LOS ANGELES, CA, March 22, 2014 (Press-News.org) Extreme weather conditions have made this winter colder than usual. Those people suffering from eczema or psoriasis, looking for the best dry skin moisturizer, personally experience the dry skin nightmare during these winter months. Cold winds, low humidity and the use of heaters can worsen just about anyone's skin but are especially hard on those with eczema and psoriasis. Finding the right dry skin moisturizer could make a big difference in how many outbreaks you face this winter.
According to the US National Library of Medicine, dry itchy skin occurs more often in winter, when cold air outside and heated air inside cause low humidity. The skin loses its moisture, may crack and peel or become irritated and inflamed, causing millions of Americans to suffer from dry skin conditions.
"When your skin gets dry and itchy in winter you know that the protective outer layer of skin has been stripped away," says Dr Brian Zogg, a board-certified dermatologist with a practice in Albert Lea, Minnesota. "Artificial moisturizers in conventional creams and lotions can send a signal to the moisture producing parts of your skin that enough moisture is present. Your skin then makes less of the natural moisture needed to resolve a dry skin problem. With a shielding lotion you replace the outer layer and protect the natural oils and moisture in your skin, so it heals faster.
"The concept of a shielding lotion is relatively new to dermatology and skin treatment. It binds to the skin in such a way that the environment cannot penetrate and desiccate the skin, essentially forming an invisible shield around and throughout the skin just like an invisible glove would. This is important as it allows the moisture to be maintained within the body and disallows, stops any products from harming the skin, like cleansers, acids and all everyday solvents that we come into contact with."
With winter still in full swing and more extreme than ever, it is important to use a natural skin care treatment now. Use a shielding lotion like Skin MD Natural that bonds with the body's skin and replaces the protective layer, so that the skin retains its own oils and moisture.
Skin MD Natural Shielding lotion is available at pharmacies throughout the United States or by calling 21st Century Formulations, Inc. located in Beverly Hills, CA. They can be reached at 800-540-4790 or can be contacted through their website: http://www.skinmdnatural.com, or emailed directly: info@skinmdnatural.com
Ongoing Extreme Winter Season Causes Skin Care Disaster
New dry skin lotion relieves dry winter skin.
2014-03-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Permafrost thaw: No upside
2014-03-21
The climate is warming in the arctic at twice the rate of the rest of the globe creating a longer growing season and increased plant growth, which captures atmospheric carbon, and thawing permafrost, which releases carbon into the atmosphere. Woods Hole Research Center (WHRC) Assistant Scientist Sue Natali and colleagues engineered first-of-a-kind warming experiments in the field to determine net gains or losses in carbon emissions. The study entitled "Permafrost degradation stimulates carbon loss from experimentally warmed tundra," published in the journal Ecology found ...
Stem cell findings may offer answers for some bladder defects and disease
2014-03-21
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) — For the first time, scientists have succeeded in coaxing laboratory cultures of human stem cells to develop into the specialized, unique cells needed to repair a patient's defective or diseased bladder.
The breakthrough, developed at the UC Davis Institute for Regenerative Cures and published today in the scientific journal Stem Cells Translational Medicine, is significant because it provides a pathway to regenerate replacement bladder tissue for patients whose bladders are too small or do not function properly, such as children with spina bifida ...
Keck Medicine of USC research may point to better predictor of prostate cancer survival
2014-03-21
New research by USC Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center scientists demonstrates that measuring circulating tumor cells (CTCs) – the cells that spread cancer through the body – may be a better predictor of patient survival than the prostate specific antigen (PSA).
The research was published March 10, 2014 in the Journal of Clinical Oncology by a team led by Amir Goldkorn, M.D., assistant professor of medicine at USC Norris, part of Keck Medicine of USC. Goldkorn's team discovered that elevated CTC counts after chemotherapy indicated as much as a five-fold higher risk of ...
