(Press-News.org) Globalization has made the world a better and more equal place for many more people than was the case a few decades ago. However, it has also created two well-defined worlds of poor countries and wealthy nations, according to Vanesa Jordá and José María Sarabia of the University of Cantabria in Spain. In an article published in Springer's journal Applied Research in Quality of Life, they studied the distribution of well-being over the last wave of globalization between 1980 and 2011.
Well-being is generally described as the state of being happy, healthy or prosperous. The researchers used the UN Human Development Index as an indicator of quality of life. It offers a realistic perspective of the national levels of well-being of 130 countries, covering almost 90 percent of the world's population. The Index also takes into account non-income dimensions such as education and health.
It shows that globalization has brought higher levels of development to more countries than was the case 30 years ago. However, the intensity by which well-being has increased differs across countries. This has created two well-defined clusters: one of least developed countries in especially Sub-Saharan Africa, and another of highly developed countries. At the same time, medium developed nations, such as China and India, have caught up with the advanced economies.
Overall, income inequality across countries has only been reduced by less than ten percent. Because of the so-called "poverty trap," poorer countries struggle to rise to the top within the competitive common global market. Such efforts are hampered by difficulties in acquiring supplies and public services in least developed countries, which makes accessing global markets difficult. Foreign money is also invested heavily in oil exporting countries rather than in countries that do not export oil. Leader countries in each region of the world are able to overcome such obstacles, and experience higher levels of development compared with the nations around them.
The greatest decrease in disparities was found in education, which presents reductions of up to 64 percent. This is thanks to enhanced efforts towards education in developing countries over the last 40 years, especially in Asia. It is consistent with the belief that globalization promotes investment in education and helps countries to develop.
On the health side, no real catch-up or convergence was seen during the nineties. However, this is changing over the past ten years thanks to the expansion of health technology and medicines. Greater access to HIV/AIDS medications, tuberculosis treatment, and insecticide-treated mosquito nets to reduce cases of malaria are of benefit.
"The benefits of globalization have increased a number of aspects of well-being in most countries. However, these advantages have not reached a group of countries which are not able to overcome the human development barriers in health and income. They are being trapped in a low pole which shows little sign of their catching up or converging to the general trend," conclude Jordá and Sarabia.
INFORMATION:
Reference: Jorda, V. & Sarabia, J.M. (2014). Well-being distribution in the globalization era: 30 years of convergence, Applied Research in Quality of Life, DOI 10.1007/s11482-014-9304-8
The full-text article is available to journalists on request.
Winners and losers in globalization of world's economy, health and education
Almost impossible for poorer countries to escape poverty trap, researchers find
2014-03-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Magnetic behavior discovery could advance nuclear fusion
2014-03-19
ANN ARBOR—Inspired by the space physics behind solar flares and the aurora, a team of researchers from the University of Michigan and Princeton has uncovered a new kind of magnetic behavior that could help make nuclear fusion reactions easier to start.
Fusion is widely considered the ultimate goal of nuclear energy. While fission leaves behind radioactive waste that must be stored safely, fusion generates helium, a harmless element that is becoming scarce. Just 250 kilograms of fusion fuel can match the energy production of 2.7 million tons of coal.
Unfortunately, it ...
Increased risk of relapse omitting RT in early PET scan negative Hodgkin lymphoma
2014-03-19
Interim analysis of the intergroup EORTC-LYSA-FIL 20051 H10 trial published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology indicates an increased risk of early relapse when omitting radiotherapy in early PET scan negative patients with stage I/II Hodgkin's lymphoma. Early outcome, however, was excellent in both arms, and the final analysis should reveal whether these initial findings are maintained over time.
Dr. J.M.M. Raemaekers of the Radboud university medical center Nijmegen, The Netherlands, and central coordinator of the study says, "The standard treatment for patients with ...
Study finds forest corridors help plants disperse their seeds
2014-03-19
A forest in South Carolina, a supercomputer in Ohio and some glow-in-the-dark yarn have helped a team of field ecologists conclude that woodland corridors connecting patches of endangered plants not only increase dispersal of seeds from one patch to another, but also create wind conditions that can spread the seeds for much longer distances.
