(Press-News.org) Pohang, Republic of Korea, March 21, 2014 – Earlier today, Korean researchers successfully showcased the installation and operation of a box-shaped, high-pressure tank for the storage of liquefied natural gas in Pohang, Republic of Korea. The development was the first of its kind in the world.
Pressure vessels have many applications and are widely used within the petrochemical, energy, and other industrial sectors where the transport and storage of many types of pressurized gases and fluids are essential. Pressure vessels must be designed, manufactured, installed, and operated strictly in accordance with the appropriate codes and standards since they can, in cases of leak or rupture, pose considerable health and safety hazards.
Pressure vessels are normally designed in the form of a cylindrical or spherical tank. These shapes are, in principle, highly efficient in withstanding internal pressure, but rather inefficient in terms of space utilization. The tanks fit very poorly within a typically prismatic-shaped room. They cannot be packed closely together, so they do not efficiently utilize the overall space. Moreover, cylindrical or spherical tanks are not easily scalable to very large sizes because the wall thickness of the tank must increase proportionally to its overall radius. Therefore, a large pressure vessel unavoidably will have very thick walls, which are difficult and expensive to manufacture, requiring a great amount of thick-walled steel to be rolled, forged, and welded together.
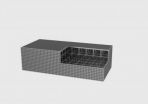
KAIST researchers, sponsored by POSCO, a multinational steel-making company based in Pohang, Republic of Korea, have taken a turnabout approach to construct a pressure vessel that is neither cylindrical nor spherical. Professors Pål G. Bergan and Daejun Chang and of Ocean Systems Engineering at KAIST developed a box-type, large size pressure vessel for the storage and transportation of liquids such as liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), compressed natural gas (CNG), or liquefied natural gas (LNG).
The box-shaped pressure vessel has an internal, load-carrying lattice-type structure. The lattice pattern is modular in all three spatial directions, thereby effectively anchoring and balancing pressure forces on the external walls of the vessel. The modular lattice can easily be adapted to prescribed pressure levels as the overall volumetric dimensions are directly linked to the number of repetitive modules. A giant prismatic pressure vessel with a size of 20,000 m3 and a design pressure of 10 atmospheres (10 barg) can be built simply by scaling up a smaller size pressure vessel. It is interesting to note that the thickness of steel walls remains unchanged and that the weight of steel per unit storage volume goes down as the vessel size increases.
Professor Chang explained the benefit of a prismatic or box-shaped pressure vessel.
"If we use cylindrical pressure vessels to supply LNG fuel for a large container ship, for example, many fuel tanks will be needed. Those tanks will take up large and valuable space onboard because the cylinders have to be lined up. In our case, however, much less space is needed. The operation of a ship becomes simpler with one fuel tank rather than with many. Furthermore, our box-type pressure vessel can be designed with dimensions that precisely fit a ship. For a container ship, there may be room for a substantially higher number of containers to be loaded than when using cylindrical vessels. In a case study on a 13,000 TEU container ship, the value of the increased transport capacity tuned out USD 8.4 million for one year of operation for one ship."
The manufacturing cost of a pressure vessel has been reduced as well. Several types of special steel for cryogenic (low temperature) applications have been investigated in design and analysis studies, and this includes a new type of high-manganese steel that is being developed by POSCO. Regardless of materials, in any instance of large pressure vessels, the new lattice tank technology can offer significant savings of combined capital and operational costs.
Professor Bergan was also upbeat regarding the impact of the KAIST technology innovation.
"Our box-type pressure vessel represents ground-breaking research. This innovative technology will dramatically change the rules of the game for industry concerning production, transportation, and storage of fluids under high pressure and at low temperatures."
The showcased prismatic pressure vessel was a scale-down model with a volume size of 80 m3 and design pressure of 10 atmospheres. The vessel complies with the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (BPVC), the international standard for the appropriateness of design, fabrication, and inspection of boilers and pressure vessels. It passed the 15 pressure testing in January 2014 and received an accreditation from the ASME BPVC (ASME U2 Stamp).
INFORMATION:
KAIST's prismatic pressure vessel will be presented and displayed at Gastech 2014, the largest global conference and exhibition in the natural gas, LNG, and hydrocarbons industry. This event will take place on March 24-27 at KINTEX in Ilsan, Republic of Korea.
For further inquires:
Dae-Jun Chang
Professor of Ocean Systems Engineering, KAIST
Offshore Process Engineering Laboratory
Tel: +82-42-350-1514
Email: djchang@kaist.ac.kr
Pål G. Bergan
Professor of Ocean Systems Engineering, KAIST
Tel: +82-42-350-1594
Email: pal.bergan@ntnu.no
Box-shaped pressure vessel for LNG developed by KAIST research team
2014-03-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers develop a novel antibacterial orthodontic bracket cement
2014-03-21
Alexandria, Va., USA – Today, at the 43rd Annual Meeting & Exhibition of the American Association for Dental Research (AADR), held in conjunction with the 38th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for Dental Research, Mary Anne Sampaio de Melo, from the University of Maryland, Baltimore, will present a research study titled "Antibacterial Orthodontic Cement Containing a Quaternary Ammonium Monomer Dimethylaminododecyl Methacrylate."
