(Press-News.org) DALLAS, March 16, 2014 — A waste product from making paper could yield a safer, greener alternative to the potentially harmful chemical BPA, now banned from baby bottles but still used in many plastics. Scientists made the BPA alternative from lignin, the compound that gives wood its
strength, and they say it could be ready for the market within five years.
They described the research here today in one of the more than 10,000 presentations at the 247th National Meeting & Exposition of the American Chemical Society (ACS), the world's largest scientific society, taking place here through Thursday.
"Approximately 3.5 million tons of BPA are produced annually worldwide," said Kaleigh Reno, a graduate student who presented the report. BPA is the component that gives shatter-proof plastic eyewear and sports equipment their strength. Additionally, BPA is used in high-performance glues, in the lining of cans and in receipt paper, she explained. The downside is that bisphenol-A, as it's called, can mimic the hormone estrogen, potentially affecting the body and brain. Some experts have suggested that it's unsafe for young children and pregnant women to consume.
To find a safer, more environmentally friendly alternative, Reno and her advisor, Richard Wool, Ph.D., who are at the University of Delaware, turned to lignin. They note that papermaking and other wood-pulping processes produce 70 million tons of lignin byproduct each year, 98 percent of which is incinerated to generate small amounts of energy.
Reno has developed a process that instead converts lignin fragments into a compound called bisguaiacol-F (BGF), which has a similar shape to BPA. She and Wool predict it will act like BPA, as well. "We expect to show that BGF has BPA-like properties within a year," said Wool, with a product ready for the market two to five years later.
Reno is confident that BGF will be a safe stand-in for BPA. "We know the molecular structure of BPA plays a large role in disrupting our natural hormones, specifically estrogen," she said. "We used this knowledge in designing BGF such that it is incapable of interfering with hormones but retains the desirable thermal and mechanical properties of BPA." The researchers also used U.S. Environmental Protection Agency software to evaluate the molecule, determining it should be less toxic than BPA.
And because BGF is made from an existing waste product, Reno believes it will be a viable alternative economically and environmentally. BPA is manufactured from compounds found in oil, a fossil fuel, while BGF's feedstock, lignin, comes from trees, a renewable resource.
The researchers chose BGF based on their unique "Twinkling Fractal Theory," which Wool explains can predict mechanical and thermal properties. "This approach considerably simplifies the design of new biobased materials since we can predetermine properties and screen for toxicity for a broad range of potential compounds from renewable resources such as lignin and plant oils," he says.
INFORMATION:
A press conference on this topic will be held Monday, March 17, at 11 a.m. Central time in Room A122/A123 of the Dallas Convention Center. Reporters can attend in person or access live video of the event and ask questions at the ACS Ustream channel http://www.ustream.tv/channel/acslive.
The researchers acknowledge funding from the U.S. Army Research Laboratory via a DoD-SERDP grant.
The American Chemical Society is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. With more than 161,000 members, ACS is the world's largest scientific society and a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Note to journalists: Please report that this research was presented at a meeting of the American Chemical Society.
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook
Title
Tackling toxicity: Designing a BPA alternative from lignin
Abstract
Over five million metric tons of bisphenol A (BPA) are produced annually for the synthesis of plastics, such as epoxy resins, vinyl ester resins, and polycarbonates. BPA can mimic estrogen in vivoand can interfere with early reproductive development and cause irreversible physical changes. Therefore, designing sustainably sourced, less toxic BPA alternatives is desirable. We synthesized bisguaiacol F (BGF) as a potential BPA alternative from two lignin model compounds, vanillyl alcohol and guaiacol. Lignin is a promising feedstock for aromatic monomers as the paper and pulping industry produces 70 million tons a year as a waste product and can be depolymerized into useful aromatic compounds. Similar to the industrial synthesis of BPA, the condensation reaction between vanillyl alcohol and guaiacol produce two regioisomers. Selectivity between regioisomers and other byproducts can be tuned by changing reaction conditions such as water content, acidic ion exchange resin proton exchange capacity, and reaction time. DSC was used to determine the effect of regioisomer content on the thermal behavior of BGF. Polyesters containing BGA and BGF were compared using thermomechanical analyses (TGA, and DSC).
Potentially safer, greener alternative to BPA could come from papermaking waste
2014-03-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
High-tech materials purify water with sunlight
2014-03-16
DALLAS, March 16, 2014 — Sunlight plus a common titanium pigment might be the secret recipe for ridding pharmaceuticals, pesticides and other potentially harmful pollutants from drinking water. Scientists combined several high-tech components to make an easy-to-use water purifier that could
work with the world's most basic form of energy, sunlight, in a boon for water purification in rural areas or developing countries.
The talk was one of more than 10,000 presentations at the 247th National Meeting & Exposition of the American Chemical Society (ACS), the world's largest ...
Better-tasting reduced-fat desserts, dressings, sauces: Coming soon?