The idea for the study emerged from modern animal conservation practices, where landscape connectivity – the degree to which landscapes facilitate movement – is being used to counteract the impacts of habitat loss and fragmentation ...
Inflammation mobilizes tumor cells
2014-03-19
Researchers of Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich have discovered a novel feedback mechanism that provides a mechanistic link between chronic inflammation and carcinogenesis.
Malignant tumors pose a major threat to survival largely because they shed mobile cells that can form secondary tumors in other tissues. This process requires a fundamental change in the character of cells within the primary tumor, insofar as members of a localized cell mass must be converted into actively migrating cells that invade into the surrounding tissue and blood vessels, and ...
IU, Regenstrief study: New noninvasive colorectal cancer screening tool highly accurate
2014-03-19
INDIANAPOLIS -- An Indiana University and Regenstrief Institute study of nearly 10,000 average-risk, asymptomatic men and women from 90 sites across the United States reports that a multi-target stool DNA test -- a new noninvasive colorectal cancer screening tool that has not yet been approved for sale by the Food and Drug Administration -- detects 92.3 percent of colon cancers, compared to only 73.8 percent of cancers detected by a fecal immunochemical test, the most commonly used noninvasive test today.
Study results were published online March 19 and in the April ...
Earliest evidence of limb bone marrow in the fin of a 370 million year old fish
2014-03-19
This week in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B, a team of French and Swedish researchers present the earliest fossil evidence for the presence of bone marrow in the fin of a 370 million-year-old fish.
Long bones, which are found in the limb of tetrapods, are not only important for locomotion and supporting the weight of the body, but also host the bone marrow. The latter plays a major role in haematopoiesis, i.e. the formation of blood cells. In a healthy adult human, about a hundred billion to one trillion new blood cells are produced every day to maintain ...
Internists must play a larger role in managing menopausal symptoms
2014-03-19
New Rochelle, NY, March 19, 2014—The number of menopausal women is projected to reach 50 million by 2020. With changing views on appropriate therapies to control symptoms and new treatments available and on the horizon, most internists lack the core competencies and experience to meet the needs of women entering menopause, according to a provocative Commentary published in Journal of Women's Health, a peer-reviewed publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Journal of Women's Health website at http://www.liebertpub.com/jwh.
The ...
Genetic test could improve colon cancer screening
2014-03-19
A non-invasive test that includes detection of the genetic abnormalities related to cancer could significantly improve the effectiveness of colon cancer screening, according to research published by a team of scientists including David Ransohoff, MD, professor of medicine at the UNC School of Medicine and UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center member. The large-scale, cross-sectional study was published online today in The New England Journal of Medicine.
The study compared two different types of tests used for screening colorectal cancer: a non-invasive, multitarget ...
Strategies for teaching common core to teens with autism show promise
2014-03-19
Scientists at UNC's Frank Porter Graham Child Development Institute (FPG) report that high school students with autism can learn under Common Core State Standards (CCSS), boosting their prospects for college and employment. Newly published recommendations from FPG's team also provide strategies for educating adolescents with autism under a CCSS curriculum.
"The number of students with autism who enter high school settings continues to grow," said Veronica P. Fleury, lead author and postdoctoral research associate with FPG's Center on Secondary Education for Students with ...
New technique makes LEDs brighter, more resilient
2014-03-19
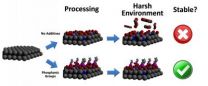
Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed a new processing technique that makes light emitting diodes (LEDs) brighter and more resilient by coating the semiconductor material gallium nitride (GaN) with a layer of phosphorus-derived acid.
"By coating polar GaN with a self-assembling layer of phosphonic groups, we were able to increase luminescence without increasing energy input," says Stewart Wilkins, a Ph.D. student at NC State and lead author of a paper describing the work. "The phosphonic groups also improve stability, making the GaN less likely ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
[Press-News.org] Winners and losers in globalization of world's economy, health and educationAlmost impossible for poorer countries to escape poverty trap, researchers find