thousands of other bacteria—many already living inside our bodies—that actually keep us healthy. His past work in mice has shown that restoring populations of beneficial bacteria can help alleviate the symptoms of inflammatory ...
Study finds increased gender variance in children with autism and ADHD
2014-03-12
Washington, DC— John F. Strang, PsyD, a pediatric neuropsychologist at Children's National Health System, and colleagues, found that children with autism spectrum disorders (ASD) or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) were more likely to exhibit gender variance, the wish to be the other gender, than children with no neurodevelopmental disorder, or a medical neurodevelopmental disorder such as epilepsy or neurofibromatosis.
The study, titled "Increased Gender Variance in Autism Spectrum Disorders and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder" was published ...
Can material rivaling graphene be mined out of rocks? Yes, if...
2014-03-12
Will one-atom-thick layers of molybdenum disulfide, a compound that occurs naturally in rocks, prove to be better than graphene for electronic applications? There are many signs that might prove to be the case. But physicists from the Faculty of Physics at the University of Warsaw have shown that the nature of the phenomena occurring in layered materials are still ill-understood and require further research.
Graphene has already been hailed as the future of electronics. Built of six-atom carbon rings arranged in a honeycomb-like structure, it forms extremely resilient ...
Transition to ICD-10 may cause information, financial losses for providers
2014-03-12
Health providers may experience information and financial loss during the mandated conversion from the current International Classification of Diseases to its new and improved version, report researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago.
The study, appearing in the March issue of the Journal of Oncology Practice, looked at coding ambiguity for hematology-oncology diagnoses to anticipate challenges all providers may face during the transition from ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM.
The researchers chose to look at hematology-oncology because prior research suggested that, ...