2014-03-16
DALLAS, March 16, 2014 — Adjusting the calcium level and acidity could be the key to developing new better-tasting, more eye-appealing and creamier reduced-fat sauces, desserts and salad dressings that could be on the market soon, researchers reported here today.
To date, a major problem with removing fat from these accompaniments is that in addition to reducing calories, it can negatively affect the flavor, appearance and texture, they said. But based on recent research it may not be too long before new, improved, lower-fat foods appear in grocery stores, the researchers ...
Tequila plant is possible sweetener for diabetics -- helps reduce blood sugar, weight
2014-03-16
DALLAS, March 16, 2014 — A sweetener created from the plant used to make tequila could lower blood glucose levels for the 26 million Americans and others worldwide who have type 2 diabetes and help them and the obese lose weight, researchers said here today.
The main reason it could be valuable, they explained, is that agavins, a natural form of sugar found in the agave plant, are non-digestible and can act as a dietary fiber, so they would not raise blood glucose. Their report was part of the 247th National Meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS), the world's ...
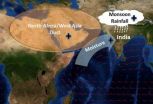
The rush to rain
2014-03-16
RICHLAND, Wash. -- A new analysis of satellite data reveals a link between dust in North Africa and West Asia and stronger monsoons in India. The study shows that dust in the air absorbs sunlight west of India, warming the air and strengthening the winds carrying moisture eastward. This results in more monsoon rainfall about a week later in India. The results explain one way that dust can affect the climate, filling in previously unknown details about the Earth system.
The study also shows that natural airborne particles can influence rainfall in unexpected ways, with ...
Researchers: Northeast Greenland ice loss accelerating
2014-03-16
COLUMBUS, Ohio—An international team of scientists has discovered that the last remaining stable portion of the Greenland ice sheet is stable no more.
The finding, which will likely boost estimates of expected global sea level rise in the future, appears in the March 16 issue of the journal Nature Climate Change [DOI:10.1038/NCLIMATE2161].
The new result focuses on ice loss due to a major retreat of an outlet glacier connected to a long "river" of ice - known as an ice stream - that drains ice from the interior of the ice sheet. The Zachariae ice stream retreated about ...
Mercury's contraction much greater than thought
2014-03-16
Washington, D.C.—New global imaging and topographic data from MESSENGER* show that the innermost planet has contracted far more than previous estimates. The results are based on a global study of more than 5,900 geological landforms, such as curving cliff-like scarps and wrinkle ridges, that have resulted from the planet's contraction as Mercury cooled. The findings, published online March 16, 2014, in Nature Geoscience, are key to understanding the planet's thermal, tectonic, and volcanic history, and the structure of its unusually large metallic core.
Unlike Earth, ...
Thermal vision: Graphene light detector first to span infrared spectrum
2014-03-16
ANN ARBOR—The first room-temperature light detector that can sense the full infrared spectrum has the potential to put heat vision technology into a contact lens.
Unlike comparable mid- and far-infrared detectors currently on the market, the detector developed by University of Michigan engineering researchers doesn't need bulky cooling equipment to work.
"We can make the entire design super-thin," said Zhaohui Zhong, assistant professor of electrical engineering and computer science. "It can be stacked on a contact lens or integrated with a cell phone."
Infrared ...
Southern Ocean iron cycle gives new insight into climate change
2014-03-16
An international team of researchers analysed the available data taken from all previous studies of the Southern Ocean, together with satellite images taken of the area, to quantify the amount of iron supplied to the surface waters of the Southern Ocean.
They found that deep winter mixing, a seasonal process which carries colder and deeper, nutrient-rich water to the surface, plays the most important role in transporting iron to the surface. The iron is then able to stimulate phytoplankton growth which supports the ocean's carbon cycle and the aquatic food chain
They ...
Regional warming triggers sustained mass loss in Northeast Greenland ice sheet
2014-03-16
Northeast Greenland, where the glacier is found, is of particular interest as numerical model predictions have suggested there is no significant mass loss for this sector, leading to a probable underestimation of future global sea-level rise from the region.
An international team of scientists, including Professor Jonathan Bamber from the University of Bristol, studied the Northeast Greenland Ice Stream which extends more than 600 km into the interior of the ice sheet: much further than any other in Greenland.
Professor Bamber said: "The Greenland ice sheet has contributed ...
Cancer therapy may be too targeted
2014-03-16
Researchers have identified two novel cancer genes that are associated with the development of a rare, highly aggressive, cancer of blood vessels. These genes may now act as markers for future treatments and explain why narrowly targeted therapies that are directed at just one target fail.
Angiosarcoma is a rare cancer of blood vessels. It occurs either spontaneously or can appear after radiotherapy treatment. Although quite rare, with approximately 100 people diagnosed with the cancer in the UK each year, the survival outcomes for the cancer are poorer than many other ...