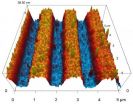
(Press-News.org) Researchers from North Carolina State University have found a way to reduce the coercivity of nickel ferrite (NFO) thin films by as much as 80 percent by patterning the surface of the material, opening the door to more energy efficient high-frequency electronics, such as sensors, microwave devices and antennas.
"This technique reduces coercivity, which will allow devices to operate more efficiently, reducing energy use and improving device performance," says Goran Rasic, a Ph.D. student at NC State and lead author of a paper describing the work. "We did this work on NFO but, because the reduced coercivity is a direct result of the surface patterning, we think our technique would work for other magnetic materials as well."
Coercivity is a property of magnetized materials and is the amount of magnetic field needed to bring a material's magnetization to zero. Basically, it's how much a material likes being magnetic. For devices that rely on switching current back and forth repeatedly – such as most consumer electronics – you want materials that have low coercivity, which improve device performance and use less energy.
Iron oxides, like NFO, have a variety of properties that are desirable for use in high-frequency devices, but they do have a down side: they have high coercivity. The new research from NC State helps address this problem.
By creating a corduroy pattern on the surface of NFO thin films, researchers have been able to lower the coercivity of the NFO by 30 to 80 percent, depending on the thickness of the film. Thinner films experience a larger reduction in coercivity. The surface pattern on the NFO films consists of raised structures that are 55 nanometers (nm) high and 750 nm wide. The structures run parallel to each other and are spaced 750 nm apart, creating the corduroy effect.
INFORMATION:
The paper, "Coercivity Reduction in Nickel Ferrite (NiFe2O4) Thin Films through Surface Patterning," is published online in IEEE Magnetics Letters. Senior author of the paper is Dr. Justin Schwartz, Kobe Steel Distinguished Professor and Department Head of the Materials Science and Engineering Department at NC State.
Researchers change coercivity of material by patterning surface
2014-03-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New research links body clocks to chronic lung diseases
2014-03-18
The body clock's natural rhythm could be utilized to improve current therapies to delay the onset of chronic lung diseases.
Scientists at The University of Manchester have discovered a rhythmic defence pathway in the lung controlled by our body clocks, which is essential to combat daily exposure to toxins and pollutants.
Internal biological timers (circadian clocks) are found in almost all living things driving diverse processes such as sleep/wake cycles in humans to leaf movement in plants. In mammals including humans, circadian clocks are found in most cells and ...
Earthquakes caused by clogged magma a warning sign of eruption, study shows
2014-03-18
New research in Geophysical Research Letters examines earthquake swarms caused by mounting volcanic pressure which may signal an imminent eruption. The research team studied Augustine Volcano in Alaska which erupted in 2006 and found that precursory earthquakes were caused by a block in the lava flow.
36 hours before the first magmatic explosions, a swarm of 54 earthquakes was detected across the 13-station seismic network on Augustine Island. By analyzing the resulting seismic waves, the authors found that the earthquakes were being triggered from sources within the ...
Eat more, die young: Why eating a diet very low in nutrients can extend lifespan
2014-03-18
A new evolutionary theory in BioEssays claims that consuming a diet very low in nutrients can extend lifespan in laboratory animals, a finding which could hold clues to promoting healthier ageing in humans.
Scientists have known for decades that severely restricted food intake reduces the incidence of diseases of old age, such as cancer, and increases lifespan.
"This effect has been demonstrated in laboratories around the world, in species ranging from yeast to flies to mice. There is also some evidence that it occurs in primates," says lead author, Dr Margo Adler, ...
Follow the ant trail for drug design
2014-03-18
This news release is available in German. The path to developing new drugs is a long one. If a target is identified for a new active agent – for instance a particular protein that plays a key role in a disease – an active molecule that binds to the target must then be developed. Pharmaceutical companies trawl through their collections of chemicals for substances that act on the target protein in the desired fashion. However, these compounds are often just the starting point for a long process of adjustment and testing. Chemists use computer simulations to design new ...
Democrats, Republicans see each other as mindless -- unless they pose a threat
2014-03-18
We are less likely to humanize members of groups we don't belong to—except, under some circumstances, when it comes to members of the opposite political party. A study by researchers at New York University and Harvard Business School suggests that we are more prone to view members of the opposite political party as human if we view those individuals as threatening.
"It's hardly surprising that we dehumanize those who are not part of our groups," says Jay Van Bavel, an assistant professor in NYU's Department of Psychology and one of the study's co-authors. "However, what ...
Research on the protein gp41 could help towards designing future vaccinations against HIV
2014-03-18
This news release is available in Spanish. Researchers from the University of Granada have discovered, for the first time, an allosteric interaction (that is, a regulation mechanism whereby enzymes can be activated or de-activated) between this protein, which forms part of the sheath of the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and the antibody 2F5 (FAB), a potent virus neutralizer. This important scientific breakthrough could help specialists to understand the mechanisms behind generating immune responses and help towards the design of future vaccines against the HIV ...
First direct evidence of cosmic inflation
2014-03-18
Almost 14 billion years ago, the universe we inhabit burst into existence in an extraordinary event that initiated the Big Bang. In the first fleeting fraction of a second, the universe expanded exponentially, stretching far beyond the view of our best telescopes. All this, of course, was just theory.
Researchers from the BICEP2 collaboration today announced the first direct evidence for this cosmic inflation. Their data also represent the first images of gravitational waves, or ripples in space-time. These waves have been described as the "first tremors of the Big Bang." ...
Immunologists present improved mass spectrometric method for proteomic analyses
2014-03-18
When it comes to analyzing cell components or body fluids or developing new medications, there is no way around mass spectrometry. Mass spectrometry is a highly sensitive method of measurement that has been used for many years for the analysis of chemical and biological materials. Scientists at the Institute of Immunology of the University Medical Center of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) have now significantly improved this analytical method that is widely employed within their field. They have also developed a software program for the integrated analysis of ...
UNH research: Positive memories of exercise spur future workouts
2014-03-18
DURHAM, N.H. – Getting motivated to exercise can be a challenge, but new research from the University of New Hampshire shows that simply remembering a positive memory about exercise may be just what it takes to get on the treadmill. This is the first study to explore how positive memories can influence future workouts.
"This study underscores the power of memory's directive influence in a new domain with practical applications: exercise behaviors. These results provide the first experimental evidence that autobiographical memory activation can be an effective tool in ...
Male, stressed, and poorly social
2014-03-18
Stress, this enemy that haunts us every day, could be undermining not only our health but also our relationships with other people, especially if we are men. In fact, stressed women apparently become more "prosocial". These are the main findings of a study carried out with the collaboration of Giorgia Silani, from the International School for Advanced Studies (SISSA) of Trieste. The study was coordinated by the Social Cognitive Neuroscience Unit of the University of Vienna and saw the participation of the University of Freiburg.
"There's a subtle boundary between the ...