Demineralized lesions in enamel around orthodontic brackets are caused by acids from biofilm accumulation. The objectives of this study ...
Researchers at LSTM unlock the secret of multiple insecticide resistance in mosquitoes
2014-03-21
Researchers at LSTM have discovered how unprecedented multiple and extreme-level resistance is generated in mosquitoes found in the rice fields of Tiassalé in southern Côte d'Ivoire. The paper, "CYP6 P450 enzymes and ACE-1 duplication produce extreme and multiple insecticide resistance in the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae" published in PLoS Genetics today, highlights the combination of stringently-replicated whole genome transcription profiling, in vivo transgenic gene expression and in vitro metabolism assays to identify and validate genes from the P450 detoxification ...
Critical illness polyneuropathy and myopathy: Nerve injury and regeneration
2014-03-21
Critical illness polyneuropathy and critical illness myopathy are frequent complications of severe illness that involve sensorimotor axons and skeletal muscles, respectively. Differentiating critical illness polyneuropathy from Guillain-Barré syndrome, especially the axonal variants, may be difficult on purely clinical grounds, as Guillain-Barré syndrome is known for its variable atypical manifestations. Prof. Hongliang Zhang and team from the First Bethune Hospital, Jilin University in China provide the latest knowledge concerning the pathophysiology of critical illness ...
Lessons offered by emerging carbon trading markets
2014-03-21
DURHAM, N.C. -- Although markets for trading carbon emission credits to reduce greenhouse gas emissions have stalled in United States federal policy-making, carbon markets are emerging at the state level within the U.S. and around the world, teaching us more about what does and doesn't work.
In a Policy Forum article in the March 21 edition of Science magazine, Duke University's Richard Newell, William Pizer and Daniel Raimi discuss the key lessons from a decade of experience with carbon markets. They also discuss what it might take for these markets to develop and possibly ...
Who reprograms rat astrocytes into neurons?
2014-03-21
To date, it remains poorly understood whether astrocytes can be easily reprogrammed into neurons. Mash1 and Brn2 have been previously shown to cooperate to reprogram fibroblasts into neurons. Dr. Yongjun Wang and team from Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine in China found that and found that Brn2 was expressed in astrocytes from 2-month-old Sprague-Dawley rats, but Mash1 was not detectable. Thus, the researchers hypothesized that Mash1 alone could be used to reprogram astrocytes into neurons. Murine stem cell virus (MSCV)-Mash1 recombinant plasmid was constructed ...
Unique chromosomes preserved in Swedish fossil
2014-03-21
Researchers from Lund University and the Swedish Museum of Natural History have made a unique discovery in a well-preserved fern that lived 180 million years ago. Both undestroyed cell nuclei and individual chromosomes have been found in the plant fossil, thanks to its sudden burial in a volcanic eruption.
The well-preserved fossil of a fern from the southern Swedish county of Skåne is now attracting attention in the research community. The plant lived around 180 million years ago, during the Jurassic period, when Skåne was a tropical region where the fauna was dominated ...
A study using Drosophila flies reveals new regulatory mechanisms of cell migration
2014-03-21
Cell migration is highly coordinated and occurs in processes such as embryonic development, wound healing, the formation of new blood vessels, and tumour cell invasion. For the successful control of cell movement, this process has to be determined and maintained with great precision. In this study, the scientists used tracheal cells of the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster to unravel the signalling mechanism involved in the regulation of cell movements.
The research describes a new molecular component that controls the expression of a molecule named Fibroblast Growth ...
Switching an antibiotic on and off with light
2014-03-21
This news release is available in German. Scientists of the KIT and the University of Kiev have produced an antibiotic, whose biological activity can be controlled with light. Thanks to the robust diarylethene photoswitch, the antimicrobial effect of the peptide mimetic can be applied in a spatially and temporally specific manner. This might open up new options for the treatment of local infections, as side effects are reduced. The researchers present their photoactivable antibiotic with the new photomodule in a "Very Important Paper" of the journal "Angewandte Chemie". ...
cfaed presents the new microchip 'Tomahawk 2' at the DATE'14 in Dresden
2014-03-21
The Center for Advancing Electronics Dresden (cfaed) presents its new microchip 'Tomahawk 2' at the DATE'14 Conference in the International Congress Center Dresden from March 24 to 28, 2014. The new Tomahawk is extremely fast, energy-efficient and resilient. It is a heterogeneous multi-processor which can easily integrate very different kinds of devices. The researchers of the Cluster of Excellence for microelectronics of Technische Universität Dresden use the new prototype to prepare the so-called 'tactile internet'. With this, very big data volumes shall be transmitted ...
New study shows we work harder when we are happy
2014-03-21
Happiness makes people more productive at work, according to the latest research from the University of Warwick.
Economists carried out a number of experiments to test the idea that happy employees work harder. In the laboratory, they found happiness made people around 12% more productive.
Professor Andrew Oswald, Dr Eugenio Proto and Dr Daniel Sgroi from the Department of Economics at the University of Warwick led the research.
This is the first causal evidence using randomized trials and piece-rate working. The study, to be published in the Journal of Labor Economics, ...