Cold snare polypectomy effective for removal of small colorectal polyps in patients on anticoagulants
2014-03-21
DOWNERS GROVE, Ill. – March 21, 2014 – In recognition of National Colorectal Cancer Awareness Month, GIE: Gastrointestinal Endoscopy has published a special issue for March on colorectal cancer. The issue includes a new study that compares cold snare polypectomy with conventional polypectomy for the removal of small colorectal polyps in anticoagulated patients. The study showed that delayed bleeding requiring hemostasis (stoppage of bleeding) occurred significantly less often after cold snare polypectomy than during conventional polypectomy despite continuation of anticoagulants. ...
Genetic signature reveals new way to classify gum disease
2014-03-21
NEW YORK, NY (March 21, 2014) — Researchers at Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC) have devised a new system for classifying periodontal disease based on the genetic signature of affected tissue, rather than on clinical signs and symptoms. The new classification system, the first of its kind, may allow for earlier detection and more individualized treatment of severe periodontitis, before loss of teeth and supportive bone occurs. The findings were published recently in the online edition of the Journal of Dental Research.
Currently, periodontal disease is classified ...
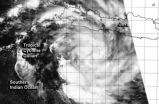
NASA sees Tropical Cyclone Gillian reborn near Java
2014-03-21
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the reborn tropical cyclone known as Gillian on March 21 and captured a visible image of the storm, located just south of the island of Java.
Java is highly populated island of Indonesia that includes the capital city of Jakarta. Java is divided into four provinces, East, West and Central Java and Banten. There are also two special regions of Java called Jakarta and Yogyakarta.
The MODIS instrument that flies aboard Aqua captured a visible image of Gillian on March 21 at 06:55 UTC/2:55 a.m. EDT. The image showed bands of thunderstorms ...
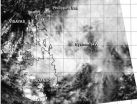
NASA's Aqua satellite sees Tropical System 94W affecting Philippines
2014-03-21
The tropical low pressure area centered just east of the southern Philippines appeared more organized on visible imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite on March 21. System 94W appears to be developing and the Philippine authorities have already issued warnings on the system locally designated as "Caloy."
The MODIS instrument (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of System 94W coming together east of the southern Philippines on March 21 at 5:25 UTC/1:25 a.m. EDT. The image revealed a circulation with ...
Deep ocean current may slow due to climate change, Penn research finds
2014-03-21
Far beneath the surface of the ocean, deep currents act as conveyer belts, channeling heat, oxygen, carbon and nutrients around the globe.
A new study by the University of Pennsylvania's Irina Marinov and Raffaele Bernardello and colleagues from McGill University has found that recent climate change may be acting to slow down one of these conveyer belts, with potentially serious consequences for the future of the planet's climate.
"Our observations are showing us that there is less formation of these deep waters near Antarctica," Marinov said. "This is worrisome because, ...
Pushing and pulling: Using strain to tune a new quantum material
2014-03-21
Research into a recently discovered class of materials shows they have the necessary characteristics to develop ultra-energy efficient electronics. Topological insulators (TI) are three-dimensional materials that conduct electricity on their surfaces, while the interior insulates.
Their surfaces are particularly unique because the motion of the electrons is "protected" by symmetry, meaning electrons will keep moving without scattering even when they encounter defects and contamination.
In fact, electrons on the surface of TIs move so robustly scientists are trying ...
Computers spot false faces better than people
2014-03-21
TORONTO, ON — A joint study by researchers at the University of California San Diego and the University of Toronto has found that a computer system spots real or faked expressions of pain more accurately than people can. The work, titled "Automatic Decoding of Deceptive Pain Expressions," is published in the latest issue of Current Biology.
"The computer system managed to detect distinctive dynamic features of facial expressions that people missed," said Marian Bartlett, research professor at UC San Diego's Institute for Neural Computation and lead author of the study. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
[Press-News.org] Ongoing Extreme Winter Season Causes Skin Care DisasterNew dry skin lotion relieves dry winter skin.